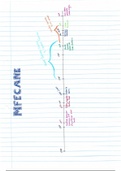
Economic boom
America was experiencing an economic boom:
Industry
❏ New production methods allowed goods to be
● Factory in production grew
produced at a faster rate
○ Natural resources: industries such as coal, petrol and gas grew quickly
❏ The availability of credit to buy new things
○ Transport: shipbuilding increased to replace ships destroyed by
❏ Advertising encouraged people to buy newly available
submarines and the railroads made modernised to transport wartime
consumer goods
goods
❏ Increased popularity in stocks and shares
○ Consumer goods: American brands, especially the cigarette smoked by
the USA soldiers were popular in Europe
Henry Ford and mass production
Agriculture
● Production on US farms grew rapidly during WW1
● Henry introduced mass production methods
● Production in Europe dropped as the farmers had to go fight in WW1
● Workers lined up along a continuously moving surface
● This created a demand for wheat and cotton for example
called a conveyor belt
● By the time that europe had begun to recover, the USA provided 30% of the
● The workers stayed at the same point and performed a
worlds wheat and 55% of the worlds cotton this changed the lives of farmers as:
single job
○ Price of goods rose by 25%
● This was extremely boring for the worker but mean
○ The average income of a farmer who owned a farm increased by
production time fell
around 30%
● In oct 1925 a model T car took 10 seconds to produce
○ Farmers began using machines and tractor sales increased rapidly
● As a result of this there was a drop in price as there
○ More and more farmers took out loans
were more made per day
Workers
● The original price was $950 and by 1925 it only cost $290
● Demand for more industrial goods meant more industrial and agricultural goods
● There was a huge increase in the demand for cars
meant more workers needed
amongst Americans
● Workers increased by 1.3 million during the last year of war, reducing
● This helped the economic boom because to construct
unemployment
cars you need parts such as:
● There was more opportunity for workers from different backgrounds
○ Steel
○ Many women joined the workforce and black Americans moved from
○ Rubber
the southern states to the northern one
○ Glass
○ Textiles
Limitations
● Whilst the use for cars increased:
● There were problems at the end of the war:
○ Petrol
○ Demand for industrial and agricultural products from the USA
○ Roads
dropped as a result
○ Returning soldiers re - entered the workforce, many lost their wartime
jobs
○ Race riots started
○ Farmers struggled to pay back their loans
, Consumerism: The social impact of the Roaring Jazz and dancing:
Hire purchase:
● Create a consumer society in which twenties ● Jazz is a mixture of black and
● The customer hired the product
buying a variety of branded goods white American folk music
from the business and paid it off
was important to ordinary people Cinema ● Jazz became popular around
by installments. Once they had
● Rather than eat one flavour of ● The movies grew very the world due to men like
paid off the cost in full, and the
yoghurt or color their hair in a couple popular. In 1920s around 40 Duke Ellington and Paul
product became theirs
of shades, people were encouraged million tickets were sold per Whiteman but it also created
● Benefited the economy as it
to buy an assortment of yogurts week opposition as it became
convinced people to keep
from a range of flavours and 10 ○ They produced films associated with immoral
buying
different shades of hair colors in colour by 1922 behaviour of youngsters
● With the consumers buying
● Shopping became a leisure activity, ○ They introduced ● It helped inspire ore forms of
goods, demand rose and
people wanted to show off that they sound in 1927 dancing
factories had a reason to keep
were better than their neighbours ○ They developed ● The charleston was a fast
buying
they could do this by buying animation dance involving sidekicks and
consumer goods techniques in 1928 a complex sequence of steps
Advertising
● This helped the economy keep ● It made actors such as Charlie
● Used big posters and coloured
growing Chaplin who became an idol Sport
papers in newspapers and
for many young Americans ● More leisure time meant that
magazines to encourage people
Stock market Americans could spend their
to buy their products
● Ordinary Americans became Extend knowledge: spare time watching their
● Overwhelmed consumers with
involved in buying shares in the Hays code - cleaning up films by favorite sports
images of their brands to change
American stock market in Wall street Hayes ● This became a popular hobby
their buying habits
● This involved borrowing money from - Developed a production code for many people
a bank or broker to invest on shares - Banned the filming ● The popularity of sports
● Radio played a central role in the
to then pay back the loan of long kisses made a lot of sporting heroes
development of advertising
- This turned ordinary people into - Childbirth ○ Baseball: Babe Ruth
● As a result alot of American
shareholders - Sex between white set a record of 60
spent their leisure time listening
- Each did it in the hope that the value and black people home runs remaining
to adverts
of the share would go up and they - And the presentation unbeaten until the
● New advertising methods
could sell it at a profit of some crimes to 1960s
helped to create a consumer
- But it was dangerous because what stop the audience ○ Swimming: Gertrude
society, encouraging people to
happened when the prices stopped copying things Ederle, a US
buy new products or spend
going up? - This was inforce until swimmer became
more on brand names
- It also led to more companies selling the rating system in the first woman to
● This boosted the economy
shares which gave them the money 1968 swim the English
because more spending created
to develop their businesses channel in 1926
