Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1
Tags
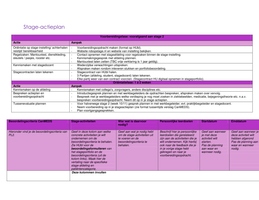
Why Firms Grow:
Increased profits
Reduce unit cost of production by benefitting from economies of scale
Increase market share and power to become a dominant force in the market
Reduce risks by diversifying into various markets
Managerial motives as senior managers may want to control larger businesses
Why Firms Stay Small:
Lack of finance for expansion
Avoiding diseconomies of scale
Providing niche products which have a low PED or high YED
To offer more personal service to consumers
May act as local monopolies - where in the local area that firm is the dominant
provider in that market
Types of Firms:
Producer Cooperatives:
Also known as Co-ops
Owned and run by their members, who can be customers, employees or
groups of businesses
Co-op Group in the UK is the biggest, followed by John Lewis Partnership
Businesses are founded and run on principles of shared ownership, shared
voice and shared profits
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 1
, Social Enterprises:
Not-just-for-profit business created to address a social problem
Profits are reinvested for one or more social purposes in the community
Examples include Fink Street Food, The Big Issue Magazine, Eden Project
Not-for-Profit & Not-for-Dividend Firms:
Charities, community organisations that are run on commercial lines
Network Rail as an example in the UK
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
When companies integrate social and environmental concerns into business
operations on a voluntary basis
Reasons for CSR:
Altruism
Contracting benefits
Customer related motivation
Lower production costs
Risk management
Improved access to capital
Principal Agent Problem
An asymmetric information problem, where the owners of a firm cannot
observe directly the day to day decisions of management, thus having to hire
managers who have different objectives - this is called the Divorce of
Ownership and Control
When the owner/stakeholder of a firm (principal) have different objectives to
the managers of the firm (agent)
Trying to monitor the decisions of the agent becomes costly and difficult to
track
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 2
, Possible conflicts of interest that may result between shareholders (principal)
and the management (agent) of a firm
Solutions to The Principal Agent Problem:
Shareholders and management of a firm may have different interests in a firm
Aligning the interests of shareholders and management of a firm is a method
to overcome The Principal Agent Problem
For example:
Employee share ownership schemes
Long term employment contracts for senior management, where security
of tenure may encourage managers to take decisions in the long term best
interest of the business
Long term stock commitment, where senior management are offered a
percentage of their salary/bonus in the form of stock of the company, so if
the company does well the manager benefits as well
Privatisation
The transfer of assets from the public (state or government) sector to the
private sector of an economy
Examples of private sector firms:
Royal Mail
British Waterways
British Gas
British Aerospace
British Telecom
Examples of public sector firms:
Network Rail
Royal Bank of Scotland
The Met Office
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 3
, Outsourcing and Contracting Out:
When private sector businesses are used to provide public services, often
after a tendering or bidding process has been held
Examples of businesses that outsource: G4S and Serco
Advantages of Outsourcing: Criticisms of Outsourcing:
Opening public services up to Firms may sacrifice quality to
competition can save tax payer lower costs
money
Doubts over employment practices
Private sector businesses more of private firms e.g. low wage,
likely to be more efficient due to poor working conditions
profit incentive
Outsourcing requires regulation
May be more innovative, less which involves extra spending
hierarchical and less prone to
diseconomies of scale
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 4
Tags
Why Firms Grow:
Increased profits
Reduce unit cost of production by benefitting from economies of scale
Increase market share and power to become a dominant force in the market
Reduce risks by diversifying into various markets
Managerial motives as senior managers may want to control larger businesses
Why Firms Stay Small:
Lack of finance for expansion
Avoiding diseconomies of scale
Providing niche products which have a low PED or high YED
To offer more personal service to consumers
May act as local monopolies - where in the local area that firm is the dominant
provider in that market
Types of Firms:
Producer Cooperatives:
Also known as Co-ops
Owned and run by their members, who can be customers, employees or
groups of businesses
Co-op Group in the UK is the biggest, followed by John Lewis Partnership
Businesses are founded and run on principles of shared ownership, shared
voice and shared profits
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 1
, Social Enterprises:
Not-just-for-profit business created to address a social problem
Profits are reinvested for one or more social purposes in the community
Examples include Fink Street Food, The Big Issue Magazine, Eden Project
Not-for-Profit & Not-for-Dividend Firms:
Charities, community organisations that are run on commercial lines
Network Rail as an example in the UK
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
When companies integrate social and environmental concerns into business
operations on a voluntary basis
Reasons for CSR:
Altruism
Contracting benefits
Customer related motivation
Lower production costs
Risk management
Improved access to capital
Principal Agent Problem
An asymmetric information problem, where the owners of a firm cannot
observe directly the day to day decisions of management, thus having to hire
managers who have different objectives - this is called the Divorce of
Ownership and Control
When the owner/stakeholder of a firm (principal) have different objectives to
the managers of the firm (agent)
Trying to monitor the decisions of the agent becomes costly and difficult to
track
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 2
, Possible conflicts of interest that may result between shareholders (principal)
and the management (agent) of a firm
Solutions to The Principal Agent Problem:
Shareholders and management of a firm may have different interests in a firm
Aligning the interests of shareholders and management of a firm is a method
to overcome The Principal Agent Problem
For example:
Employee share ownership schemes
Long term employment contracts for senior management, where security
of tenure may encourage managers to take decisions in the long term best
interest of the business
Long term stock commitment, where senior management are offered a
percentage of their salary/bonus in the form of stock of the company, so if
the company does well the manager benefits as well
Privatisation
The transfer of assets from the public (state or government) sector to the
private sector of an economy
Examples of private sector firms:
Royal Mail
British Waterways
British Gas
British Aerospace
British Telecom
Examples of public sector firms:
Network Rail
Royal Bank of Scotland
The Met Office
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 3
, Outsourcing and Contracting Out:
When private sector businesses are used to provide public services, often
after a tendering or bidding process has been held
Examples of businesses that outsource: G4S and Serco
Advantages of Outsourcing: Criticisms of Outsourcing:
Opening public services up to Firms may sacrifice quality to
competition can save tax payer lower costs
money
Doubts over employment practices
Private sector businesses more of private firms e.g. low wage,
likely to be more efficient due to poor working conditions
profit incentive
Outsourcing requires regulation
May be more innovative, less which involves extra spending
hierarchical and less prone to
diseconomies of scale
Size and Types of Firms 3.1.1 4