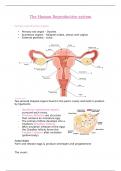
The Human Reproductive system
Female reproductive organs
• Primary sex organ – Ovaries
• Accessory organs – fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina
• External genitalia - vulva
Ovaries
Two almond shaped organs found in the pelvic cavity and held in position
by ligaments
- Germinal epithelium layers
surround each ovary.
- Primary follicles are structure
that contains an immature egg.
- The primary follicle develops into a
(mature) Graafian follicle.
- After ovulation (release of the egg),
the Graafian follicle forms the
Corpus Luteum after ovulation
(yellow body)
FUNCTIONS
Form and release eggs & produce oestrogen and progesterone
The ovum:
, Vagina
Muscular passage between the uterus and the outside of the body.
- Elastic folded walls allow stretch during intercourse and childbirth
- Acid pH keeps it infection free.
FUNCTIONS:
Sperm deposit & Birth canal
Uterus (womb)
A hollow, muscular, thick walled organ which enlarges during pregnancy.
Uterine wall:
- Myometrium (thick involuntary muscle
layer)
- Endometrium (blood vessel lining)
v During ovulation progesterone causes
endometrium to thicken to prepare for
implantation.
v If fertilization does not occur the
endometrium becomes detached –
menstruation.
v The sphincter muscles of the cervix
keep the uterus closed during pregnancy preventing a miscarriage.
FUNCTIONS
• Blastocyst implants, develops and grows into a foetus.
• Contains myometrium which enables a baby to be pushed out
during birth.
BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE
UTERUS
Female reproductive organs
• Primary sex organ – Ovaries
• Accessory organs – fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina
• External genitalia - vulva
Ovaries
Two almond shaped organs found in the pelvic cavity and held in position
by ligaments
- Germinal epithelium layers
surround each ovary.
- Primary follicles are structure
that contains an immature egg.
- The primary follicle develops into a
(mature) Graafian follicle.
- After ovulation (release of the egg),
the Graafian follicle forms the
Corpus Luteum after ovulation
(yellow body)
FUNCTIONS
Form and release eggs & produce oestrogen and progesterone
The ovum:
, Vagina
Muscular passage between the uterus and the outside of the body.
- Elastic folded walls allow stretch during intercourse and childbirth
- Acid pH keeps it infection free.
FUNCTIONS:
Sperm deposit & Birth canal
Uterus (womb)
A hollow, muscular, thick walled organ which enlarges during pregnancy.
Uterine wall:
- Myometrium (thick involuntary muscle
layer)
- Endometrium (blood vessel lining)
v During ovulation progesterone causes
endometrium to thicken to prepare for
implantation.
v If fertilization does not occur the
endometrium becomes detached –
menstruation.
v The sphincter muscles of the cervix
keep the uterus closed during pregnancy preventing a miscarriage.
FUNCTIONS
• Blastocyst implants, develops and grows into a foetus.
• Contains myometrium which enables a baby to be pushed out
during birth.
BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE
UTERUS