CAN FIT PRO EXAM PREP 2024(ALL POSSIBLE QUESTIONS WITH 100% CORRECT ANSWERS
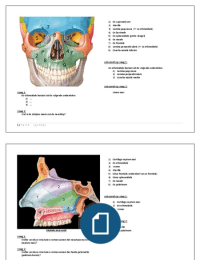
CAN FIT PRO EXAM PREP 2024(ALL POSSIBLE QUESTIONS WITH 100% CORRECT ANSWERS) How many calories in a gram of carbohydrates ? correct answers 4 How many calories are in 1lbs of fat? correct answers 3500 What does RICE stand for? correct answers rest, ice, compression, elevation What are the 5 SMART goals? correct answers Specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time sensitive What does EPOC stand for? correct answers excess post-exercise oxygen consumption What is a compound exersice? correct answers multi-joint exercises that works several muscle or groups at once Name 5 compound exercises. correct answers Squat, burpees, barbell hip raises, deadlifts, incline bench press, clean and press, parallel dips, pull ups, bent over rows, seated cable rows, landmines. What is a isolation exercise? correct answers Movements that involves limited joint or muscle group. Name 5 isolation exercises correct answers Bicep Curls, tricep push downs, leg extensions, legl Curls, shrugs, concentration Curls, barbell curl, preacher Curls. What are the 4 primary components of fitness? CMFB correct answers Cardio respiratory capacity, muscle strengthening, flexibility, body composition How would you describe or explain Body Composition to a client? What is body composition? correct answers It's the percentage of fat, bone, water and muscle in the human body. Define energy correct answers the ability to do physical work What is the byproduct of anaerobic glycolysis correct answers lactic acid Define metabolism correct answers The sum of all chemical reactions in the body that either use or create energy What is the daily recommended intake of water for both men and women correct answers 3.7 l a day for men 2.7 l a day for women What is the Canfitpro promise? correct answers to inspire Healthy Living Through Fitness education What does AMRAP stand for? correct answers As many reps as possible What does FITT stand for? correct answers Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type How many calories does it take to burn 1lbs of fat? correct answers 3500 cal What are the 9 principles of canfitpro-pro training ? FISPRSARM correct answers FITT individualization specificity progressive overload recovery structural tolerance all around development reversibility maintenance What are the 5 stages of change? correct answers Pre-contemplation, Contemplation, Preparation, Action, Maintenance What are the 7 secondary components of fitness? correct answers Balance, Coordination, Agility, Reaction time, Speed, Power, Mental capability. Which is not a Primary Component of Fitness correct answers Agility How many ATP are given during the ATP-CP process? correct answers 1 atp How long does the ATP-CP system provide energy for? correct answers 10sec How long does anaerobic glycolysis provide energy for? correct answers Up to 2 mins Which aerobic energy system provides fuel for more than two minutes at moderate intensity ? correct answers Aerobic glycolysis What energy system is 38 ATP? correct answers aerobic glycolysis How many ATP are given during fatty acid oxidation correct answers Which energy system delivers 2-3 ATP? correct answers Anaerobic (without oxygen). When the aerobic system can no longer give ATP the Anaerobic system kicks in what is this called? correct answers Lactate threshold What is an average resting heart rate correct answers 72bpm Canfitpro's recommendation frequency for Muscle Strengthening Activity per week? correct answers Major muscle groups 3 or more days /week What does bioenergetics mean? correct answers The study of how energy flows in the human body Canfitpro's recommendation frequency for Flexibility Activity per week? correct answers 4 or more days / week What does ATP stand for and what is it? correct answers Adenosine triphosphate; high energy phosphate molecules required to provide energy for cellular function. It is produced both aerobically and anaerobically What is osmosis? correct answers Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane What is a membrane? correct answers flat sheets of flexible tissue that cover or line a body structure How do you calculate BMI? correct answers (weight (lbs) x 703) / (ht(inches)^2) or 190 x 703 divided by 5.11 squared What are the benefits of cardio-respiratory Training ? Hint 6 correct answers Less stress on the heart, more stamina, fat loss, stabilized body composition, reduced blood pressure and lower risk of heart disease. What is cardio respiratory endurance? correct answers the ability of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels to utilize and send fuel and oxygen to the body's tissues during long periods of moderate- to-vigorous activity What is the purpose of cardio-respiratory recovery? correct answers To gradually reduce exercise intensity How can you gradually reduce exercise intensity correct answers Reducing intensity of and impact of an exercise, Reducing range of motion of the activity and completing active recovery. What is active recovery? correct answers The client continues to move instead of stopping which helps the heart and circulatory system in a re-distributing blood to all parts of the body abruptly stopping activity puts considerable stress on the cardio respiratory system. When talking about FITT, what should you consider? Hint 4 correct answers 1. Number of sessions client is able to commit to. 2. Clients current fitness level. 3. Clients exercise experience. 