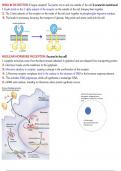
INSULIN RECEPTOR (Enzyme receptor) Two parts: one in and one outside of the cell. (Located in membrane)
1. Insulin binds to the 2 alpha subunit of the receptor on the outside of the cell, bringing them together.
2. The 2 beta subunits of the receptor on the inside of the cell work together to phosphorylate thyrosine residues.
3. This leads to processes favouring the transport of glucose, fatty acids and amino acids into the cell.
7
NUCLEAR HORMONE RECEPTOR: (located in the cell)
1. Lipophilic hormones come from the blood stream (attached to globolins) and are released from transporting protein.
2. Hormone travels via the membrane to the cytoplasm.
3. Hormone attaches to receptor, causing a change in the confirmation of the receptor.
4. 2 Hormone receptor complexes bind in the nucleus to the structure of DNA in the hormone response element.
5. This activates RNA polymerase, which will synthesize a messenger RNA.
6. mRNA exits nucleus, traveling to ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs.
1. Insulin binds to the 2 alpha subunit of the receptor on the outside of the cell, bringing them together.
2. The 2 beta subunits of the receptor on the inside of the cell work together to phosphorylate thyrosine residues.
3. This leads to processes favouring the transport of glucose, fatty acids and amino acids into the cell.
7
NUCLEAR HORMONE RECEPTOR: (located in the cell)
1. Lipophilic hormones come from the blood stream (attached to globolins) and are released from transporting protein.
2. Hormone travels via the membrane to the cytoplasm.
3. Hormone attaches to receptor, causing a change in the confirmation of the receptor.
4. 2 Hormone receptor complexes bind in the nucleus to the structure of DNA in the hormone response element.
5. This activates RNA polymerase, which will synthesize a messenger RNA.
6. mRNA exits nucleus, traveling to ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs.