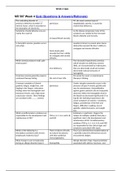
_______ is a serious allergic reaction that has a rapid onset of symptoms and, if unrecognized,
can lead to respiratory arrest.
A. Hypersensitivity
B. A localized reaction
C. Anaphylaxis
D. A toxicity reaction - ANS-C. Anaphylaxis
_______ is maintained when the supply of oxygen is sufficient to meet the cellular demands of
the body.
A. pH balance
B. Homeostasis
C. Hemostasis
D. Lactic acid - ANS-B. Homeostasis
_______ is maintained when the supply of oxygen is sufficient to meet the cellular demands of
the body.
A. pH balance
B. Homeostasis
C. Hemostasis
D. Lactic acid - ANS-B. Homeostasis
_______ occurs when one or more of the components of the immune system is damaged or
non-functioning.
A. Infection
B. Immunocompromise
C. Immunodeficiency
D. Hypersensitivity - ANS-C. Immunodeficiency
_______ requires the use of specialized equipment and specialized training for paramedics and
nurses.
A. Advanced life support
B. Fixed-wing air medical evacuation
C. Specialty care transport, as defined by CMS
,D. Interfacility transport - ANS-C. Specialty care transport, as defined by CMS
8. You are preparing a trauma patient with a closed head injury and blunt chest trauma for a
2-hour, fixed-wing transport. The patient is intubated, paralyzed, and sedated. Vital signs are:
blood pressure, 110/76 mm Hg; respirations, 16 breaths/minute by ventilator; heart rate, 118
beats/minute and showing sinus tachycardia on the monitor; and an SaO2 of 96% with 0.5
FIO2. The CT scan shows a moderate subarachnoid bleed and chest x-ray reveals a 25%
pneumothorax on the right. You are currently at 500' (152 m) above sea level, and the aircraft
will reach a cabin pressure of 8,000' (2.4 km) en route to the tertiary care facility. Which of the
following is your best option during this flight?
A. Increase FIO2 to 1.0 to counteract the effects of Dalton's Law.
B. Make sure that the cabin stays cool while at altitude to counteract the effects of Gay-Lussac's
Law.
C. Increase positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) to e - ANS-D. Place a chest tube prior to
departure to counteract the effects of Boyle's Law.
A "sterile cockpit" refers to a:
A. Method of decontaminating the aircraft.
B. Communication technique during critical phases of flight.
C. Pilot's absolute control over radio communications.
D. Completely locked and separate cockpit. - ANS-B. Communication technique during critical
phases of flight.
A 48-year-old male suffered multi-system trauma after an automobile accident. Physical Exam
revealed decreased heart tones, JVD and hypotension. What is the appropriate immediate
intervention for this condition?
A. Pericardiocentesis
B. Needle decompression
C. Chest tube insertion
D. ET Intubation - ANS-A. Pericardiocentesis
A child in shock will fail quickly when the child's compensatory systems:
A. Are in overdrive
B. Fail
C. Thrive
D. Are functioning normally - ANS-B. Fail
A left axis deviation is normally seen:
A. In children
,B. In pregnant women
C. Due to dextrocardia
D. Due to hypokalemia - ANS-B. In pregnant women
A leftward shift in the oxy-hemoglobin dissociation curve causes _______ for oxygen by
hemoglobin.
A. Decreased affinity
B. Increased unloading ability
C. Increased affinity
D. Unchanged affinity - ANS-C. Increased affinity
A patient in compensatory shock will increase his or her respiratory rate to bring about which of
the following changes?
A. A decrease in pH and an increase in minute volume
B. Increased oxygen intake to blow off excess carbon dioxide
C. A decrease in minute volume and an increase in pH
D. Dilation of the capillary bed and diffusion gradient - ANS-B. Increased oxygen intake to blow
off excess carbon dioxide
A patient presenting with a bacterial infection would typically demonstrate a / an
______________________ number of lymphocytes.
A. Unchanged
B. Decreased
C. Increased
D. Varied - ANS-C. Increased
A patient presenting with a viral infection would typically demonstrate a / an
______________________ number of lymphocytes.
A. Unchanged
B. Varied
C. Increased
D. Decreased - ANS-D. Decreased
A patient's pneumothorax increasing in size as altitude increases is an example of _______
Law.
A. Charles'
B. Boyle's
C. Dalton's
D. Fick's - ANS-B. Boyle's
, A prolonged erection of the penis, which typically occurs in male patients with a spinal cord
injury, sickle cell anemia, penile vessel spasm or clot formation is called a:
A. Polyuria
B. Priapism
C. Kehr's sign
D. None of the above - ANS-B. Priapism
A rightward shift in the oxy-hemoglobin dissociation curve causes _______ for oxygen by
hemoglobin.
A. Decreased affinity
B. Increased affinity
C. Unchanged affinity
D. Decreased unloading ability - ANS-A. Decreased affinity
A root cause of esophageal varices is/are:
A. Mallory-Weiss syndrome
B. Reactive gastritis
C. Cirrhosis
D. Peptic ulcers - ANS-C. Cirrhosis
A standard and key assessment of the critical care musculoskeletal system is:
A. Checking for neurovascular status of each extremity
B. Measuring compartment pressures
C. Checking for hepato-jugular reflux
D. Auscultation of a popliteal bruit - ANS-A. Checking for neurovascular status of each extremity
A systemic inflammatory response is initiated in burns greater than:
A. 5%
B. 10%
C. 15%
D. 25% - ANS-D. 25%
A variety of causes are thought to result in decreased cardiac output in burned patients,
including all of the following EXCEPT:
A. The inflammatory response and its mediators
B. Cyanide poisoning
C. Carbon monoxide poisoning