4. Clients goals for cardiorespiratory training. What does HRR mean? correct answers heart rate reserve What is heart rate reserve? correct answers difference between max heart rate and resting heart rate What does THR stand for? correct answers target heart rate How do you calculate Target Heart Rate (THR) 2 methods ? correct answers HR max method = 220 - age x intensity HRR method = 220 - age - resting heart rate x intensity READ CARD correct answers Your clients experience in feelings in an exercise setting may be significantly different from yours you need to understand your clients fear uncertainties and any negative perceptions of exercise. READ CARD correct answers Your clients may have several other beliefs or perceptions : unrealistic expectations from themselves fear of failure fear of not knowing what to do or how to do it perception that everyone will be looking at them belief that they are the only ones who feel the way they do. READ CARD correct answers Here are some actions you can take to help your clients and manage these perceptions: Get them talking about their Previous achievements no matter how far back tractor success and remind them of their accomplishments along the way. Celebrate their success have fun ensure them that they are not alone in their journey towards optimal health and that others have felt the same way as them who they want to share their success with establish a focus they can use when the wave forward becomes difficult. What will motivate them to carry on and move forward and empower them with knowledge in guidance on how to exercise commend them on remembering key cues and techniques remind them that their choice is to get active and exercise is rewarding share stories of other clients with permission or introduce them to others who have felt the same way so that they believe that success is possible for them to What is the cycle of client fulfilment? Hint 4 correct answers Explain exercise Demo exercise Coach to motivate with purpose Empower clients belief and ability Name some key qualities of effective personal training specialists correct answers Listening, curious, intuitive knowledgable, supportive, respectful model of healthy behaviour , Trustworthy, enthusiastic, innovative patient, sensitive, flexible, self-aware resourceful, committed to providing timely in specific feedback, capable of providing clear reasonable instructions and programming, able to generate expectations of success Transtheoretical Model of Change? Hint 6 correct answers 1. Precontemplation 2. Contemplation 3. Preparation 4. Action 5. Maintenance 6. Relapse Describe the Precontemplation stage correct answers Not ready! Do not intend to start Describe the Contemplation stage correct answers Getting ready! They have started to think about exercising or changing behaviour and have most likely identified a course of action. More aware of the benefits of changing Describe the Preparation stage correct answers Ready! Clients are ready to start taking action and they takes small steps that they believe can help and make the healthy behavior a part of their lives. They may start talking about it with friends and family or social media. They are excited Describe the Action stage correct answers Actively making changes. At this stage people have begun to take the necessary action but not much time is passed since they started making a change clients at this stage have change the behavior in need to work hard to keep moving ahead. Describe the Maintenance stage correct answers Adherence to change. The stage begins after the person has successfully adhere to an exercise program for assisting. Approximately six months or more people at the stage of change their behavior but they need to be aware of situations that may tempt them to the back into the old unhealthy behavior particularly stressful situations. Intervention strategies for stages of change (Preparation Stage) hint 3 correct answers Evaluate support system and barriers Provide personalize exercise design Work on goalsetting an action plan READ CARD correct answers Motivating clients Try asking clients the following: When you reach your fitness goal of (whatever the client is striving for) describe what that will look like! what will you be saying ? what will others be saying ? how will that feel ? what will you do then? Give examples of general motivational strategies correct answers Recall the purpose or goal they are working toward. Make the workouts fun. Let clients know what to expect as the workout proceeds in one setting up their next appointment. Provide positive behavioural feedback and comments specifically on what clients are doing right. Asked client how their personal circle is supporting them with the behavioural change. Ask whom they are sharing their success with encourage group participation in group support. Include variety in complexity to decrease boredom and increase enjoyment. Provide periodic assessment to give information about progress toward goal and offer positive reinforcement. Ask clients what they like about a work out when they felt successful or strong. Use behavioural change strategies such as personal goal setting journalling contracting and self management to foster a greater sense of competency and personal control. Always keep workout logs to chart progress display progress. Recognize goal achievement in progress through appropriate recognition. Ask what healthy reward they can provide for themselves when they reach milestones our goals along with journey. Ask what activities clients enjoy doing and incorporate them in their plan and workout programs. SMART goals: describe S correct answers Specific: What exactly do you mean by get in shape and feel better? How do you want to feel? What do you want to change? SMART goals: describe M correct answers Measurable: scale or body fat measurement. Where they see themselves on a scale of 1 to 10. Measure something else maybe like energy on a 1 to 5 scale. Could be want to play with kids more any scale really. What is adipose tissue? correct answers fat SMART goals: describe A correct answers Attainable: assign specific attainable action example = 3 sessions a week or loose 2 lbs a week over day 10 to 20 weeks. SMART goals: describe R correct answers Realistic: set realistic time frames and goals, educate clients on the realities and problems with quick fix programs. SMART goals: describe T correct answers Time sensitive: the time frame, all goals should have a date set to it, long term vs short term. What is a realistic fat loss goal per week? correct answers 1 to 2lbs a week What is a realistic fat loss goal for 6 to 8 weeks ? correct answers 5 to 7lbs What does SMARTERS stand for correct answers Specific Measurable Attainable Realistic Time sensitive Evaluate Realign Success SMARTERS goals: describe E correct answers Evaluate: At predetermined dates is the client on tracked was the ultimate goal? what area has the client succeeded? where is more attention and effort needed? SMARTERS goals: describe R correct answers Realign: After evaluation if the client is off track, modify the program to ensure timely progress towards the ultimate goal SMARTERS goals: describe S correct answers Success: if progress is on track be sure to reward to success READ CARD correct answers With respect to behaviour the best predictor of a persons likelihood to participate in an exercise program is -> previous experience an exercise program Chapter 1 Review Questions: What does the acronym SMART represent? correct answers A method of setting short term and long term goals with a client. Chapter 1 Review Questions: Explain the importance of providing the client with the "WHY" behind an exercise selected for her or his program. Give an example of a why for a squat. correct answers It's important for the client to know that this exercise or muscle group will help towards achieving their goals example of squats. Squats are a good compound exercise that works lots of muscles at once, saving you time and strengthening your legs faster. Chapter 1 Review Questions: When a fitness consumer is transitioning to become a personal training specialist what stage of change is he or she in when researching certification requirements, completing goalsetting and evaluating barriers in opportunities correct answers The 3rd stage, PREPARATION! Chapter 1 Review Questions: What is a useful presupposition for personal training specialist to have before meeting with a client? correct answers C, The client will be on time, enthusiastic, excepting of feedback and appreciative of the work the personal training specialist has done to prepare for the session Chapter 1 Review Questions: Which strategy can a personal training specialist use to assist a client in the action stage of change? correct answers Talk to the client About self monitoring and self reinforcement As well as provide encouragement. Chapter 1 Review Questions: When a fitness consumer is transitioning to become a personal training specialist what stage of change is he or she in when researching certification requirements, completing goalsetting and evaluating barriers in opportunities correct answers The 3rd stage, PREPARATION! Chapter 1 Review Questions: What would be the best way to engage with a client whose personality trait is a thinker? correct answers A. Provide direct and clear feedback? B. Give plenty of genuine compliments? C. Allow extra time to perfect exercises? D. None of the above? Answer is: A Chapter 1 Review Questions: What is a useful presupposition for personal training specialist to have before meeting with a client? correct answers C, The client will be on time, enthusiastic, excepting of feedback and appreciative of the work the personal training specialist has done to prepare for the session Chapter 1 Review Questions: Which strategy can a personal training specialist use to assist a client in the action stage of change? correct answers Talk to the client About self monitoring and self reinforcement As well as provide encouragement. Chapter 1 Review Questions: What is the most common reason for clients not exercising? correct answers There is not enough time! What are some Benefits of regular physical activity? correct answers Reduce risk of premature death, strengthens the heart, cardiovascular system and respiratory system, decreases resting, heart rate normalizes, resting blood pressure, improves heart efficiency, decreases body fat, increases HDL good cholesterol and decreases LDL bad cholesterol, keeps body fat in control, increases cellular sensitivity to insulin and helps to regulate blood sugar levels, promotes joint stability and increased strength of all connective tissue, increase muscular strength, strengthens bones, increase muscular mass and decrease body fat, increases resting metabolism, improve core strength by strengthening the abdominal and back muscles, improve balance, coordination and agility, improves body image and self-esteem, reduces depression and anxiety, assists in stress management and gives a person a positive way to deal with stress. What does ADL stand for? correct answers Activities of daily life READ CARD correct answers Physical activity as a personal training specialist we spent a great deal of time inspiring in assisting others in the pursuit of improved health education is an important aspect of this process we must help people understand why they should be active and promote the benefits of regular physical activity for all clients. Why should you eat healthy? correct answers Enhancing nutrition will improve your overall health and body composition the balance of body fat and then tissue Advice on nutrition for beginners? correct answers Start by reducing your poor food choices while introducing new healthier choices increasing consumption of cruciferous vegetables like broccoli cabbage bok choy and so on whenever possible. Benefits of cardiorespiratory exercise correct answers Reduces the risk of non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease cancers respiratory disease and diabetes it also lowers your resting heart rate. How long should a clients first cardio session be? correct answers 10mins How many minutes of moderate intensity aerobic exercise should a person