2:
The
Nervous
System
Introduction
to
Neurons
and
Glia
Types
of
Glial
Cells:
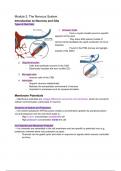
1.
Schwann
Cells
:
-
Form
a
myelin
sheath
around
a
specific
segment
of
the
axon
-
They
leave
little
spaces
(nodes
of
ranvier)
which
facilitates
the
rapid
conduction
of
nerve
impulses
-
Found
in
the
PNS
(nerves
and
ganglia
outside
of
the
CNS)
2.
Oligodendrocytes
-
Cells
that
myelinate
neurons
in
the
CNS
-
Electrically
insulates
the
axon
(unlike
SC)
3.
Microglial
cells
-
Immune
cells
of
the
CNS
4.
Astrocytes
-
Support
neurons
metabolically
-
Maintain
the
extracellular
environment
of
neurons
-
Important
in
processes
such
as
synapse
formation
Membrane
Potentials
→
Membrane
potentials
are
voltage
differences
across
the
cell
membrane
,
which
are
crucial
for
cellular
communication,
particularly
in
neurons.
Dynamics
of
Sodium
and
Potassium:
→
the
sodium-potassium
ATPase
pump
creates
a
concentration
gradient
by
pumping
sodium
out
and
potassium
into
the
cell
which
leads
to…
-
High
sodium
concentration
outside
the
cell
-
High
potassium
concentration
inside
the
cell
Ion
Channels
and
Membrane
Potential:
→
Ion
channels
are
embedded
in
the
cell
membrane
and
are
specific
to
particular
ions
(e.g.,
potassium
channels
allow
only
potassium
to
pass).
-
Channels
can
be
gated
(open
and
close
in
response
to
signals
which
ensures
controlled
ion
flow) -
When
potassium
channels
open
without
any
electrical
gradient
but
with
a
chemical
gradient
present,
potassium
ions
flow
out
of
the
cell,
making
the
inside
more
negatively
charged
and
establishing
a
negative
membrane
potential.
Equilibrium
Potential:
→
Over
time,
as
potassium
continues
to
exit,
the
growing
negative
charge
inside
pulls
some
potassium
back
into
the
cell.
Eventually,
the
movement
of
potassium
in
and
out
of
the
cell
balances,
reaching
what
is
called
the
equilibrium
potential
for
potassium
.
This
potential
is
determined
by
the
ratio
of
the
concentration
of
potassium
inside
versus
outside
the
cell
and
is
typically
negative.
Membrane
Potential
Changes:
-
Depolarization
:
opening
sodium
channels
decreases
the
negative
charge
inside
(becomes
less
negative)
-
Repolarization
:
opening
potassium
channels
after
sodium
channels
makes
the
cell
more
negative
again,
moving
back
towards
the
potassium
equilibrium
potential
-
Hyperpolarization
:
If
potassium
channels
remain
open
longer,
the
inside
becomes
even
more
negative
than
the
resting
potential.
Graded
Potentials
:
changes
in
the
membrane
potential
that
vary
in
magnitude
depending
on
the
strength
of
the
stimulus.
They
occur
when
ligand-gated
ion
channels
open
in
response
to
a
neurotransmitter,
causing
localized
charge
How
to
Calculate
the
Equilibrium
Potential:
→
The
Nernst
Equation
determines
the
voltage
at
which
the
net
flow
of
ions
across
the
cell
membrane
is
zero,
balancing
the
chemical
and
electrical
driving
forces
for
that
ion.
E
:
equilibrium
potential
for
the
ion
R
:
gas
constant
(8.314
J/(mol
x
K))
T
:
temperature
in
Kelvin
Z
:
valence
(change)
of
the
ion
F
:
faraday
constant
(96485
C/mol)
[C]out
and
[C]in
are
the
concentrations
of
the
ion
outside
and
inside
the
cell
Important
Ion
Concentrations:
Action
Potentials