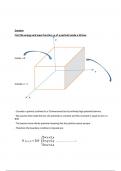
Processor Components
The processor cpu is madeup of the control unit buses ALU and dedicated registers
CU The part of the processor that coordinates the activity of all other components
Bus Buses consist of a series of connectors that transfer signals between internal components
They usually consist of 816,32or64lines
The system bus consists of 3 separate buses which carry control signals addresses and
data
Memory read causesdatafromRAMtobeplaced on
Control Data Address the databus
I I I I I I v I Memory write causes data on thedatabusto b
written to RAM
Von Neumann architecture only has one set
of Bus realest indicates a request to usedataby
buses system bus This is because dataand Bus grant indicates granted access todatabus
instructions are stored together in memory the CPU
by
Clock synchronises operations
ALU Theproblemsolving part of the processor that performsarithmeticlogicalandshiftoperation
t
not t x v leftand
A Operation
Ito
pantyhose Zesu ANDOR
NOTXOR
right
Dedicated Regisers Opcode and Operand
C holdsthe memory address of the next the opcode is theinstruction executed bythe
instruction to be executed CPU and the operand is thedata or memory
C holds the current instruction when location used to execute that instruction
split into opcode and operand seebelow
MAZ hods the address in memory where the 0000 H end
processor is required to fetch or store 0001 A add
data from or to 0010 503 subtract
MR emporarily holds data moving between 0011 SA store
0101 JA load opcode
Acc the pities is
gemeramainpurposemregister
0110 33A
332
branch always
thatstores the intermediate results of 0111 branch if ACC O
instructions from the ALU 1000 333 branch if ACC O
1001 a input output
Execuing nsrucions
In order to execute an instruction the processorhasto temporarilyholdthecurrent instruction
being executed it has to hold the address of the data that it needs and also the
data itself and it hasto keep track of the address of the next instruction to be
.
executed The CU coordinates components to work together in order to do all of this
Fetch address of next instruction copied from PC MAR that instruction is copied to theMDR
atthe sametime the PC contents are incremented then MDR contents copied to CIR
Decode the instruction at the Clr is decoded split into opcode and operand and passed
to the accumulator
Execute instruction is executed and the result is stored in accumulator or memory
, Composite 1 - Components of a Computer
Processor Performance
Memory is dividedup in equal unitscalled words Theword length size refers to the amount of data that
can be handled at one time the processor Word
by is usually 816.32 or 64 bits Eachword
length
has its own separate memory address
thesize of the processor registers and the width of thedata bus are designed tobe equal to th
word length
thelargerthe word size the greater the amount of data that can be transferred to the CPU in
onepass Therefore the greaterthe word length thequicker the processor can access data and
instructions so the better the performance
Address Bus the width ofthe address bus determines the number of bits that can be used to form
an address of a memory location Therefore not only does the processor benefit from
a larger main memory its performance is further improved due to a reduced reliance
on slower virtual memory and secondary storage
memory
addresses 2 where n is the width of theaddressbus in bits
Data Bus thewidth determines the number of bitsthat canbe transferred
to or from in one operatio
the larger the databus thebetter the processor performance as the greater the
width the more data canbetransferred between the internal components simultaneously
width of bus in bits bits transferred in one operation
Cores Clock Speed Cache
Computers with morethan one h
unit core are called multicore that produces signals to synchronise capacity setof locationsthat sit
the operations of the processor closeto theprocessor whichstores
hasthe more instructions if clock speed is measured in GHz frequently used data and
can execute simultaneously so a speed of 3.6GHz is capable instructions
however the
efficiency depends of performing 3.6billion instructions Irl smelliestcapacitybutfastest
on thenature the required
of persecond
a however this is
only theoretical v3 largest capacity but slowes
Pipelining a technique used to improve processor performance where multiple instructions are overlapped
during execution e.g overlapping stages of theFDE cycle
before pipelining can occur thetask must firstbebroken down into subtasks
Parallel Processing tasks so that multiple sub
where a computation is divided into sub tasks can be carried
out at one time
this is therefore only possible on multicore systems
e level one cache can be split into instruction and data cache for simultaneous
g
fetching
Clock the system clock generates pulses by emitting an oscillating signal between a low107 and a
highC't state
lowto high risingedge and high to low fallingedge
thetimebetweentwosequential rising edges is called the clock period which signifies one cycle
clock frequency I clockperiod
, Composite 1 - Components of a Computer
Types of Processor
Stored program concept a program must be loadedinto main memory tobeexecuted by the processor
the instructions are fetched oneby one decodedand executed by the processor
thesequence can only be changed by a conditional or unconditional jumpinstruction
VonNeumann architecture
consists of a processor a memory unit can communicate directly with the processor connections for input
output devices and secondary storage for saving backing updata
instructions and data are stored in a common main memory and transferred using the data bus
address bus usedto identify the addressed location
data bus used to transfer the contents to from that location
control bus used and control operations
for synchronisation
Harvard architecture
Keeps instructions and data in separate memories which are accessed using separatedata and addressbuses
used a lot in embedded systems and microcontroller devices
8
M
p
A
R
I
N
S
RISC reducedinstructionsetcomputer
The instruction set consists of simple commands designed to take the same time cute one
instruction per clock cycle
therefore lowlevel programs are longer and take up more memory
however pipelining is possible less circuitry is required it's cheaper to designand produce it
gives
off less heat and it consumes less power
CISC complex instruction set computer
The instruction set is made up of a large number of complex variable length instructions
makes very efficient use of RAM
Today's desktop processorsare typically comprised of features of rise and cisc to make the mostof both
Individually RISC is typically used in small specialist devices mobile phones
e.g