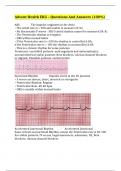
Afib - The impulse originates in the Atria
• The Atrial rate is > 300 and unable to measure [N/A]
• No discernable P waves - PRI & Atrial rhythm cannot be measured [N/A]
• The Ventricular rhythm is irregular
• QRS within normal limits
• If the Ventricular rate is <100 the rhythm is controlled A-fib;
if the Ventricular rate is > 100 the rhythm is uncontrolled A-fib
• This is a chronic rhythm for some patients
Treatment: controlled patients: anticoagulants and antiarrythmics;
uncontrolled but stable patients: Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers,
or digoxin; Unstable patients: cardioversion
Junctional Rhythm - Impulse starts in the AV junction
• P waves are absent, short, inverted or retrograde
• Ventricular Rhythm: Regular
• Ventricular Rate: 40-60 bpm
• QRS is usually within normal limits
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm - Accelerated Junctional
Same criteria as Junctional Rhythm, except the Ventricular rate is 60-100
For stable patients: IV access, vagal maneuvers, adenosine, O2, Beta
blockers, calcium channel blockers
,Idioventricular Rhythm (IVR) - Impulse originates in the ventricles
▪ Rhythm: Ventricular is usually regular
▪ Rate: Ventricular between 20-40
▪ QRS: ≥ 0.12
▪ Atrial rate, rhythm, and PRI: N/A
- Treatment: assess pt, check for DNR in chart, transcutaneous pacing,
atropine. NEVER GIVE ANTI-ARRYTHMICS MEDICATIONS
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm - Follows the same criteria as
IVR, except Ventricular rate is 40-100.
• If no intervention happens, the patient will deteriorate.
- Treatment: assess pt, atropine, transcutaneous pacing. NEVER GIVE ANTI-
ARRHYTHMIC MEDICATIONS
Ventricular Pacing - • The pacemaker lead is placed in to right
ventricle.
• The pacemaker generator fires an impulse Initiating ventricular activity.
• The right ventricle will contract first followed by the left ventricle. This
results in a wide QRS
• Atrial activity is typically absent. Therefore, Atrial rhythm, rate, and PRI
are non- measurable
• Rhythm: Ventricular regular
, • Rate: Ventricular within set pacer limits. Measured from pacer spike to
pacer spike
• QRS: Wide; Pacer spike seen before each QRS. Measured from pacer spike
to end
of QRS
Atrial-ventricular Pacing - One pacemaker lead is placed into the
right atria and another is placed into the right
ventricle.
• The pacemaker generator fires an impulse to the atria and then to the
ventricle sequentially
causing atrial then ventricular contraction.
• Rhythm: Atrial and Ventricular regular
• Rate: Atrial and Ventricular same & within set limits
• P waves: Pacer spike seen at beginning of atrial activity P waves may or
may not be seen
(lead type dependent)
• PRI: WNL - Measured from atrial spike to ventricular spike
• QRS: Wide - Measured from ventricular spike to end of QRS
Failure to capture - A pacer spike note followed by the appropriate
atrial or ventricular response
• Can be a potentially lethal situation!