do a day? correct answers 43mins or 22mins of vigorous intensity How many minutes of moderate intensity aerobic exercise should a person accumulate in a week? correct answers 300mins or 150mins of vigorous intensity benefits of muscle training correct answers Resistance training activities strengthen muscles increase muscular capacity and improve functional fitness the ability to conduct daily activities with greater ease while also reducing the risk of several non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancers in respiratory disease and diabetes What is a noncommunicable disease? correct answers a disease that is not transmitted from one host to another How many days a week should you do strength training? correct answers 3 or more days per week How many reps should beginners do? correct answers Slow, low intensity movements 3 to 8 exercises 1 set 12 to 15 reps What does callisthenics mean? correct answers Body weight exercises. Strength, endurance, flexibility and coordination. How many days a week should you include stretching in your routine ? correct answers 4 or more Define FITT correct answers Frequency: how often client should be performing a particular components. Intensity: the difficulty lvl of the program component (heart rate, load,reps, watts, etc). Time: how long each components should last and rest. Type: choice or exercise (exercise, equipment or activity). Define Individualization? correct answers Available training time, starting fitness lvl, experience, etc Define Specific? correct answers Clients want to improve a particular aspect of their performance such as better runner or bigger muscles Define Progressive Overload? correct answers Clients must continuously challenge to see significant improvement over time. Increase weight, reps, sets, duration, intensity, complexity. Define Recovery? correct answers The recovery period must allow clients to return to the next workout at least as fit as they entered the previous one, if not more. Define Structural Tolerance? correct answers Refers to the strengthening of joints ( tendons and ligaments) this will result in the ability to sustain subsequently greater stresses When in the maintenance phase, what is the volume clients can train? correct answers Clients can train as little as 1/3 the volume at the same intensity for up to 12 weeks Food is absorbed by the body. This occurs primarily in the small intestine. What is the % off all absorption made here? correct answers 90% Where is water absorbed? correct answers Small Intestine What is another name for the Large Intestine? correct answers Colon What is the definition of Bioenergetics correct answers The study of how energy flows in the human body. The molecule that the body uses as it's energy currency is called ? correct answers Adenosine Triphosphate. ATP Bioenergetics Terminology for Energy: correct answers Energy is the ability to do physical work. Bioenergetics Terminology for Metabolism: correct answers Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body that either use or create energy. It's the combination of the catabolic and anabolic processes. What do you call the energy either used or created from all the metabolic processes is called ? correct answers Adenosine Triphosphate What are the 4 systems when forming ATP? A.A.A.F correct answers ATP-CP (phosphagen) 10sec Anaerobic (glycolytic) up to 2min Aerobic (glycolytic) 2min+ Fatty Acid Oxidation 2min+ What does Aerobic mean? correct answers With oxygen Explain why cardio is a good way to burn calories and fat : correct answers ATP is created by the Aerobic system by using stored fat and carbohydrates in order to fuel bouts of activity. In other words, your body uses fat and carbs and transforms it into energy or ATP Why does ATP-CP stand for ? correct answers Adenosine Triphosphate - Creatine Phosphate. READ CARD correct answers CP is the back up for ATP. Where is glucose found in the body? correct answers In the blood Chapter 2 Review Questions: List and name 3 of the secondary fitness components. correct answers 1. Agility: move or change direction quickly 2. Speed: Ability to move rapidly 3. Power: The product of strength and speed 4. Mental: Ability to concentrate during training Chapter 2 Review Questions: How would you explain body composition to a client who wants to achieve weight loss? correct answers Body composition: Is the proportion of fat free mass (muscle, bone, blood, organs and fluids) to fat mass (adipose tissue deposited under the skin and around organs) Once we know the amount of fat we can measure the amount lost to determine your progress. Chapter 2 Review Questions: Which components of the mind are as important as physical health? correct answers Mental health, Social health and Emotional Health. Chapter 2 Review Questions: What are the primary fitness components? correct answers Cardiorespiratory capacity Muscular capacity Flexibility Body composition Chapter 2 Review Questions: Which of CANFITPRO's nine training principles is best demonstrated by the fallowing example? A client who has a goal of running a marathon should have included in their program some exercises that target the ankles, knees, hips, and back, because marathon training will stress those areas. correct answers A) Specificity? B) Individualization C) Structural Tolerance D) FITT Answer is: C Structural Tolerance Chapter 2 Review Questions: Which of the following accurately represents CANFITPRO's recommendation for cardiorespiratory activity? correct answers A) 300 mins of moderate- intensity activity per week B) 22 mins of vigorous-intensity activity per day C) 150 mins of vigorous-intensity activity per week D) All of the above Answer is: D) All of the above Chapter 2 Review Questions: What principle suggest that after training ceases, the body gradually returns to a pre-training state? correct answers A) Reversibility B) Maintenance C) Recovery D) Specificity Answer is: