Les 1: Chapter 1 The origins of science
Logic of Inquiry - Logica van onderzoek
Method of inquiry - Methode van onderzoek (science)
Epistemology – the science of knowing; systems of knowledge
Methodology – the science of finding out; procedures for scientific investigation
Biases – prejudice. the degree of disturbance of the received signal
self-fulfilling prophecies - zelfvervullende voorspelling
Plato: a priori thinking. Aristotle: empirical reality
Ancient Greek a lot of research before scientific revolution
Science is learning & knowing about the world (method of inquiry)
assertion needs empirical and logical support
Science focus on the knowledge of reality by generating new knowledge
systematic (the scientific method)
Every type of science has an object, BA contains all aspects of
organization, relation within between and its environment
research has content (what subject) and methodological side (the way).
Methodology ‘’theory behind methods’’ (logic of inquiry)
learning instrumental & conceptual
Science -> knowing -> agreement reality (Looking, thinking, knowing) on
working, watching, translation (epistomology)
Science deals with logic and real world; no metaphysics, belief, opinion,
ethical values
Shortcoming:
o Overgeneralization
o illogical reasoning
o Inaccurate observation
o Group think
o Selective observation/perception
o (confirmation) Biases
Authority (right direction, hinder own ideas) & Tradition (stand your
ground, no go areas)
researchers needs to be curious, sceptic, creative, perseverant, thinking a
lot
,Les 1: Chapter 2 The scientific method
Enumeration = full induction is an ‘’opsomming’’
Context of discovery = the situation ideas are conceived (Induction, Abduction)
Context of justification = evidence explanation is correct (Deduction)
Implicit or mental models = simplified models of the ‘’world’’ around us. To
communicate -> explicit
Explicit or computer models = physical and conceptual (verbal, schematic and
mathematical)
Normative concept of law= what should and what should not (god)
Establishing concept of law= certain pattern or regularity, need to be always true
Experiment = artificial research setting, testing hypothesis
Hypothesesis = tentative, testable, statement predicts finding empirical data (not
facts but relations)
Theory = facts and statements ordered logical end consistent. Not empirically
verifiable. Conclusions (hypotheses) are
Theoretical concepts = gravity, electromagnetic field
Deductive Logic and research Inductive Logic and research
a) All humans are mortal a) I have seen a number of trees
b) Dutch people are human b) All those trees have green
c) Dutch people are mortal leaves
c) All trees have green leaves
Deduction reasoning is syllogism = Induction problem in science:
universal (general) / individual / observation influenced,
specific interpretation, limited number of
Two premises (P) and conclusion observations
(C) it’s almost impossible to observe
Logical reasoning -> all subjects, therefore there may
Modus Ponens = If p then q, p always be a possibility of
holds, therefore q disproving the empirical
Modus Tollens = If p then q, not q, generalization
therefore not p David Hume -> Not certain
In mathematics, geometry and statements about unobserved
logic situations
Francis Bacon -> One should
observe all different forms
In economics, sociology and
natural (often)
, Induction and abduction leads to new knowledge. Deduction
test/evaluate theory
Abduction starts with observation or empirical generalization then
hypothesis confirmed trough deduction
Induction and abduction leads to new knowledge. Deduction
test/evaluate theory
Scientific revolution -> scientific method (observe pattern, hypotheses,
test one by one, conclusion)
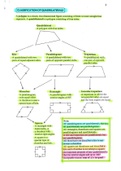
Figure 1. ''The wheel of science'' Empirical Cycle
Logic of Inquiry - Logica van onderzoek
Method of inquiry - Methode van onderzoek (science)
Epistemology – the science of knowing; systems of knowledge
Methodology – the science of finding out; procedures for scientific investigation
Biases – prejudice. the degree of disturbance of the received signal
self-fulfilling prophecies - zelfvervullende voorspelling
Plato: a priori thinking. Aristotle: empirical reality
Ancient Greek a lot of research before scientific revolution
Science is learning & knowing about the world (method of inquiry)
assertion needs empirical and logical support
Science focus on the knowledge of reality by generating new knowledge
systematic (the scientific method)
Every type of science has an object, BA contains all aspects of
organization, relation within between and its environment
research has content (what subject) and methodological side (the way).
Methodology ‘’theory behind methods’’ (logic of inquiry)
learning instrumental & conceptual
Science -> knowing -> agreement reality (Looking, thinking, knowing) on
working, watching, translation (epistomology)
Science deals with logic and real world; no metaphysics, belief, opinion,
ethical values
Shortcoming:
o Overgeneralization
o illogical reasoning
o Inaccurate observation
o Group think
o Selective observation/perception
o (confirmation) Biases
Authority (right direction, hinder own ideas) & Tradition (stand your
ground, no go areas)
researchers needs to be curious, sceptic, creative, perseverant, thinking a
lot
,Les 1: Chapter 2 The scientific method
Enumeration = full induction is an ‘’opsomming’’
Context of discovery = the situation ideas are conceived (Induction, Abduction)
Context of justification = evidence explanation is correct (Deduction)
Implicit or mental models = simplified models of the ‘’world’’ around us. To
communicate -> explicit
Explicit or computer models = physical and conceptual (verbal, schematic and
mathematical)
Normative concept of law= what should and what should not (god)
Establishing concept of law= certain pattern or regularity, need to be always true
Experiment = artificial research setting, testing hypothesis
Hypothesesis = tentative, testable, statement predicts finding empirical data (not
facts but relations)
Theory = facts and statements ordered logical end consistent. Not empirically
verifiable. Conclusions (hypotheses) are
Theoretical concepts = gravity, electromagnetic field
Deductive Logic and research Inductive Logic and research
a) All humans are mortal a) I have seen a number of trees
b) Dutch people are human b) All those trees have green
c) Dutch people are mortal leaves
c) All trees have green leaves
Deduction reasoning is syllogism = Induction problem in science:
universal (general) / individual / observation influenced,
specific interpretation, limited number of
Two premises (P) and conclusion observations
(C) it’s almost impossible to observe
Logical reasoning -> all subjects, therefore there may
Modus Ponens = If p then q, p always be a possibility of
holds, therefore q disproving the empirical
Modus Tollens = If p then q, not q, generalization
therefore not p David Hume -> Not certain
In mathematics, geometry and statements about unobserved
logic situations
Francis Bacon -> One should
observe all different forms
In economics, sociology and
natural (often)
, Induction and abduction leads to new knowledge. Deduction
test/evaluate theory
Abduction starts with observation or empirical generalization then
hypothesis confirmed trough deduction
Induction and abduction leads to new knowledge. Deduction
test/evaluate theory
Scientific revolution -> scientific method (observe pattern, hypotheses,
test one by one, conclusion)
Figure 1. ''The wheel of science'' Empirical Cycle