----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
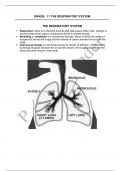
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
§ Respiration refers to a chemical process that takes place within cells. Oxygen is
used to break down organic compounds (food) to release energy.
§ Breathing or ventilation is a mechanical process, which involves the intake of
oxygen-rich air into the lungs and the release of carbon dioxide-rich air from the
lungs.
§ Gaseous exchange is a physical process by means of diffusion. It involves the
exchange of gases between the air and the blood in the lungs and between the
blood and other tissues of the body.
, STRUCTURE DESCRIPTION & FUNCTION(S)
The air passages Lined with hairs that remove dust from inhaled air.
(Nostrils and nasal cavities) Lined with ciliated epithelium with goblet cells that secrete
mucus. Air is warmed and filtered of dust and germs by the
mucus and cilia.
Pharynx Passage that connects the nasal cavities with the trachea via
the epiglottis.
Epiglottis A valve-like, leaf-shaped piece of cartilage that covers the
larynx. It closes during swallowing to prevent food or drink
from entering the trachea.
Larynx (voice box) Found in the entrance to the trachea and is covered by the
epiglottis. The larynx produces sound when air moves
through it.
Trachea The trachea is held open by a series of C-shaped cartilage
rings. The inside of the trachea is lined with a layer of ciliated
epithelium. Air is filtered of dust and germs by cilia.
Bronchi and bronchioles The trachea divides into two bronchi, which enters each of the
lungs. Each of these then branches into a number of smaller
passages called bronchioles. The bronchi are held open by
a series of O-shaped cartilage rings. The bronchioles have no
cartilage.
2