A) Reversibility Where is glycogen found in the body? correct answers In the muscles What happens when you run out of glycogen in the muscles and run out of glucose in the blood stream ? correct answers A by-product called Lactic Acid is produced! What is the lactate threshold? correct answers The point at which the body begins to form lactic acid, beyond what it can metabolize with the oxygen present. (So max reps max effort phase when your spent!) What happens when you produce too much lactic acid in the muscle ? correct answers Lowers the cellular pH and begins to slow the speed and strength of muscular contraction. (This is where you feel the ) When Lactic Acid lvls are high enough, it can result in temporary muscle failure (no further contraction can occur) this is called ? correct answers Lactic Acidosis How is CO2 and H2O diffused ? correct answers In the bloodstream and taken away for disposal (carbon dioxide is exhaled and water is used elsewhere or lost through sweat) Mitochondria is ? correct answers The cellular structures with specialized enzymes to assist in aerobic metabolism, uses either glucose or fat for fuel to create ATP. With a continuous supply of oxygen from the Aerobic system, the muscle cells begin to breakdown glucose. What waste product is created by this? correct answers Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Water (H2O) as well as heat. What is Oxygen Deficit? correct answers The lack in oxygen uptake at the beginning of exercise What does BMR stand for and what is it? correct answers basal metabolic rate, number of calories the body uses while at rest What is the formula for converting LBS to KG and INCHES to CM and FEET to INCHES? correct answers Your LBS / 2.2046 = KG Your INCHES x 2.54 = CM 1 FOOT = 12 INCHES How do you calculate BMR? correct answers For men: BMR = 10 x weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) - 5 x age (years) + 5 EXAMPLE: 929 + 180.34 - 170 +5 = 944.34 For women: BMR = 10 x weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) - 5 x age (years) - 161 How to calculate caloric expenditure correct answers Exercise Met lvl x kg / 60mins Should beginners participate in anaerobic interval training ? correct answers No How many times per week should you do anaerobic interval training ? correct answers 2 or 3 then add light cardio training Chapter 3 Review Questions: Describe the relationship between metabolism and the energy used. For muscle contraction. correct answers Energy is the ability to do work, and metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body that either use or create energy. Our bodies are constantly converting chemical energy from food into mechanical energy to contact muscles. Chapter 3 Review Questions: Describe EPOC and it's role in exercise recovery. correct answers Excess postexercise oxygen consumption helps the body repay the oxygen dept created during the exercise session. After the workout is complete and the need for a higher supply of energy diminishes or ends, the body continues to take in extra oxygen to repay oxygen dept and begin cellular repair created by exercise. EPOC helps the body recover from both aerobic and anaerobic activities. Chapter 3 Review Questions: The ATP-CP phosphagen system produces ATP per molecule of créatine phosphate ? correct answers A. 1 B. 2 C. 20 D: 3 Answer is: A.1 Chapter 3 Review Questions: What type of relief makes up the rest interval for developing the anaerobic glycolytic system. correct answers A: rest relief B: work relief C: passive relief D: hard jogging Answer is: B:work relief Chapter 3 Review Questions: EPOC is used for all the following processes EXCEPT!! correct answers A: atp replenishment B: cp replenishment C: digestion of carbohydrates to glucose D: conversion of lactate to glucose Answer is: c: digestion of carbohydrates to glucose Chapter 3 Review Questions: The aerobic oxidative energy system is fueled by And produces up to ........... atp per unit of fuel. correct answers A: fat, 39 B: glucose or glycogen , 2 to 3 C: glycogen , 100 or more D: glucose and fat, 100 or more Answer: D: glucose and fat m, 100 or more Chapter 3 Review Questions: What terminology best describes the point at which the aerobic system can't supply enough ATP for the needs of the body, forcing the anaerobic systems to increase their contribution of ATP? correct answers A: homeostasis B: lactate threshold C: anaerobic glycolysis D: catabolic metabolism Answer is: b: lactate threshold READ CARD!!: The heart ️ and blood correct answers Blood travels in arteries either to the lungs from the right side of the ♥️ or to the body from the left side. It returns to the ♥️ through veins, which bring back to the left atrium from the lungs or to the right atrium from body tissue. How many litres of blood does the average adult circulate every minute at rest ? correct answers 5 litres of During maximal effort, how many litres of blood are circulated every minute in a typical adult ? correct answers 6 or 7 times the amount of circulated at rest What is blood pressure? correct answers Blood being forced out of the ventricles and exerting force against arterial walls What is the average blood pressure at rest ? correct answers 120/80 Understanding BP correct answers Top number or 120 = systolic pressure Bottom number or 80 = diastolic pressure. What is systolic pressure? correct answers The pressure exerted on the walls of the arteries as the ️ contracts, representing peak pressure in the system. What is diastolic pressure? correct answers The pressure exerted on the walls of the arteries as the heart relaxes and fills again, representing the lowest pressure in the arteries READ CARD!! correct answers During activities such as resistance training, arteries are compressed, increasing pressure and potentially compromising circulation. If these straining activities are done improperly, they may cause dizziness or faintness and can be dangerous, especially for people with high pressure. It's important that Personal training specialists coach appropriate breathing during exercise training, and follow the FITT principle, to ensure client safety. What is the average at rest beats per minute ? correct answers 72 bpm Where can you take a pulse? correct answers Radial artery: in the arm / wrist Temporal artery: side of the head / temples Carotid artery: in the neck your right side their left Best place for PTS to take pulse? correct answers The radial pulse, taken at the wrist along the outer edge of the lateral tendons is the preferred place for a HR measurement. READ CARD!! correct answers When monitoring a clients HR manually, place your fingertips, NOT YOUR THUMB, over the artery, as the thumb has a very strong pulse of its own and could cause an error in calculation. What is stroke volume? correct answers the amount of blood ejected by left vertical in one beat. What is the average resting stroke volume for a typical male ? correct answers 70 millilitres What is cardiac output (Q)? correct answers The amount of blood that the heart ejects in 1 minute. How to calculate Cardiac Output (Q)? correct answers Q = HR x SV The lungs what is ventilation? correct answers The mechanical process of moving air in and out of the lungs . Simple What is diffusion? correct answers The way gases are exchanged in the lungs The respiratory system consists of ? Hint 8 m,n,nc,p,l,t,bt,l correct answers Mouth Nose Nasal cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchial tree Lungs Tiny air sacs on the end of the bronchioles are called ? correct answers Alveoli What is the purpose of the alveoli? correct answers Air fills the alveoli which are surrounded by capillaries, where oxygen rapidly moves from the alveoli into by a process called diffusion. The alveoli helps remove carbon dioxide through exhalation and defuses oxygen into the blood . What does cardiorespiratory fitness reflect? correct answers The efficiency of the cardiovascular, respiratory , and muscular systems How many alveoli are there in the ? correct answers Over 300 million What is the abbreviation for Cardiorespiratory Capacity? correct answers VO2max What is VO2 max? correct answers The maximum amount of oxygen the body can extract and use in the process of energy production. READ CARD!! Recovery ️ correct answers The fast portion of recovery ️ helps replenish ATP-CP stores and remove lactic acid. The slower portion of recovery ️ supports muscles tissue repair and adaptations that occur because of the exercise. Is active recovery ️ better then passive recovery ? correct answers Yes!! Less stress on the cardiorespiratory system. What are 3 ways you can gradually reduce exercise intensity correct answers Reducing the intensity and impact of the exercise (reps, tempo, sets, weight) Reduce the range of motion or movements Instructing clients to begin an active recovery (slow jog or walk) What are the benefits of cardiorespiratory training ? correct answers - Reduce ♥️ disease - Reduce resting ♥️ rate - Normalize resting pressure - Improve the ability to perform daily activities READ CARD!!! Other peripheral improvements as a result of cardiorespiratory training. correct answers - Increased capillary density - Increased size and numbers of mitochondria - Increased aerobic enzymes Provides more vessels for efficient nutrient delivery and waste removal. Improved aerobic production of ATP. Enhanced ability to use oxygen. Canfitpro's recommendations for Cardiorespiratory Fitness ? correct answers •Up to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week (about 43 minutes per day) or •150 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week (about 22 minutes per day). In FITT, what does Frequency refer to? correct answers The number of times that the cardiorespiratory system is intentionally stressed each week. The frequency depends on the intensity and duration of each training period. Considerations for FITT frequency ? correct answers Number of sessions client can commit to Slow increase in activity level Optimal effects for cardio tends to require how many sessions per week? correct answers 3 to 5 In FITT, intensity refers to ? correct answers The rate of work being performed. Speed, weight, HR READ CARD!! correct answers Training intensity can have a significant effect on the success of the workout because it has considerable physiological and psychological effects on the client. For example, if the workout is too difficult the client may be unable to complete the planned activity. From a psysiological standpoint the client's body is unable to supply the required energy and from a psychological standpoint the client might not enjoy the exercise session because it is too difficult. How can you plan or evaluate intensity? correct answers Oxygen uptake HR monitoring Perceived exertion HRmax equation? correct answers 220-age Exp: 220-34 = 186 bpm for me no higher. In general what is the appropriate range of recommended exercise intensity? correct answers Between 55% and 90% of HRmax This is blue as the heart ♥️ rate TRAINING ZONE How to calculate training zone using HRmax? correct answers (220-age) x intensity say .55 for 55% .9 for 90% and so on. What is the target TRAINING ZONE for beginners ? correct answers 55% to 64% What is the target TRAINING ZONE for an intermediate? correct answers 65% to 74% What is the target TRAINING ZONE for an advanced ? correct answers 75% to 90% READ CARD!! correct answers Fit clients need to train at higher intensity to continue to develop the cardiorespiratory system. What is HRR? correct answers heart rate reserve What is the HRR formula? correct answers HRmax - RHR What is the intensity range for HRR? correct answers Between 50% and 85% What is the HRR formula? correct answers ( HRmax-RHR )x intensity % + RHR. ( 220-age - resting HR )x % + resting HR Which is more accurate to determine the TRAINING ZONE the HRmax