Learninggoals case 2
1. What is the structure of a muscle?
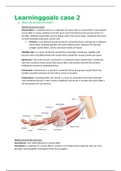
Skeletal muscle structure
Muscle fibers = a skeletal muscle is a collection of muscle cells, or muscle fibers. Each skeletal
muscle fiber is a long, cylindrical cell with up to several hundred nuclei near the surface of
the fiber. Skeletal muscle fibers are the largest cells in the human body, created by the fusion
of many individual embryonic muscle cells.
Fascicles = each skeletal muscle sheated in connective tissue, with groups of adjacent
muscle fibers bundled together into units called fascicles. Between the fascicles
collagen, elastic fibers, nerves and blood vessels are found.
Satellite cells = is a stem cell that lie outside the muscle fiber membrane. Satellite cells
become active and differentiate into muscle when needed for muscle growth and repair.
Epimysium = the entire muscle is enclosed in a connective tissue sheath that is continuous
with the connective tissue around the muscle fibers and fascicles and with the tendons
holding the muscles to underlying bones.
Perimysium = Perimysium is a sheath of connective tissue that groups muscle fibers into
bundles (anywhere between 10 and 100 or more) or fascicles.
Endomysium = meaning within the muscle, is a layer of connective tissue that ensheaths
each individual myocyte. It also contains capillaries and nerves. It overlies the muscle fiber's
cell membrane: the sarcolemma
Skeletal muscle fiber structure
Sacrolemma = the cellmembrane of a muscle fiber
Sacroplasm = cytoplasm of a muscle fiber it contains a lot of glycosomes (granules that can store
glycogen) and myoglobin (red pigment that stores oxygen).
,Myofibrils = the main intracellular structures in striated muscles are myofibrils, highly organized
bundles of contractile and elastic proteins that carry out the work of contraction. The cytosol
between myofibrils contain a lot of glycogen.
Sacroplasmic reticiulum (SR) = a form of modified endoplasmatic reticulum that wraps around each
myofibril like a piece of lace ( = gaas). The SR consists of longitudinal tubules with enlarged end
regions called the terminal cisternae. The sacroplasmatic reticulum concentrates and sequesters
Ca2+ with the help of Ca2+ ATPase in the SR membrane. Calcium release from SR creates signals that
play a key role in contraction of all types of muscle.
Transverse tubulus (T-tubulus) = the terminal cisternae are adjacent to and closely associated with a
branching network of T-tubulus. One t-tubule and its two flanking terminal cisternae are called . The
membranes of t-tubulus are a continuation of the muscle fiber membrane, which makes the lumen
of t-tubulus continuous with extracellular fluid. The T-tubulus allows action potentials to move
rapidly from the cell surface into the interior of the fiber so that they reach the terminal cisternae
quickly.
Myofibril structure
Sacromere = each myofibril is composed of several types of proteins organized in repeating
contractile structures called sacromeres, they contain smaller structures called myofilaments.
, Myofibril proteins =
Myosin = create the thick filaments. Is a motor protein with the ability to create
movement. Various isoforms of myosin occur in different types of muscle and help
determine the muscle’s speed of contraction. Each myosin molecule is composed of
protein chains that intertwine to form a long tail and pair of tadpole-like (=
kikkervisje) heads. Each myosin head has two proteins, a heavy chain and a smaller
light chain. The heavy chain (myosin ATPase) is the motor domain that binds ATP and
uses the energy to create movement. The heavy chain also contains a bindingsite for
actin.
Actin = creates thin filaments. One polypeptide subunit of actin is called globular
actin (G actin) which contains the active sites were the myosin heads can attach to,
two of those G actins polymerised and intertwined are called filamentous actin (F
actin) and forms the thin filament backbone.
On the actin are found regulatory proteins.
o Tropomysosin in a relaxed muscle fiber, they block myosin-binding sites
on actin so that myosin heads on the thick filaments cannot bind to the thin
filaments.
o Troponin is a three-polypeptide complex. TnI an inhibitory subunit that
binds to actin. Another (TnT) binds to tropomyosin and helps position it on
actin. The third (TnC) binds calcium ions.
The elastic filament is composed of the giant protein titin. Tintin holds the thick
filaments in place, thus maintaining the organization of the A band, and helps the
muscle cell spring back into shape after stretching. Titin does not resist stretching in
the ordinary range of extension, but it stiffens as it uncoils, helping the muscle resist
excessive stretching, which might pull the sarcomeres apart.
o Tintin is helped by nebulin, an inelastic protein that lies alongside thin
filaments and attached an to the Z disk. Nebulin helps align the actin
filaments of the sarcomere.
