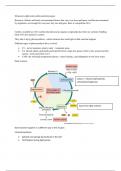
\Resources-light,water,carbon,nutrients,space
Resource- Abiotic and biotic environmental factors that vary over time and space, and that are consumed
by organisms. not enough for everyone, they use and gone, there is competition for it
Carbon: available as CO2 (carbon dioxide) and as organic compounds also there are primary building
block 95% dry material is carbon
They take it up by photosynthesis , carbon fixation also need light in dark reaction happens
Different types of photosynthesis have evolved:
• C3 – no hot summers ,plenty water , temperate areas
• C4- african safane, grasslands and tropical forests large area grassy where is dry season and rain
season , warm areas then in C3
• CAM- dry with high temperature,dessert , water limiting , need adaptation to not loose water
Dark reaction:
rubisco = ribulose biphosphate,
carboxylase/oxygenase
Input from light reaction
Dark reaction happens in a different way in this 3 types
C3 photosynthesis:
• palisade and spongy parenchyma in the leaf
• CO2 fixation during light period
, • fixation of CO2 by Rubisco
• relatively high photorespiration by Rubisco ( can do both
reactions)
Photorespiration ( oxygenation)
• mainly at high O2/CO2 ratios and higher temperatures
• competition with carboxylation
• evolutionary relict or overflow mechanism?
• role in nitrate metabolism
• Loose carbon not fix it proveri
C4 photosynthesis:
Many chloroplast. Co2 fixated and carbon transportet to bundle sheet
cell and all CO2 released in the same time
• Krantz or bundle sheath anatomy
• CO2 fixation during light period in mesophyll cell
• first fixation of CO2 via PEP carboxylase not rubisco
• almost no photorespiration due to high local CO2
• low Km(affinity for the enzyme) for CO2 fixation, but not for the Rubisco reaction
• energetically less efficient (recycling PEP costs ATP)
• sensitive to low temperatures, regeneration doesn’t work as efficiently because enzyme is
sensitive to low temperature / pyruvate Pi dikinase (PEP formation)
•
SLIKA
,Less efficient with energy than C3
There are some C4 plants in Netherlands south east because of temperature , also at places with sandy
dunes and in cities
C4 slower at piclking up CO2 Km is higher it has less
afinity to CO2 , but you have more CO2 at the ends
PEP- km lower then C3 rubisco ,
Types of C4:
1. - malate transport and release CO2 in chloroplast bundle sheet(NADP-ME)
2. asparagine transport and release of CO2 in mitochondria bundle sheet
3. asparagine and malate transport and release CO2 in mitochondria and cytoplasm bundle sheet
Scientist trying to convert some crops (rice) to C4 plants so they can survive better and grow faster in
warmer environments/ gus is often used for this experimetns
, CAM photosynthesis :
• Crassulacean acid metabolism
• mainly in plants that live in extremely dry regions
• CO2 fixation (mostly) during the dark period stomata open during night
• first fixation CO2 via PEP carboxylase
• strongly reduced water loss
Some plants have C3 mechanism, but they can switch to CAM if there is drought
In C4 you need a specific anatomy of leaves but here not
Malate is stored in vacuole
No photorespiration because ration of Co2 and oxygen is tilted towards CO2 because concentration is
high
Malic acid promotes plant growth by increasing chlorophyll content and mitigating stress damage to
photosynthetic structures,
Resource- Abiotic and biotic environmental factors that vary over time and space, and that are consumed
by organisms. not enough for everyone, they use and gone, there is competition for it
Carbon: available as CO2 (carbon dioxide) and as organic compounds also there are primary building
block 95% dry material is carbon
They take it up by photosynthesis , carbon fixation also need light in dark reaction happens
Different types of photosynthesis have evolved:
• C3 – no hot summers ,plenty water , temperate areas
• C4- african safane, grasslands and tropical forests large area grassy where is dry season and rain
season , warm areas then in C3
• CAM- dry with high temperature,dessert , water limiting , need adaptation to not loose water
Dark reaction:
rubisco = ribulose biphosphate,
carboxylase/oxygenase
Input from light reaction
Dark reaction happens in a different way in this 3 types
C3 photosynthesis:
• palisade and spongy parenchyma in the leaf
• CO2 fixation during light period
, • fixation of CO2 by Rubisco
• relatively high photorespiration by Rubisco ( can do both
reactions)
Photorespiration ( oxygenation)
• mainly at high O2/CO2 ratios and higher temperatures
• competition with carboxylation
• evolutionary relict or overflow mechanism?
• role in nitrate metabolism
• Loose carbon not fix it proveri
C4 photosynthesis:
Many chloroplast. Co2 fixated and carbon transportet to bundle sheet
cell and all CO2 released in the same time
• Krantz or bundle sheath anatomy
• CO2 fixation during light period in mesophyll cell
• first fixation of CO2 via PEP carboxylase not rubisco
• almost no photorespiration due to high local CO2
• low Km(affinity for the enzyme) for CO2 fixation, but not for the Rubisco reaction
• energetically less efficient (recycling PEP costs ATP)
• sensitive to low temperatures, regeneration doesn’t work as efficiently because enzyme is
sensitive to low temperature / pyruvate Pi dikinase (PEP formation)
•
SLIKA
,Less efficient with energy than C3
There are some C4 plants in Netherlands south east because of temperature , also at places with sandy
dunes and in cities
C4 slower at piclking up CO2 Km is higher it has less
afinity to CO2 , but you have more CO2 at the ends
PEP- km lower then C3 rubisco ,
Types of C4:
1. - malate transport and release CO2 in chloroplast bundle sheet(NADP-ME)
2. asparagine transport and release of CO2 in mitochondria bundle sheet
3. asparagine and malate transport and release CO2 in mitochondria and cytoplasm bundle sheet
Scientist trying to convert some crops (rice) to C4 plants so they can survive better and grow faster in
warmer environments/ gus is often used for this experimetns
, CAM photosynthesis :
• Crassulacean acid metabolism
• mainly in plants that live in extremely dry regions
• CO2 fixation (mostly) during the dark period stomata open during night
• first fixation CO2 via PEP carboxylase
• strongly reduced water loss
Some plants have C3 mechanism, but they can switch to CAM if there is drought
In C4 you need a specific anatomy of leaves but here not
Malate is stored in vacuole
No photorespiration because ration of Co2 and oxygen is tilted towards CO2 because concentration is
high
Malic acid promotes plant growth by increasing chlorophyll content and mitigating stress damage to
photosynthetic structures,