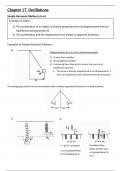
Simple Harmonic Motion (s.h.m)
A motion in which:
1) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to its displacement from an
equilibrium point/position &
2) The acceleration and the displacement are always in opposite directions.
Examples of Simple Harmonic Motions:
1)
3 Requirements for s.h.m of a mechanical system
1) A mass that oscillates
2) An equilibrium position
3) A restoring force that acts to return the mass to its
equilibrium position
• The force is directly proportional to its displacement. X
from its equilibrium and is directed towards that point.
The swinging pendulum has an acceleration that is always oppositely directed to its displacement.
2) 3)
a = g (a is constant) Provided string
obeys Hooke’s Law.
a is not proportional
a is proportional to
to its displacement.
its x.
,Angular Frequency
Complete oscillation (a cycle of s.h.m) = 2π rad
Angular Frequency
𝟐𝝅 Unit: rad s-1
𝝎 = 𝟐𝝅𝒇 𝝎=
𝑻
ω = angular frequency (rad s-1)
f = frequency (Hz)
T = period (1 complete oscillation) (s)
The Defining Equation for Simple Harmonic Motion
𝒂 = −𝝎𝟐 𝒙
a = acceleration of an object moving in s.h.m
x = displacement from the equilibrium
ω = angular frequency
From the equation:
1) 𝑎 ∝ 𝑥
▪ The constant of proportionality is ω2.
Acceleration is directly proportional to displacement.
2) − 𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛
▪ Shows when object is displaced to the right, the direction of its acceleration is to the left and
vice versa.
Acceleration is always directed towards the equilibrium position. (in the opposite direction to the
displacement)
, Example of Simple Harmonic Motion
1) Simple pendulum
2) Spring-mass system
3) Oscillations of liquid columns
Derivation of equations for the period of certain examples of s.h.m
Steps:
1. Use Newton 2nd Law
2. Relate a with x
3. Sign direction
4. Proportionality
1) Simple Pendulum
1.
Restoring force (towards equilibrium point)
𝐹 = 𝑊𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
= 𝑚𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
If is small,
𝑥
𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜃 ≃ 𝐹 = 𝑚𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
𝑙
𝑥
𝐹 = 𝑚𝑔 ( )
𝑙
2 & 3. Since F and x are in opposite directions,
𝑥
𝑚𝑎 = −𝑚𝑔 ( )
𝑙
𝑔
𝑎 = −( )𝑥
𝑙
-ve A constant
a is opposite to x 𝑎 ∝ 𝑥
# s.h.m motion