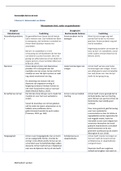
Lucy Kerr
1084899 Question: How does this compare to the expected value? Remember that our atmosphere
is approximately 80 % N2 and 20% O2.
* ③ (206483 glmol) Uglmol)
f
①
-
128
Atmosphere
.
MM of N2 : 28
g/mol x 100
Physics 1080 Lab #3 28 . 8
glmol
MM of O2 : 32
g/mo = (0 8) (28)
.
+ 10 2)(32)
.
28 82 7168 65
glmo
= =
. .
Part A
82/6
28
②
.
.
022x1023 mol
- 26
My experimental average molar
=
4 78x10 mass was much larger than the
kg
.
actual molar mass of air.
Calculated percent error is over
7000%.
Part B .
Water
Question: Using the slope of your best-fit line, calculate the average Paper Clip
mass of the molecules that make up our atmosphere (You will be
asked to submit this calculation at the end of the lab).
mg
-
Slope = -0 .
00824 slope =
Kb T
g
= 9 . 81m/s
Ky 1 38x10 235/k
-
=
rearrange
.
T= 23 : C F
=
296 15 K
(slope)(kp)(T)
.
m -
=
9
-
=
1 -
0 . 00824)(1 38x1023)(296 IS)
. .
9 8 .
=
3 .
43x10-22kg
Observations
A drop of soap was added, and the
= 3 .
43x10-22kg + paperclip sank almost instantly. This
occurred as a result of the dish soap
breaking the water's molecular
19g(6 02x1023) cohesiveness, which in turn affected
-
= 3 43x10
.
.
the water's surface tension. The
=
206486g/mo) paperclip lost support and sank as a
result of the surface tension
weakening.
Part C
hpgr
U =
2CoSE
Water
Soapy
① water mixture
100s Part B and C
029)(1000981
10 .
.
h= 2 9 . cm/100 r =
= 0 029m
Briefly describe your observations in experiments B.1, B.2 and C, and comment on the influence of
soap on the surface tension of water.
.
=
0 .
0995715
p
= 1000ksim 2 Cos (SS)
9 81m/s2
g = .
= 0 . 0868 N/m
00035
r = 0 .
In part B.1 of the experiment, I had trouble setting the paperclip on the water's surface since it sank if the
O = SS water's surface was even slightly disturbed. This can be explained by the cohesion forces of water, which are
particularly strong at the surface when molecules lack neighbours above, creating stronger interactions with
those next to and below them. The denser paperclip (compared to water) can float because of the surface
② Soapy Mix
10 . 023)(1000) (9 81)(0 00035) .
.
tension produced by this cohesive force. However, the paperclip can no longer stay floating and sinks right to
h = 23 cm/100 r = 2cos(SS) the bottom when the surface tension is too low, as happens when a drop of dish soap is added.
= 0 023m
0 078970S
.
- .
1000ksim 2 Cos (SS)
p
=
In part B.2 of the experiment, the water was unable to adhere to the nickel as well as it could have without
9 81m/s2 0 0688 N/m
dish soap. This is because dish soap molecules are good at dissolving oils that water cannot separate
=
g = . .
r = 0 .
00035 because they have both hydrophilic (attracts water) and hydrophobic (repels water) ends. The
hydrophilic end of soap adheres to water molecules when it is introduced, breaking the hydrogen bonds
O = SS
that give water its surface tension and so reducing it.
In part C of the experiment, the addition of soap lowers the surface tension of water, as demonstrated by the
fact that the surface tension of soapy water (0.069 N/m) was much lower than that of water (0.087 N/m). The
reason for this reduction is that the presence of soap molecules weakened the tension forces between water
molecules. The soap molecules successfully reduce the surface tension of the entire mixture by widening the
distance between the water molecules.
1084899 Question: How does this compare to the expected value? Remember that our atmosphere
is approximately 80 % N2 and 20% O2.
* ③ (206483 glmol) Uglmol)
f
①
-
128
Atmosphere
.
MM of N2 : 28
g/mol x 100
Physics 1080 Lab #3 28 . 8
glmol
MM of O2 : 32
g/mo = (0 8) (28)
.
+ 10 2)(32)
.
28 82 7168 65
glmo
= =
. .
Part A
82/6
28
②
.
.
022x1023 mol
- 26
My experimental average molar
=
4 78x10 mass was much larger than the
kg
.
actual molar mass of air.
Calculated percent error is over
7000%.
Part B .
Water
Question: Using the slope of your best-fit line, calculate the average Paper Clip
mass of the molecules that make up our atmosphere (You will be
asked to submit this calculation at the end of the lab).
mg
-
Slope = -0 .
00824 slope =
Kb T
g
= 9 . 81m/s
Ky 1 38x10 235/k
-
=
rearrange
.
T= 23 : C F
=
296 15 K
(slope)(kp)(T)
.
m -
=
9
-
=
1 -
0 . 00824)(1 38x1023)(296 IS)
. .
9 8 .
=
3 .
43x10-22kg
Observations
A drop of soap was added, and the
= 3 .
43x10-22kg + paperclip sank almost instantly. This
occurred as a result of the dish soap
breaking the water's molecular
19g(6 02x1023) cohesiveness, which in turn affected
-
= 3 43x10
.
.
the water's surface tension. The
=
206486g/mo) paperclip lost support and sank as a
result of the surface tension
weakening.
Part C
hpgr
U =
2CoSE
Water
Soapy
① water mixture
100s Part B and C
029)(1000981
10 .
.
h= 2 9 . cm/100 r =
= 0 029m
Briefly describe your observations in experiments B.1, B.2 and C, and comment on the influence of
soap on the surface tension of water.
.
=
0 .
0995715
p
= 1000ksim 2 Cos (SS)
9 81m/s2
g = .
= 0 . 0868 N/m
00035
r = 0 .
In part B.1 of the experiment, I had trouble setting the paperclip on the water's surface since it sank if the
O = SS water's surface was even slightly disturbed. This can be explained by the cohesion forces of water, which are
particularly strong at the surface when molecules lack neighbours above, creating stronger interactions with
those next to and below them. The denser paperclip (compared to water) can float because of the surface
② Soapy Mix
10 . 023)(1000) (9 81)(0 00035) .
.
tension produced by this cohesive force. However, the paperclip can no longer stay floating and sinks right to
h = 23 cm/100 r = 2cos(SS) the bottom when the surface tension is too low, as happens when a drop of dish soap is added.
= 0 023m
0 078970S
.
- .
1000ksim 2 Cos (SS)
p
=
In part B.2 of the experiment, the water was unable to adhere to the nickel as well as it could have without
9 81m/s2 0 0688 N/m
dish soap. This is because dish soap molecules are good at dissolving oils that water cannot separate
=
g = . .
r = 0 .
00035 because they have both hydrophilic (attracts water) and hydrophobic (repels water) ends. The
hydrophilic end of soap adheres to water molecules when it is introduced, breaking the hydrogen bonds
O = SS
that give water its surface tension and so reducing it.
In part C of the experiment, the addition of soap lowers the surface tension of water, as demonstrated by the
fact that the surface tension of soapy water (0.069 N/m) was much lower than that of water (0.087 N/m). The
reason for this reduction is that the presence of soap molecules weakened the tension forces between water
molecules. The soap molecules successfully reduce the surface tension of the entire mixture by widening the
distance between the water molecules.