Vertebrate Body Plan b/c = because
b/w = between
Monday, August 12, 2019 10:29 AM
w/ = with
expt = experiment
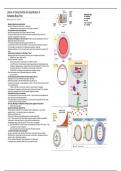
• Mesoderm Migration during Gastrulation ex. = example
• Mesoderm cells migrates into the embryo -> Invagination
○ Mesoderm becomes NS, laying more on the ventral side of drosophila.
• D/V specification occurs during oogenesis.
• Nurse cell pumps protein into oocyte, which will become the embryo.
• Oocyte surrounded by follicle cells. Determines the anterior and posterior ends of oocyte. Also
responsible for establishment of DV gradient.
• Activation of Toll Receptor on the Ventral Side **Embryo is still a syncytial blastoderm at this time.**
• Spätzle (SPZ): ligand for the Toll receptor.
• Toll receptors are distributed throughout egg plasma membrane. Yet…
• Localized release of SPZ around ventral midline -> ensures receptors only activated on ventral side.
• Toll is activated in a "graded manner," w/ highest point of gradient on ventral side.
• Perivitelline membrane: a fluid that surrounds nuclei in embryo. Above molecules move around in this
space.
• Graded Nuclear Localization of the Morphogen "Dorsal"
• Morphogen Dorsal located in the nucleus on ventral side, yet in the cytoplasm on dorsal side.
○ KNOW Dorsal, Cactus, Spätzle and Toll.
• Specifying Ventral Side in drosophila:
○ Cactus-Dorsal complex is always located in the cytoplasm. However…
○ Once SPZ binds to Toll, their interaction induces kinase activities which phosphorylates Cactus
morphogen -> degrades Cactus in cytoplasm! When alone, Dorsal migrates to the nucleus. That is
why Dorsal is NOT present in the cytoplasm on the ventral side, but in the nuclei.
○ CONCLUSION: Toll signaling controls graded nuclear localization of Dorsal!
• Similar mechanisms are used to differentiate lymphocytes in mammals.
○ Ex. Dorsal: NF-kB
• The Dorsal protein provides positional information along the D/V axis.
• Patterning of the D/V axis controlled by maternal gene "Dorsal (dl)."
• REVIEW Dorsal protein is uniformly distributed evenly along the egg. Yet…
• In response to Toll signaling -> causes degradation of Cactus -> DI protein enters the embryo nuclei of
cells in a graded manner.
○ Highest concentration in ventral nuclei, lowest in the dorsal nuclei (all in cytoplasm).
• In the absence of Toll signaling -> the DI protein is bound to Cactus, which keeps DI in the cytoplasm.
• Dl encodes a transcription factor (Twist) and regulates target gene expression.
• Dorsal protein functions as a morphogen.
• In MT dorsal embryos, DI protein cannot enter the nuclei. -> Ventral side cannot be specified from the
Dorsal. Both sides become Dorsal (dorsalized).
• In MT cactus embryos, all DI protein enters nuclei. -> Dorsal side cannot be specified from the Ventral
side. Both sides become Ventral (ventralized).
• Dorsal as a Morphogen and Regulation of Region-specific Zygotic Gene Expression
○ KNOW twist and dpp genes.
• Zygotic Gene Expression along D/V Axis
• Dl (maternal gene->protein) binds to the regulatory regions of zygotic genes in a concentration-
dependent manner. -> Can activate or repress some zygotic genes.
• HIGH levels of Dl activate Twist.
• LOW levels of Dl activate noeuroectodermal genes like short gastrulation (Sog).
• Twist: TF that is expressed in the ventral midline; required for mesoderm induction and gastrulation.
Dorsal protein in nuclei needs to reach a certain threshold to activate twist gene.
• Decapentaplegic (dpp): growth factor apart of TFGB, and acts as a morphogen.
○ Dpp is repressed when DI protein is present, and activated when DI protein is NOT present. -> Dpp
is expressed in the nuclei on Dorsal side.
○ Dpp is secreted from the cell and is pumped into the Perivitelline membrane.
• A Gradient of Dpp Patterns the Dorsal Region.
• Sog gene is expressed in lower half sides of Ventral region -> Sog protein. Acts as an inhibitor…
• Sog binds to dpp -> prevents dpp from acting on receptor on cell surface -> Dpp becomes inactive in
presence of Sog. -> Sog regions are dpp-free.
• Causes a gradient of Dpp activity, highest concentration in the Dorsal region.
• In vertebrates dpp is homologous to BMP4, and Sog to vertebrate Chordin.