method of the HRR method? correct answers HRR Considerations for FITT intensity correct answers Beginners should start between 55% and 64% intensity Intermediates should be between 65% and 74% intensity Considerations for FITT time correct answers Beginners should start with 10 to 15 mins of activity and add 5min increments every week as they progress Intermediate 15 to 30 mins Fit between 30 to 60 mins Improving cardio efficiency requires more then 20 mins of elevated ♥️ rate. In FITT what does time refer to? correct answers The duration, the length of time that a training stimulus is applied without rest. Exp: 10 min warm up 25 min jog 5 min cool down = 25mins of training Research shows that health improves with how much time spent training in the TARGET HR ZONE? correct answers 20 to 30 mins In FITT what does type refer to ? correct answers The mode/type of activity performed. What are 3 factors that affect exercise difficulty ? correct answers Skill, coordination, caloric expenditure Considerations for FITT type correct answers Beginners should start with equipment with minimal skill, coordination and caloric expenditure Limit movement in the vertical plain Involves less muscle and less complex movements The rockport walking test should be given as a pro luminary assessment. How long is the walk ? correct answers 1.6km walk as quickly as possible What is the frequency for nonexerciser? correct answers 1-4 / week What is the intensity for nonexerciser? correct answers HRmax 55% to 64% HRR 50% to 85 % RPE 2-4 What is the time for nonexerciser? correct answers 10-30 mins What is the frequency for occasional exerciser? correct answers 1-4 / week What is the intensity for occasional exerciser? correct answers HRmax 55% to 64% HRR 50% to 85% RPE 2-4 What is the time for occasional exerciser? correct answers 15-30 mins What is the frequency for recreational exerciser? correct answers 3-5 / week What is the intensity for recreational exerciser ? correct answers HRmax 65% to 74% HRR 50% to 85% RPE 4-6 What is the time for recreational exerciser? correct answers 20-45 mins What is the frequency for committed and dedicated exercisers or athletes? correct answers 3-5 /week What is the intensity for committed or dedicated exercisers or athletes ? correct answers HRmax 75% to 90% HRR 50% to 85% RPE 4-9 What is the time for committed or dedicated exercisers or athletes ? correct answers 20-60 mins True or false ? Each cardiorespiratory training session should start with a warm-up? And followed by a cool-down? correct answers True and True READ CARD!! - Oxygen delivery and energy production at rest. correct answers 1. Air goes to the lungs . oxygen goes to capillaries from alveoli, carbon dioxide is exhaled, himoglobin in the red blood cell binds with oxygen and Carries it. 2. Blood goes to left atrium via veins, left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood through the aorta to all parts of the body including muscles 3. Oxygenated blood through the arteries artérioles and capillaries to the muscle cells, dissolved nutrients from food are also delivered. 4. The muscle cell breaks down stored glycogen or glucose in the presence of the oxygen to produce ATP ( if using aerobic metabolism. 5. Carbon dioxide and water are the waste products and are carried away in the blood . Veins carry the deoxygenated blood back to the right atrium of the heart ♥️. 6. The deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right ventricule to the via the pulmonary artery. Carbon dioxide is exhaled and fresh oxygen is supplied to the . The cycle of oxygen transfer and energy creation takes about 2 secs to occur. READ CARD!!! Oxygen delivery and energy production during exercise. correct answers Same as at rest but quicker, more blood pumped, more oxygen, higher BP, stroke volume, cardiac output, systolic pressure. Basically everything goes up. Chapter 4 Review Questions: Explain the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure. correct answers Systolic is the amount of force exerted on the arterial walls while the heart ♥️ contracts and pumps blood out of the ♥️ Diastolic is the amount of force generated on the arterial walls as the heart relaxes and fills up with blood again. Systolic is the higher number and diastolic the lower. 120/80 Chapter 4 review questions: list appropriate program focus areas for a client who is deconditioned and has minimal exercise experience. correct answers - Improve overall health profile - Increase energy and endurance - Make activities of daily life easier - Lose weight Chapter 4 review questions: stroke volume is the amount of blood ? correct answers A: Ejected per hour B: Ejected by the right ventricle per beat C: Ejected by the left ventricle per beat D: Ejected per minute Answer is: C Chapter 4 review questions: why would a personal training specialist never take a clients pulse with the thumb? correct answers A: it has a pulse off it's own B: it gives too much pressure and will occlude the radial artery C: the thumb should be used only if the client is measuring her or his own pulse D: the other fingers have a stronger pulse than the thumb Answer is: A Chapter 4 review questions: cardiac output is equal to? correct answers A: Stroke volume x ♥️ heart rate B: Stroke volume x blood pressure C: blood pressure x ♥️ heart rate D: ♥️ heart rate x blood pressure Answer is: A Chapter 4 review questions: the value 3.5 ml/kg/min represents the volume of oxygen consumed correct answers A: at rest B: during steady state exercise C: during vigorous exercise D: during body-weight-supported exercise Answer is: A Chapter 4 review questions: which of the following is the most accurate description for the acronym RPE correct answers A: rate of physical exertion, The primary method of designing exercise intensity B: rate of perceived exertion, the primary method of designing exercise intensity C: rate of physical exertion, close related to the