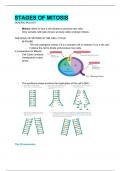
STAGES OF MITOSIS
GENERAL BIOLOGY
- Mitosis refers to how a cell divides to produce new cells.
- Only somatic cells (also known as body cells) undergo mitosis.
THE ROLE OF MITOSIS IN THE CELL CYCLE
- M-PHASE
- The cell undergoes mitosis if it is a somatic cell or meiosis if it is a sex cell.
- It allows the cell to divide and produce new cells.
In preparation for Mitosis:
- Cell Cycle conducts
checkpoints to spot
errors.
- The synthesis phase involves the duplication of the cell’s DNA
The Chromosome
, DNA in interphase is found in the form of chromatin which condenses during mitosis.
● Each chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids.
Haploid and Diploid Cells
The human genome has 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes in
each cell. 23 is the haploid number whereas 46 is the diploid number.
● Haploid is often represented as n while diploid is 2n.
● The number of sets of chromosomes that a cell or an organism has is known as
ploidy.
THE PHASES OF MITOSIS
GENERAL BIOLOGY
- Mitosis refers to how a cell divides to produce new cells.
- Only somatic cells (also known as body cells) undergo mitosis.
THE ROLE OF MITOSIS IN THE CELL CYCLE
- M-PHASE
- The cell undergoes mitosis if it is a somatic cell or meiosis if it is a sex cell.
- It allows the cell to divide and produce new cells.
In preparation for Mitosis:
- Cell Cycle conducts
checkpoints to spot
errors.
- The synthesis phase involves the duplication of the cell’s DNA
The Chromosome
, DNA in interphase is found in the form of chromatin which condenses during mitosis.
● Each chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids.
Haploid and Diploid Cells
The human genome has 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes in
each cell. 23 is the haploid number whereas 46 is the diploid number.
● Haploid is often represented as n while diploid is 2n.
● The number of sets of chromosomes that a cell or an organism has is known as
ploidy.
THE PHASES OF MITOSIS