Deep Learning is a transformative field in Artificial Intelligence (AI) that focuses on
training algorithms to learn from vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and
make decisions with minimal human intervention. Drawing inspiration from the
human brain, Deep Learning uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to
mimic the cognitive processes that enable humans to learn complex tasks. These
neural networks can process large datasets and make predictions with
remarkable accuracy, particularly in fields like image recognition, natural language
processing (NLP), and speech recognition.
What is Deep Learning?
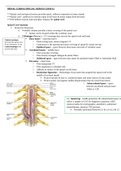
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that involves networks of artificial
neurons—structures designed to mimic the interconnectedness of neurons in the
human brain. These networks, known as artificial neural networks, consist of
several layers that perform a sequence of computations to transform the input
data into an output, such as predictions or classifications.
In a deep learning model, the "depth" refers to the number of hidden layers
between the input and output layers. The deeper the network, the more abstract
the features it can learn, making deep learning particularly effective for tasks
involving large, complex datasets, such as images, audio, and text.
Key Characteristics of Deep Learning
1. Multiple Layers: Deep learning models utilize networks with many layers,
known as deep neural networks (DNNs). Each layer is responsible for
processing different aspects of the data and building a hierarchical
understanding of it.
2. Feature Extraction: Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms, deep
learning models are capable of automatic feature extraction, eliminating
the need for manual intervention in designing features. This capability is
, especially useful when dealing with unstructured data such as images or
speech.
3. Large Data Requirements: Deep learning models require a vast amount of
labeled data for training. The more data these models are trained on, the
better their performance, making deep learning ideal for applications with
abundant data available, such as in large-scale image and video analysis.
4. High Computational Power: Training deep learning models requires
significant computational resources, such as Graphics Processing Units
(GPUs), which allow the network to process multiple operations
simultaneously. These powerful hardware tools have greatly accelerated
the development of deep learning over the last decade.
How Does Deep Learning Work?
Deep learning works through a process known as backpropagation, where a
neural network learns by adjusting weights and biases in response to errors in its
predictions. Here’s an overview of how this works:
1. Input Layer: Data enters the network through the input layer. This data
could be anything from pixel values in an image to text data in the form of
word embeddings.
2. Hidden Layers: The data passes through multiple hidden layers, each
performing mathematical operations to extract features and patterns.
These layers gradually learn more complex features as data moves through
them.
3. Weights and Biases: Each connection between neurons has an associated
weight, which determines the strength of the connection. These weights
are adjusted during training to minimize errors in predictions. The bias
allows the model to shift the activation function, making it more flexible.
4. Activation Function: Each neuron uses an activation function (such as ReLU,
Sigmoid, or Tanh) to introduce non-linearity, enabling the network to learn
complex patterns that linear models would miss.
5. Output Layer: The final layer generates the output. For classification tasks,
this might be a probability distribution over different classes. For regression
tasks, the output might be a continuous value.