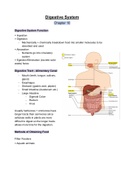
GEOG 1300 - Lab Notes
Map Interpretation (Lab 1)
● Coordinate Systems:
○ Lines of latitude (parallels)
■ Measured in degrees (°), minutes (‘), and seconds (‘’) north or south of the
equator
○ Lines of longitude (meridians)
■ Measured in degrees (°), minutes (‘), and seconds (‘’) east or west of
Greenwich, England
○ There are 60 minutes in 1 degree
● Rectangular Grid System:
○ Arbitrary numbers (grid lines begin at an arbitrarily chosen point)
○ Numbers increase west to east (left to right)
○ Numbers increase south to north (bottom to top)
○ Common grid system is the Universal Transverse Mercator System (UTM)
● Compass Quadrant Bearings:
○ Always measure from either north or south
● Azimuth:
○ Always start from zero degrees (North) and measure clockwise
● Looking North:
○ True North:
■ Geographic north pole
■ This is where the meridians (longitudinal lines) converge
○ Magnetic North:
■ Direction a compass points
■ Controlled by the Earth’s magnetic field
○ Grid North:
■ Direction of the vertical lines on a topographic map
● Magnetic Declination:
○ The angle between true north and magnetic north
○ Magnetic north varies with time and location
○ On the map you are given the angle between magnetic north and grid north
● Calculating Magnetic Declination:
○ Use the angle between true north and magnetic north
○ Angle between grid north and magnetic north - angle between grid north and true north
○ Annual rate of change x (current year - map publication year)
● Map Scale:
○ Representative Fraction: is a ratio of similar units
○ How to make a representative fraction from a scale of mixed units:
■ Reduce to a common unit
■ A representative fraction is always 1: a number
■ Make sure you show your work and how the units cancel
● Topographic Maps:
○ Contour Lines - lines of equal altitude above mean sea level
■ Contour interval and index contours
■ The closer the lines the steeper the slope
Energy at the Earth’s Surface (Lab 2):
, ● Energy reaching the earth’s surface can be endogenic (arises from within) or exogenic
(externally derived)
● Amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface at a given location varies throughout the
year due to the Earth’s tilt and rotation around the sun
● Sun Angle - the position of the noon sun over the Earth
○ Influences the amount of energy from the Sun (insolation) that is received at the
Earth’s surface
○ Equinox - sun’s rays are perpendicular to equator
■ Occurs around March 21st and September 22nd
○ Solstice - Sun’s rays are perpendicular to either of the tropics
■ Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees N) on June 22nd
■ Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees S) on December 22nds
○ Declination - latitude that receives direct overhead (perpendicular) insolation on a given
day
○ Equation for calculating noon sun angle:
■ Sun angle = 90 degrees - (latitude of observation +/- declination)
■ Add if the latitude of observation and declinate are in different hemispheres
■ Subtract if latitude of observation and declination are in the same hemisphere
■ You will never have a sun angle greater than 90 degrees
● The Energy Budget:
○ Albedo is the reflective quality of a surface
○ Albedo is the percent of insolation that is reflected
○ Albedo = reflected shortwave radiation / incoming shortwave radiation
○
● Net Radiation:
○
○ Rn = net radiation
○ Q = direct (beam) shortwave radiation
○ q = indirect (diffuse) shortwave
○ Alpha = albedo
○ L↓ = incoming longwave radiation from the air (the atmosphere)
○ L↑ = outgoing longwave radiation from the Earth’s surface
○ Unit are W/m2
● Heat Balance:
○ The surplus radiation is available to do work
○ Generally converted to heat
○ Heat is then transferred to an from the surface = heat fluxes
○ Rn = H + G + LE
○ H (Sensible heat) = transfer of energy back and forth between the air and the Earth’s
surface
○ LE (Latent heat of evaporation) = is the energy that is stored in water vapor as water
Map Interpretation (Lab 1)
● Coordinate Systems:
○ Lines of latitude (parallels)
■ Measured in degrees (°), minutes (‘), and seconds (‘’) north or south of the
equator
○ Lines of longitude (meridians)
■ Measured in degrees (°), minutes (‘), and seconds (‘’) east or west of
Greenwich, England
○ There are 60 minutes in 1 degree
● Rectangular Grid System:
○ Arbitrary numbers (grid lines begin at an arbitrarily chosen point)
○ Numbers increase west to east (left to right)
○ Numbers increase south to north (bottom to top)
○ Common grid system is the Universal Transverse Mercator System (UTM)
● Compass Quadrant Bearings:
○ Always measure from either north or south
● Azimuth:
○ Always start from zero degrees (North) and measure clockwise
● Looking North:
○ True North:
■ Geographic north pole
■ This is where the meridians (longitudinal lines) converge
○ Magnetic North:
■ Direction a compass points
■ Controlled by the Earth’s magnetic field
○ Grid North:
■ Direction of the vertical lines on a topographic map
● Magnetic Declination:
○ The angle between true north and magnetic north
○ Magnetic north varies with time and location
○ On the map you are given the angle between magnetic north and grid north
● Calculating Magnetic Declination:
○ Use the angle between true north and magnetic north
○ Angle between grid north and magnetic north - angle between grid north and true north
○ Annual rate of change x (current year - map publication year)
● Map Scale:
○ Representative Fraction: is a ratio of similar units
○ How to make a representative fraction from a scale of mixed units:
■ Reduce to a common unit
■ A representative fraction is always 1: a number
■ Make sure you show your work and how the units cancel
● Topographic Maps:
○ Contour Lines - lines of equal altitude above mean sea level
■ Contour interval and index contours
■ The closer the lines the steeper the slope
Energy at the Earth’s Surface (Lab 2):
, ● Energy reaching the earth’s surface can be endogenic (arises from within) or exogenic
(externally derived)
● Amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface at a given location varies throughout the
year due to the Earth’s tilt and rotation around the sun
● Sun Angle - the position of the noon sun over the Earth
○ Influences the amount of energy from the Sun (insolation) that is received at the
Earth’s surface
○ Equinox - sun’s rays are perpendicular to equator
■ Occurs around March 21st and September 22nd
○ Solstice - Sun’s rays are perpendicular to either of the tropics
■ Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees N) on June 22nd
■ Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees S) on December 22nds
○ Declination - latitude that receives direct overhead (perpendicular) insolation on a given
day
○ Equation for calculating noon sun angle:
■ Sun angle = 90 degrees - (latitude of observation +/- declination)
■ Add if the latitude of observation and declinate are in different hemispheres
■ Subtract if latitude of observation and declination are in the same hemisphere
■ You will never have a sun angle greater than 90 degrees
● The Energy Budget:
○ Albedo is the reflective quality of a surface
○ Albedo is the percent of insolation that is reflected
○ Albedo = reflected shortwave radiation / incoming shortwave radiation
○
● Net Radiation:
○
○ Rn = net radiation
○ Q = direct (beam) shortwave radiation
○ q = indirect (diffuse) shortwave
○ Alpha = albedo
○ L↓ = incoming longwave radiation from the air (the atmosphere)
○ L↑ = outgoing longwave radiation from the Earth’s surface
○ Unit are W/m2
● Heat Balance:
○ The surplus radiation is available to do work
○ Generally converted to heat
○ Heat is then transferred to an from the surface = heat fluxes
○ Rn = H + G + LE
○ H (Sensible heat) = transfer of energy back and forth between the air and the Earth’s
surface
○ LE (Latent heat of evaporation) = is the energy that is stored in water vapor as water