HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- Homeostasis = maintaining a constant environment
- Nervous and endocrine systems enable animals to respond to external changes
and to control conditions inside their body
CHEMICAL COORDINATION
- May be described as slow, prolonged process of communicating info throughout
body by way of hormones (chemicals)
- Variety of hormones are secreted by special glands or tissue called endocrine
glands
WHAT IS A HORMONE
- An organic chemical substance
- Usually a protein, sometimes a steroid secreted by endocrine gland and carried in
bloodstream to target organs where it regulates metabolic reactions
- Blood stream is slower but it lasts longer
- Hormones do not last long in body as they are broken down by enzymes
WHAT IS A TARGET ORGAN
- Although hormones are carried in blood, they only affect certain cells
- Specific cells that respond to hormone have receptor sites for that hormone
- These cells are known as target tissues or organs
- Can be a single gland or organ scattered throughout body
WHAT IS AN ENDOCRINE GLAND
- A vascular, ductless gland that secretes hormones which are carried in
bloodstream to target organs
- Effectors
HOW DO EXO- AND ENDOCRINE GLANDS DIFFER
- Secretions of exocrine gland are carried in ducts to where they are needed
- Endocrine glands do not have ducts and their secretions are carried in
bloodstream to target organs
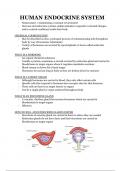
, ENDOCRINE GLANDS IN THE BODY
- Hypothalamus, pituitary
gland, thyroid gland,
pancreas, adrenal
glands, gonads
1. HYPOTHALAMUS
- Part of brain situated
above pituitary gland
- Secretes hormones such
as ADH (antidiuretic
hormone) and oxytocin
Role of ADH:
- Osmoreceptors in blood
vessels of hypothalamus
detect increase in
osmolarity (low water
levels) of blood
- Hypothalamus responds
and releases ADH
- ADH helps conserve
water if body is
dehydrated
- Does this by causing
more water to be
reabsorbed back into
blood from the collecting
ducts of kidney, so less
water is lost in urine
2. PITUITARY GLAND
- Controlled by hypothalamus
- Acts as the chemical co-ordinator of most other endocrine glands and is therefore
often called the ‘master gland’
- AKA hypophysis
- Attached to hypothalamus at base of brain by short stalk
- Anterior lobe = purely glandular, makes hormones
- Posterior lobe = stores hormones
- Homeostasis = maintaining a constant environment
- Nervous and endocrine systems enable animals to respond to external changes
and to control conditions inside their body
CHEMICAL COORDINATION
- May be described as slow, prolonged process of communicating info throughout
body by way of hormones (chemicals)
- Variety of hormones are secreted by special glands or tissue called endocrine
glands
WHAT IS A HORMONE
- An organic chemical substance
- Usually a protein, sometimes a steroid secreted by endocrine gland and carried in
bloodstream to target organs where it regulates metabolic reactions
- Blood stream is slower but it lasts longer
- Hormones do not last long in body as they are broken down by enzymes
WHAT IS A TARGET ORGAN
- Although hormones are carried in blood, they only affect certain cells
- Specific cells that respond to hormone have receptor sites for that hormone
- These cells are known as target tissues or organs
- Can be a single gland or organ scattered throughout body
WHAT IS AN ENDOCRINE GLAND
- A vascular, ductless gland that secretes hormones which are carried in
bloodstream to target organs
- Effectors
HOW DO EXO- AND ENDOCRINE GLANDS DIFFER
- Secretions of exocrine gland are carried in ducts to where they are needed
- Endocrine glands do not have ducts and their secretions are carried in
bloodstream to target organs
, ENDOCRINE GLANDS IN THE BODY
- Hypothalamus, pituitary
gland, thyroid gland,
pancreas, adrenal
glands, gonads
1. HYPOTHALAMUS
- Part of brain situated
above pituitary gland
- Secretes hormones such
as ADH (antidiuretic
hormone) and oxytocin
Role of ADH:
- Osmoreceptors in blood
vessels of hypothalamus
detect increase in
osmolarity (low water
levels) of blood
- Hypothalamus responds
and releases ADH
- ADH helps conserve
water if body is
dehydrated
- Does this by causing
more water to be
reabsorbed back into
blood from the collecting
ducts of kidney, so less
water is lost in urine
2. PITUITARY GLAND
- Controlled by hypothalamus
- Acts as the chemical co-ordinator of most other endocrine glands and is therefore
often called the ‘master gland’
- AKA hypophysis
- Attached to hypothalamus at base of brain by short stalk
- Anterior lobe = purely glandular, makes hormones
- Posterior lobe = stores hormones