a need for increased production
America was experiencing an economic boom:
Industry
❏ New production methods allowed goods to be
● Factory in production grew
produced at a faster rate
○ Natural resources: industries such as coal, petrol and gas grew quickly
❏ The availability of credit to buy new things
○ Transport: shipbuilding increased to replace ships destroyed by
❏ Advertising encouraged people to buy newly available
submarines and the railroads made modernised to transport wartime
consumer goods
goods
❏ Increased popularity in stocks and shares
○ Consumer goods: American brands, especially the cigarette smoked by
the USA soldiers were popular in Europe
Henry Ford and mass production
Agriculture
● Production on US farms grew rapidly during WW1
● Henry introduced mass production methods
● Production in Europe dropped as the farmers had to go fight in WW1
● Workers lined up along a continuously moving surface
● This created a demand for wheat and cotton for example
called a conveyor belt
● By the time that europe had begun to recover, the USA provided 30% of the
● The workers stayed at the same point and performed a
worlds wheat and 55% of the worlds cotton this changed the lives of farmers as:
single job
○ Price of goods rose by 25%
● This was extremely boring for the worker but mean
○ The average income of a farmer who owned a farm increased by
production time fell
around 30%
● In oct 1925 a model T car took 10 seconds to produce
○ Farmers began using machines and tractor sales increased rapidly
● As a result of this there was a drop in price as there
○ More and more farmers took out loans
were more made per day
Workers
● The original price was $950 and by 1925 it only cost $290
● Demand for more industrial goods meant more industrial and agricultural goods
● There was a huge increase in the demand for cars
meant more workers needed
amongst Americans
● Workers increased by 1.3 million during the last year of war, reducing
● This helped the economic boom because to construct
unemployment
cars you need parts such as:
● There was more opportunity for workers from different backgrounds
○ Steel
○ Many women joined the workforce and black Americans moved from
○ Rubber
the southern states to the northern one
○ Glass
○ Textiles
Limitations
● Whilst the use for cars increased:
● There were problems at the end of the war:
○ Petrol
○ Demand for industrial and agricultural products from the USA
○ Roads
dropped as a result
○ Returning soldiers re - entered the workforce, many lost their wartime
jobs
○ Race riots started
○ Farmers struggled to pay back their loans
, Consumerism: The social impact of the Roaring Jazz and dancing:
Hire purchase:
● Create a consumer society in which twenties ● Jazz is a mixture of black and
● The customer hired the product
buying a variety of branded goods white American folk music
from the business and paid it off
was important to ordinary people Cinema ● Jazz became popular around
by installments. Once they had
● Rather than eat one flavour of ● The movies grew very the world due to men like
paid off the cost in full, and the
yoghurt or color their hair in a couple popular. In 1920s around 40 Duke Ellington and Paul
product became theirs
of shades, people were encouraged million tickets were sold per Whiteman but it also created
● Benefited the economy as it
to buy an assortment of yogurts week opposition as it became
convinced people to keep
from a range of flavours and 10 ○ They produced films associated with immoral
buying
different shades of hair colors in colour by 1922 behaviour of youngsters
● With the consumers buying
● Shopping became a leisure activity, ○ They introduced ● It helped inspire ore forms of
goods, demand rose and
people wanted to show off that they sound in 1927 dancing
factories had a reason to keep
were better than their neighbours ○ They developed ● The charleston was a fast
buying
they could do this by buying animation dance involving sidekicks and
consumer goods techniques in 1928 a complex sequence of steps
Advertising
● This helped the economy keep ● It made actors such as Charlie
● Used big posters and coloured
growing Chaplin who became an idol Sport
papers in newspapers and
for many young Americans ● More leisure time meant that
magazines to encourage people
Stock market Americans could spend their
to buy their products
● Ordinary Americans became Extend knowledge: spare time watching their
● Overwhelmed consumers with
involved in buying shares in the Hays code - cleaning up films by favorite sports
images of their brands to change
American stock market in Wall street Hayes ● This became a popular hobby
their buying habits
● This involved borrowing money from - Developed a production code for many people
a bank or broker to invest on shares - Banned the filming ● The popularity of sports
● Radio played a central role in the
to then pay back the loan of long kisses made a lot of sporting heroes
development of advertising
- This turned ordinary people into - Childbirth ○ Baseball: Babe Ruth
● As a result alot of American
shareholders - Sex between white set a record of 60
spent their leisure time listening
- Each did it in the hope that the value and black people home runs remaining
to adverts
of the share would go up and they - And the presentation unbeaten until the
● New advertising methods
could sell it at a profit of some crimes to 1960s
helped to create a consumer
- But it was dangerous because what stop the audience ○ Swimming: Gertrude
society, encouraging people to
happened when the prices stopped copying things Ederle, a US
buy new products or spend
going up? - This was inforce until swimmer became
more on brand names
- It also led to more companies selling the rating system in the first woman to
● This boosted the economy
shares which gave them the money 1968 swim the English
because more spending created
to develop their businesses channel in 1926
a need for increased production