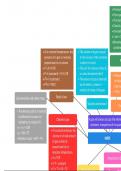
Pressure
Force pe
The stan
Directly
Inversely
1 atm = 7
Manome
containe
At a constant temperature, the The volume of a gas is equal
pressure of a gas is inversely to the volume of the container
proportional to its volume in which it is held. P
P α (1÷V) OR The unit for volume is litres (L)
P= k (constant) × (1÷V) OR or cubic decimetres (dm³). Always
PV= k (constant) The amount of gas is denoted in Kelvi
P1V1 = P2V2 by the letter n, where n = that inv
number of moles of the gas T (K) = T
Gas densities and molar mass Boyle's law
Volume and amount
Tem
The density (ρ/d) of a material
is defined as its mass (m)
Charles's law A gas will always occupy the whole
divided by its volume (V).
container, irrespective of its quant
ρ = m ÷ V OR
At constant pressure, the
ρ = PM ÷ RT
volume of a fixed amount
M(molar mass) = mRT ÷ PV GASES
of gas is directly
proportional to its
absolute temperature.
V α T OR Amontons’s/G
V÷T = constant
V1 ÷ T1 = V2 ÷ T2
Force pe
The stan
Directly
Inversely
1 atm = 7
Manome
containe
At a constant temperature, the The volume of a gas is equal
pressure of a gas is inversely to the volume of the container
proportional to its volume in which it is held. P
P α (1÷V) OR The unit for volume is litres (L)
P= k (constant) × (1÷V) OR or cubic decimetres (dm³). Always
PV= k (constant) The amount of gas is denoted in Kelvi
P1V1 = P2V2 by the letter n, where n = that inv
number of moles of the gas T (K) = T
Gas densities and molar mass Boyle's law
Volume and amount
Tem
The density (ρ/d) of a material
is defined as its mass (m)
Charles's law A gas will always occupy the whole
divided by its volume (V).
container, irrespective of its quant
ρ = m ÷ V OR
At constant pressure, the
ρ = PM ÷ RT
volume of a fixed amount
M(molar mass) = mRT ÷ PV GASES
of gas is directly
proportional to its
absolute temperature.
V α T OR Amontons’s/G
V÷T = constant
V1 ÷ T1 = V2 ÷ T2