Most of the time the parallel thick and thin filaments are connected by myosin crossbridges that span
the space between the filaments. Each actin molecule has a myosin-binding site and each myosin
1. What is the structure of a muscle?
Skeletal muscle structure
Muscle fibers = a skeletal muscle is a collection of muscle cells, or muscle fibers. Each skeletal
muscle fiber is a long, cylindrical cell with up to several hundred nuclei near the surface of
the fiber. Skeletal muscle fibers are the largest cells in the human body, created by the fusion
of many individual embryonic muscle cells.
Fascicles = each skeletal muscle sheated in connective tissue, with groups of adjacent
muscle fibers bundled together into units called fascicles. Between the fascicles
collagen, elastic fibers, nerves and blood vessels are found.
Satellite cells = is a stem cell that lie outside the muscle fiber membrane. Satellite cells
become active and differentiate into muscle when needed for muscle growth and repair.
Epimysium = the entire muscle is enclosed in a connective tissue sheath that is continuous
with the connective tissue around the muscle fibers and fascicles and with the tendons
holding the muscles to underlying bones.
Perimysium = Perimysium is a sheath of connective tissue that groups muscle fibers into
bundles (anywhere between 10 and 100 or more) or fascicles.
Endomysium = meaning within the muscle, is a layer of connective tissue that ensheaths
each individual myocyte. It also contains capillaries and nerves. It overlies the muscle fiber's
cell membrane: the sarcolemma
Skeletal muscle fiber structure
Sacrolemma = the cellmembrane of a muscle fiber
Sacroplasm = cytoplasm of a muscle fiber it contains a lot of glycosomes (granules that can store
glycogen) and myoglobin (red pigment that stores oxygen).
,Myofibrils = the main intracellular structures in striated muscles are myofibrils, highly organized
bundles of contractile and elastic proteins that carry out the work of contraction. The cytosol
between myofibrils contain a lot of glycogen.
Sacroplasmic reticiulum (SR) = a form of modified endoplasmatic reticulum that wraps around each
myofibril like a piece of lace ( = gaas). The SR consists of longitudinal tubules with enlarged end
regions called the terminal cisternae. The sacroplasmatic reticulum concentrates and sequesters
Ca2+ with the help of Ca2+ ATPase in the SR membrane. Calcium release from SR creates signals that
play a key role in contraction of all types of muscle.
Transverse tubulus (T-tubulus) = the terminal cisternae are adjacent to and closely associated with a
branching network of T-tubulus. One t-tubule and its two flanking terminal cisternae are called . The
membranes of t-tubulus are a continuation of the muscle fiber membrane, which makes the lumen
of t-tubulus continuous with extracellular fluid. The T-tubulus allows action potentials to move
rapidly from the cell surface into the interior of the fiber so that they reach the terminal cisternae
quickly.
Myofibril structure
Sacromere = each myofibril is composed of several types of proteins organized in repeating
contractile structures called sacromeres, they contain smaller structures called myofilaments.
, Myofibril proteins =
Myosin = create the thick filaments. Is a motor protein with the ability to create
movement. Various isoforms of myosin occur in different types of muscle and help
determine the muscle’s speed of contraction. Each myosin molecule is composed of
protein chains that intertwine to form a long tail and pair of tadpole-like (=
kikkervisje) heads. Each myosin head has two proteins, a heavy chain and a smaller
light chain. The heavy chain (myosin ATPase) is the motor domain that binds ATP and
uses the energy to create movement. The heavy chain also contains a bindingsite for
actin.
Actin = creates thin filaments. One polypeptide subunit of actin is called globular
actin (G actin) which contains the active sites were the myosin heads can attach to,
two of those G actins polymerised and intertwined are called filamentous actin (F
actin) and forms the thin filament backbone.
On the actin are found regulatory proteins.
o Tropomysosin in a relaxed muscle fiber, they block myosin-binding sites
on actin so that myosin heads on the thick filaments cannot bind to the thin
filaments.
o Troponin is a three-polypeptide complex. TnI an inhibitory subunit that
binds to actin. Another (TnT) binds to tropomyosin and helps position it on
actin. The third (TnC) binds calcium ions.
The elastic filament is composed of the giant protein titin. Tintin holds the thick
filaments in place, thus maintaining the organization of the A band, and helps the
muscle cell spring back into shape after stretching. Titin does not resist stretching in
the ordinary range of extension, but it stiffens as it uncoils, helping the muscle resist
excessive stretching, which might pull the sarcomeres apart.
o Tintin is helped by nebulin, an inelastic protein that lies alongside thin
filaments and attached an to the Z disk. Nebulin helps align the actin
filaments of the sarcomere.
Most of the time the parallel thick and thin filaments are connected by myosin crossbridges that span
the space between the filaments. Each actin molecule has a myosin-binding site and each myosin