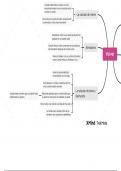
Genetic engineering
Gene therapy
Inserting a new gene into an organisms’
DNA that it didn’t originally have so it The aim is to use genetic modification to treat an inherited
can produce a particular protein. disease by providing the sufferer with a corrected copy of the
defective gene so a functioning protein is produced
Used...
This may mean replacing the faulty gene or supplementing it
In the medical industry without removing existing ones.
To make plants resistant to pests
To make the organism last longer Viruses are used as vectors to transfer the correct genes into the
To increase the vitamin and cells
mineral content
Human genes can be mass produced, Cloning plants
makes pure proteins, used to make mice
mimic humans to find cures, improves Undertaken when genetically identical plants / animals are
growth rates and bigger yields of plants required and made of individuals who are medically or
and animals for food production, reduces commercially valuable
the pesticides needed which is better for Cuttings:
biodiversity
1. A small section of a plant with desirable characteristics is
GM foods may affect human health, cut off and removed and some leaves are removed to
ethical objections – GM crops could lead decrease water lost by transpiration
to GM foetus’, could affect wildlife and 2. The cutting is dipped in rooting hormone to encourage root
biodiversity growth so the plant is able to take up water
How is it done? 3. The cutting is placed in water and a clear plastic bag is
placed around it to make the atmosphere humid and
1. Enzymes used to isolate the decrease transpiration until a root system develops but still
required gene allow light through for photosynthesis
2. A vector – plasmids for bacteria or
viruses for plants and animals - is Simple, quick, cheap, new plants all have desired characteristics
used to transfer the gene into There’s a limit to the number of clones that can be produced from
the required organisms’ cells at one adult plant, all offspring susceptible to same diseases
an early stage in their
development Tissue culture:
3. The DNA is removed form the
1. A few cells taken from adult plant
vector and cut open with an
2. Cells put in specific culture medium to help with growth
enzyme
3. A small group of cells begins to grow
4. The isolated gene is inserted into
4. Callus is put into growth medium to encourage root and
the vector’s DNA
shoot growth
5. The modified DNA is put back
5. Kept in greenhouse to acclimatise after the sterile
into the vector
environment
6. The vector reproduces asexually,
very fast to produce lots of Used for mass production of plants with no seeds and plants with
vectors with the modified medicinal compounds and conservation of endangered plants
genetic material
Thousands of plants produced from a few cells, offspring
This is how insulin is made – under genetically identical, generates whole plants from genetically
certain conditions the insulin gene can engineered cells
be switched on and the insulin protein
Loss of genetic diversity, decreases gene pool so risk of species
produced can be given to diabetics
being wiped out, requires expensive equipment and training
Gene therapy
Inserting a new gene into an organisms’
DNA that it didn’t originally have so it The aim is to use genetic modification to treat an inherited
can produce a particular protein. disease by providing the sufferer with a corrected copy of the
defective gene so a functioning protein is produced
Used...
This may mean replacing the faulty gene or supplementing it
In the medical industry without removing existing ones.
To make plants resistant to pests
To make the organism last longer Viruses are used as vectors to transfer the correct genes into the
To increase the vitamin and cells
mineral content
Human genes can be mass produced, Cloning plants
makes pure proteins, used to make mice
mimic humans to find cures, improves Undertaken when genetically identical plants / animals are
growth rates and bigger yields of plants required and made of individuals who are medically or
and animals for food production, reduces commercially valuable
the pesticides needed which is better for Cuttings:
biodiversity
1. A small section of a plant with desirable characteristics is
GM foods may affect human health, cut off and removed and some leaves are removed to
ethical objections – GM crops could lead decrease water lost by transpiration
to GM foetus’, could affect wildlife and 2. The cutting is dipped in rooting hormone to encourage root
biodiversity growth so the plant is able to take up water
How is it done? 3. The cutting is placed in water and a clear plastic bag is
placed around it to make the atmosphere humid and
1. Enzymes used to isolate the decrease transpiration until a root system develops but still
required gene allow light through for photosynthesis
2. A vector – plasmids for bacteria or
viruses for plants and animals - is Simple, quick, cheap, new plants all have desired characteristics
used to transfer the gene into There’s a limit to the number of clones that can be produced from
the required organisms’ cells at one adult plant, all offspring susceptible to same diseases
an early stage in their
development Tissue culture:
3. The DNA is removed form the
1. A few cells taken from adult plant
vector and cut open with an
2. Cells put in specific culture medium to help with growth
enzyme
3. A small group of cells begins to grow
4. The isolated gene is inserted into
4. Callus is put into growth medium to encourage root and
the vector’s DNA
shoot growth
5. The modified DNA is put back
5. Kept in greenhouse to acclimatise after the sterile
into the vector
environment
6. The vector reproduces asexually,
very fast to produce lots of Used for mass production of plants with no seeds and plants with
vectors with the modified medicinal compounds and conservation of endangered plants
genetic material
Thousands of plants produced from a few cells, offspring
This is how insulin is made – under genetically identical, generates whole plants from genetically
certain conditions the insulin gene can engineered cells
be switched on and the insulin protein
Loss of genetic diversity, decreases gene pool so risk of species
produced can be given to diabetics
being wiped out, requires expensive equipment and training