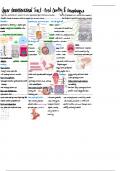
Cell Division G2 Checkpoint
Cell division is divided into two major Checks for:
phases: o DNA replication completeness
The second checkpoint found after the
Interphase (formerly known as the second gap phase ensures that cell division
resting phase) goes smoothly.
M phase, where the cell actively If errors or damages are detected, the cell
divides will pause for repairs.
If the damage is irreparable, the cell may
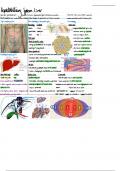
G1 Phase undergo apoptosis.
Also known as the first gap phase. M Phase
Cell grows physically larger.
Creates duplicates of organelles. Involves two distinct division processes:
Accumulates building blocks of DNA,
proteins, and energy reserves for DNA Karyokinesis: During karyokinesis, cell
replication. growth and protein production stop. All of
the energy is focused on the complex and
G1 Checkpoint orderly division of DNA into two sets.
Cytokinesis: The splitting of the
Checks for: cytoplasm into two, resulting in two new
o Cell size cells. Cytokinesis usually begins just as
o Nutrients mitosis is ending.
o Growth factors
o DNA damage Spindle Checkpoint
Before proceeding to the next phase, a
checkpoint checks if the cell has made the Checks for:
correct changes. o Chromosome attachment to spindle
The G1 checkpoint is the main decision at the metaphase plate
point for a cell. Once a cell passes this, it The last checkpoint, known as the M
becomes irreversibly committed to checkpoint or spindle checkpoint, is found
division. in the metaphase stage of M phase.
If a cell does not qualify to proceed to the It looks for stragglers and aligns them to
next phase, it enters the G0 phase. the center. If abnormalities are not
G0 Phase, also known as the quiescence corrected, the cell will undergo apoptosis.
or resting stage, is a phase outside the
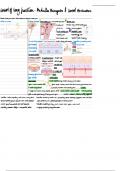
replicative cell cycle. Cytokinesis
S Phase Takes place differently in animal and plant
cells:
Also known as the synthesis phase. o Animal Cells: A band of
Synthesizes a complete copy of DNA. cytoskeletal fibers called the
Duplicates the microtubule-organizing contractile ring contracts inwards
structure known as centrosome. and pinches the cell into two, a
process known as contractile
G2 Phase cytokinesis. The indentation
produced as the ring contracts
Also known as the second gap phase. inward is called the cleavage
Replenishes energy. furrow.
Synthesizes protein for chromosome o Plant Cells: The cell is more rigid
manipulation. due to the cell wall and vacuole
Some cell organelles are duplicated. pressure. Plant cells divide by
Cytoskeletons are dismantled. building a new structure between
Contents are reorganized. the middle of the cell known as the
Cell division is divided into two major Checks for:
phases: o DNA replication completeness
The second checkpoint found after the
Interphase (formerly known as the second gap phase ensures that cell division
resting phase) goes smoothly.
M phase, where the cell actively If errors or damages are detected, the cell
divides will pause for repairs.
If the damage is irreparable, the cell may
G1 Phase undergo apoptosis.
Also known as the first gap phase. M Phase
Cell grows physically larger.
Creates duplicates of organelles. Involves two distinct division processes:
Accumulates building blocks of DNA,
proteins, and energy reserves for DNA Karyokinesis: During karyokinesis, cell
replication. growth and protein production stop. All of
the energy is focused on the complex and
G1 Checkpoint orderly division of DNA into two sets.
Cytokinesis: The splitting of the
Checks for: cytoplasm into two, resulting in two new
o Cell size cells. Cytokinesis usually begins just as
o Nutrients mitosis is ending.
o Growth factors
o DNA damage Spindle Checkpoint
Before proceeding to the next phase, a
checkpoint checks if the cell has made the Checks for:
correct changes. o Chromosome attachment to spindle
The G1 checkpoint is the main decision at the metaphase plate
point for a cell. Once a cell passes this, it The last checkpoint, known as the M
becomes irreversibly committed to checkpoint or spindle checkpoint, is found
division. in the metaphase stage of M phase.
If a cell does not qualify to proceed to the It looks for stragglers and aligns them to
next phase, it enters the G0 phase. the center. If abnormalities are not
G0 Phase, also known as the quiescence corrected, the cell will undergo apoptosis.
or resting stage, is a phase outside the
replicative cell cycle. Cytokinesis
S Phase Takes place differently in animal and plant
cells:
Also known as the synthesis phase. o Animal Cells: A band of
Synthesizes a complete copy of DNA. cytoskeletal fibers called the
Duplicates the microtubule-organizing contractile ring contracts inwards
structure known as centrosome. and pinches the cell into two, a
process known as contractile
G2 Phase cytokinesis. The indentation
produced as the ring contracts
Also known as the second gap phase. inward is called the cleavage
Replenishes energy. furrow.
Synthesizes protein for chromosome o Plant Cells: The cell is more rigid
manipulation. due to the cell wall and vacuole
Some cell organelles are duplicated. pressure. Plant cells divide by
Cytoskeletons are dismantled. building a new structure between
Contents are reorganized. the middle of the cell known as the