Unit 5 - Labour and Employee Relations
Introduction to Industrial Relations, Employee Relations and Labour Relations
Industrial Relations
• Includes all the employment issues and relationships governing the workplace
• For example:
• The organization of the work environment
• Employment contracts
• Human Resources Management
• Employment relations
• Conflict Management
• Employee attitudes and behaviours at work
Employee Relations
• Refers to the direct employer-employee relationship
• Policies describing the company’s philosophy, rules and procedures for addressing employee-
related matters and resolving problems
• Employee relations representatives work to ensure that company policies are followed, both fairly
and consistently
• ER Reps job is to ensure policy is followed
• An employee relations program is not a one-size-fits-all solution
Labour Relations
• Refers to the relationship between a union or professional association representing employees and
their employer
• Union certification
• Collective Bargaining
• Conflict management
• Maintenance of agreements
, Discipline
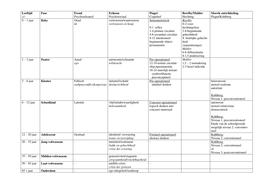
• Constructive dismissal - When an employer commits a fundamental breach of the contract such as by
unilaterally changing a key term of the contract, the employee can treat the breach as a termination
• Summary dismissal - When a nonunion employer terminates an employee without notice because the
employee has committed a serious breach of contract
• Wrongful dismissal - A lawsuit filed in a court by an employee alleging that he or she was dismissed
without proper contractual or reasonable notice
• Hot-stove rule - A rule of discipline that can be compared with a hot stove in that it gives warning, is
effective immediately, is enforced consistently, and applies to all employees in an impersonal and
unbiased way.
• Zero Tolerance Policy
• Discipline - Treatment that punishes, orderly behaviour in an organizational setting, or training that
moulds and strengthens desirable conduct - or corrects undesirable conduct - and develops self-control
• Progressive Discipline - Application of corrective measures by increasing degrees
• Positive, or nonpunitive discipline - A system of discipline that focuses on early correction of employee
misconduct, with the employee taking total responsibility for correcting the problem
• Peer-review system - A system for reviewing employee complaints that utilizes a group composed of
equal numbers of employee representatives and management appointees, which functions as a jury
because its members weigh evidence, consider arguments, and, after deliberation, vote independently
to render a final decision.
• Open-door policy - A policy of settling grievances that identifies various levels of management above
the immediate supervisor for employee contact
• Ombudsperson - A designated individual from whom employees may seek counsel for resolution of
their complaints
• Mediation - The use of an impartial neutral to reach a compromise decision in employment disputes
• Mediator - A third party in an employment dispute who meets with one party and then the other in order
to suggest compromise solutions or to recommend concessions from each side that will lead to an
agreement
Dismissal: An example of Differences
• Non-Union Workers
• Employee dismissal without cause would lead to two options
• Action under employment standards legislation
• Adjudication through the courts
• Best outcome is reasonable notice and/or money in lieu
• Unionized Workers
• Can seek redress, including reinstatement
• Grievance-arbitration with burden of proof on employer
• Substantial protection against arbitrary dismissal
• Can bump others with less seniority in the case of downsizing
Communication is Key
• Employees need to be informed of what’s going on with the company, including management’s plans
and how those plans may affect their job
• Withholding information can result in mistrust and damage employee morale
• Keep workers informed by any number of means, including email announcements, newsletters,
employee portals, regular meetings, surveys, focus groups, suggestion boxes, and special
communication events.
• Informal day to day interaction, management by walking around, and social events enhance
communication
• Effective Communication
• In non-union - effective organization can determine whether become unionized or not
• In union - can save money on mediation
Introduction to Industrial Relations, Employee Relations and Labour Relations
Industrial Relations
• Includes all the employment issues and relationships governing the workplace
• For example:
• The organization of the work environment
• Employment contracts
• Human Resources Management
• Employment relations
• Conflict Management
• Employee attitudes and behaviours at work
Employee Relations
• Refers to the direct employer-employee relationship
• Policies describing the company’s philosophy, rules and procedures for addressing employee-
related matters and resolving problems
• Employee relations representatives work to ensure that company policies are followed, both fairly
and consistently
• ER Reps job is to ensure policy is followed
• An employee relations program is not a one-size-fits-all solution
Labour Relations
• Refers to the relationship between a union or professional association representing employees and
their employer
• Union certification
• Collective Bargaining
• Conflict management
• Maintenance of agreements
, Discipline
• Constructive dismissal - When an employer commits a fundamental breach of the contract such as by
unilaterally changing a key term of the contract, the employee can treat the breach as a termination
• Summary dismissal - When a nonunion employer terminates an employee without notice because the
employee has committed a serious breach of contract
• Wrongful dismissal - A lawsuit filed in a court by an employee alleging that he or she was dismissed
without proper contractual or reasonable notice
• Hot-stove rule - A rule of discipline that can be compared with a hot stove in that it gives warning, is
effective immediately, is enforced consistently, and applies to all employees in an impersonal and
unbiased way.
• Zero Tolerance Policy
• Discipline - Treatment that punishes, orderly behaviour in an organizational setting, or training that
moulds and strengthens desirable conduct - or corrects undesirable conduct - and develops self-control
• Progressive Discipline - Application of corrective measures by increasing degrees
• Positive, or nonpunitive discipline - A system of discipline that focuses on early correction of employee
misconduct, with the employee taking total responsibility for correcting the problem
• Peer-review system - A system for reviewing employee complaints that utilizes a group composed of
equal numbers of employee representatives and management appointees, which functions as a jury
because its members weigh evidence, consider arguments, and, after deliberation, vote independently
to render a final decision.
• Open-door policy - A policy of settling grievances that identifies various levels of management above
the immediate supervisor for employee contact
• Ombudsperson - A designated individual from whom employees may seek counsel for resolution of
their complaints
• Mediation - The use of an impartial neutral to reach a compromise decision in employment disputes
• Mediator - A third party in an employment dispute who meets with one party and then the other in order
to suggest compromise solutions or to recommend concessions from each side that will lead to an
agreement
Dismissal: An example of Differences
• Non-Union Workers
• Employee dismissal without cause would lead to two options
• Action under employment standards legislation
• Adjudication through the courts
• Best outcome is reasonable notice and/or money in lieu
• Unionized Workers
• Can seek redress, including reinstatement
• Grievance-arbitration with burden of proof on employer
• Substantial protection against arbitrary dismissal
• Can bump others with less seniority in the case of downsizing
Communication is Key
• Employees need to be informed of what’s going on with the company, including management’s plans
and how those plans may affect their job
• Withholding information can result in mistrust and damage employee morale
• Keep workers informed by any number of means, including email announcements, newsletters,
employee portals, regular meetings, surveys, focus groups, suggestion boxes, and special
communication events.
• Informal day to day interaction, management by walking around, and social events enhance
communication
• Effective Communication
• In non-union - effective organization can determine whether become unionized or not
• In union - can save money on mediation