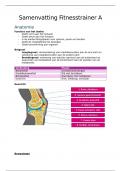
• VET 212 Anesthesia Study Guide (Answered) Complete Solution
• VET 212 Anesthesia Study Guide (Answered) Complete Solution Chapter 1 1) List 2 North American professional organizations that offer specialization in anesthesia and analgesia to credentialed individuals, and summarize the aims of each ACADEMY of VETERINARY TECHNICIANS IN ANESTHESIA and ANALGESIA (AVTAA) -- promotes patient safety, consumer protection, professionalism and excellence in anesthesia care AMERICAN COLLEGE of VETERINARY ANESTHESIA and ANALGESIA (ACVAA) -- 2) Define anesthesia, and differentiate topical, local, regional, general, and surgical anesthesia TOPICAL ANESTHESIA→loss of sensation of a localized area produced by administration of a local anesthetic directly to a body surface or surgical or traumatic wound (small areas) LOCAL ANESTHESIA→ loss of sensation in a small area of the body produced by administration of a local anesthetic agent in proximity to the area of interest (small areas) REGIONAL ANESTHESIA→ loss of sensation in a limited area of the body produced by administration of a local anesthetic or other agent in proximity to sensory nerves (nerve blocks, epidural anesthesia, large areas) GENERAL ANESTHESIA→reversible state of unconsciousness, immobility, muscle relaxation, and loss of sensation throughout the entire body produced by one or more anesthetic agents SURGICAL ANESTHESIA→ specific state of general anesthesia in which there is a sufficient degree of analgesia (loss of sensitivity to pain) and muscle relaxation to allow surgery to be performed without patient pain or movement 3) Differentiate sedation, tranquilization, hypnosis, and narcosis SEDATION→ drug induced CNS depression and drowsiness that vary in intensity from light to deep TRANQUILIZATION→ drug induced state of calm in which the patient is reluctant to move and is aware of but unconcerned about its surroundings HYPNOSIS→ drug induced sleep like state that impairs the ability of the patient to respond appropriately to stimuli---sleep like state from which the patient can be aroused with sufficient stimulation NARCOSIS→ drug induced sleep, the patient is not easily aroused, most often associated with administration of narcotics 4) Explain the concept of balanced anesthesia and the advantages of this approach Balanced anesthesia (the administration of multiple drugs to the same patient during one anesthetic event) maximizes benefits, minimizes adverse effects, and gives the anesthetist the ability to produce anesthesia with the degree of CNS depression, muscle relaxation, analgesia, and immobilization appropriate for the patient and the procedure Example: premedication, then maintenance with inhalant, the post op medication for analgesia 5) List common indications for anesthesia GENERAL ANESTHESIA→ most common, fully immobilizes the patient, procedures can be performed quickly and safely, inexpensive, uses balanced techniques SEDATION→ can be mild or heavy, neuroleptanalgesia, used for minor procedures, diagnostics, physical examination 6) Describe fundamental challenges and risks associated with anesthesia -most anesthetic agents have a narrow therapeutic index so care and attention to detail are critical when dosages are calculated and rates are adjusted -most anesthetic agents cause significant changes in cardiovascular and pulmonary function and can be dangerous or fatal--vital signs must be closely monitored -the potential for patient harm during administration of anesthetics is relatively high -must keep detailed and accurate anesthetic records 7) List the qualities and abilities of a successful veterinary anesthetist -the anesthetist must accurately interpret a wide spectrum of visual, tactile, and auditory information -the anesthetist must have a comprehensive understanding of the significance of physical parameters and machine generated data Chapter 2 1) Explain the importance of effective communication and the role of the veterinary technician in communication. -veterinarians depend on accurate information at all stages of the procedure to make effective patient care decisions -clients need clear instructions and answers to questions before the procedure, progress reports, and home care instructions afterwards -the technician acts as a liaison between the dr and the client 2) List the reasons for preoperative patient evaluation. -to uncover hidden problems that may increase risk or alter patient management 3) List the parts of a minimum patient database. -used to make patient care decisions -patient history, including the patient signalment -complete physical examination findings -results of a preanesthetic diagnostic workup 4) Take a complete history, and identify findings that affect anesthetic event planning. -when taking a history emphasize open-ended questions, avoid leading questions or questions that can be answered yes or no -gather signalment, current and past diseases, medications, allergies, statues of preventative care -when gathering historical information about signs of illness always ask the following: -the duration (how long has it been going?) -the volume or severity (how much or how severe?) -the frequency (how often?) -the character or appearance (what does it look like?) 5) Identify ways in which patient signalment influences the anesthetic procedure and patient management. SPECIES→ each species has unique responses to anesthetic agents and unique needs associated with anesthesia...horses and cats are more sensitive to opioids, horses have rougher recoveries, ruminants are prone to bloat BREED→ differences in anatomy and physiology among various breeds may affect an animal’s response to anesthetic agents...brachycephalic animals are difficult to intubate, sighthounds are sensitive to barbiturates, draft horses are sensitive to sedatives AGE→ determines what drugs to use...neonates and pediatric patients are less able to metabolize injectable drugs SEX and REPRODUCTIVE STATUS→animals in heat make a spay more difficult, ace is contradicted in stallions 6) Discuss the rationale for obtaining the owner’s consent for anesthesia. -it is illegal in more jurisdictions to undertake surgery or anesthesia on an animal without an owner’s written or oral consent -the owner is warned beforehand of risks associated with the procedure -the owner gets a written estimate of the expected charges and obtain a signed consent form authorizing anesthesia and surgery 7) Perform a preanesthetic physical assessment. PATIENT IDENTIFICATION→ identification collars must be placed on all patients. Proper patient identification is essential, ensure correct surgery if being performed on the correct area BODY WEIGHT→ all animals must be accurately weighed immediately before any anesthetic procedure BODY CONDITION SCORE→ can range from 1-5 or 1-9, with 1 being emaciated and 9 being grossly obese, helps assess overall wellbeing of the patient as well as drug calculation (drug calculation based on lean body weight) ASSESSMENT OF HYDRATION→ dehydrated patients may need to be stabilized prior to anesthetic induction, look at MM, tent the skin, look at the eyes LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS→ BAR, QAR, Lethargic, obtunded, comatose, decreased level of consciousness indicates abnormal brain function
Geschreven voor
- Instelling
- • VET 212 Anesthesia
- Vak
- • VET 212 Anesthesia
Documentinformatie
- Geüpload op
- 11 juni 2024
- Aantal pagina's
- 47
- Geschreven in
- 2023/2024
- Type
- Tentamen (uitwerkingen)
- Bevat
- Vragen en antwoorden
Onderwerpen
-
vet 212 anesthesia study guide answered compl