clients heart rate D: rate of perceived exertion, closely related to the clients heart rate. How many bones are in the human body? correct answers 206 How many bones are babies born with ? correct answers 270 soft By what age do the 270 soft bones finish fusing together? correct answers 25 True or false? Bones are 50% fluid and 50% solid. correct answers True READ CARD!! Flat correct answers Flat bones are broad, thin layers of bone such as those of the skull or sternum that offer protection to vital organs, but little motion, as well as bones such as the ribs and scapula, which provide protection and a broad site of muscular attachment. What are the 4 types of bone? correct answers - Long bones (femur, humerus) - Short bones (tarsals "ankle" and carpals "wrist") - Flat bones (ribs, scapulae) - Irregular bones (ischium, pubis, vertebrae) What are the 2 parts of the skeleton ? correct answers axial and appendicular What does the axial skeleton consist of? correct answers skull, vertebral column (spine), ribs and sternum What is the purpose of the axial skeleton correct answers Provides the longitudinal axis of the trunk to which the limbs attach, and it protects the vital organs of the body How many bones in the axial skeleton? correct answers 80 What does the appendicular skeleton consist of? correct answers Shoulder girdle, upper limbs, pelvic girdle, lower limbs What is the purpose of the appendicular skeleton? correct answers Includes the bones of the appendages How many bones in the appendicular skeleton? correct answers 126 64 in the shoulders 62 in pelvis and lower limbs What are the 3 classifications of joints? correct answers Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial What are ligaments? correct answers Tough short bands of fibrous connective tissue composed mainly of long stringy collagen molecules. What is the function of a ligament ? correct answers To connect bones to other bones and holding them together in an articulation. What do you called ligament injuries? correct answers Sprains What's the function of fibrous joints correct answers Connects Bone to bone, allows very little if any movement skull, pelvis, forearm (radius & ulna) What's the function of cartilaginous joints ? correct answers separates bone by cartilage, allows little or no movement, between ribs and sternum and between the vertebrae in the spine What's the function of synoviale joints ? correct answers Freely movable, absorb shock, enclosed in capsule that holds synovial fluid inside the joint cavity How many types of synovial joints are there ? correct answers 6 What are the 3 most common synoviale joint that personal trainers need to know? correct answers Hinge Condyloid Ball and socket Can you name all 6 ? correct answers Gliding Pivot HINGE CONDYLOID Saddle BALL AND SOCKET READ CARD!! Synoviale Hinge joint correct answers Allows movement in one direction or plane of movement (elbows and knees) READ CARD!! Synovial Condyloid joint correct answers Allows movement in 2 directions or planes of motion (knuckles in each finger and in the wrist and ankle) READ CARD!! Synovial ball and socket joint correct answers Allows movement in 3 directions of planes of motion (shoulders, hip joints) How many cardinal planes of movement are there ? correct answers 3 What are the 3 cardinal planes of movement ? correct answers Sagittal plane Transverse plane Frontal plane What way does the frontal plane go ? correct answers From shoulder to shoulder move side to side What way does the transverse plane go? correct answers Across the abdomen, horizontal, separates upper and lower. Twisting or rotations. What way does the sagittal plane go ? correct answers Between the eyes. Move forward or move back Describe anterior and posterior correct answers front and back of the body Describe medial and lateral correct answers Medial: towards the midline Lateral: away from the midline Describe superior and inferior correct answers Body part above another Body part bellow another Describe supine and prone correct answers Supine: Lying on the back. Facing UP in the sUPine position. Prone: Lying on your stomach facing downward. Describe dorsal and plantar correct answers Foot pointing up, top of foot Foot pointing down, bottom of foot Describe joint flexion, extension and hyper extension correct answers Bending a joint. The angle decreases Straighten a joint. The angle increases Beyond normal joint range Describe joint abduction and adduction correct answers Bone moves away from midline Bone moves towards the body Describe joint circumduction correct answers Reducing angle, bone moves away from midline, increase angle moves bone away from midline (shoulder joint and hip joint) Describe joint elevation and depression correct answers Shoulders: Shrugging shoulders up Lowering the shoulders bellow normal (shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle) Describe joint medial and lateral rotation. correct answers Rotation towards midline Rotation away from midline Describe joint supination and pronation correct answers Forearms : Forearm rotated away from body externally so palms are up Forearm rotated towards body internally so palms are down Describe joint inversion and eversion correct answers Ankle joint : Turning the inner part of the foot towards midline Turning the outer side away from midline Describe joint dorsiflexion and plantar flexion correct answers Ankle: foot flexing upwards Foot flexing downwards True or false ? When designing programs you should always Keep in mind clients bone density and back health? correct answers True How many major sections in the spine ? correct answers 4 plus tail bone Name the sections of the spine correct answers Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccyx How many vertebrae in the cervical section ? correct answers 7 How many vertebrae in the thoracic section ? correct answers 12 How many vertebrae in the lumbar section ? correct answers 5 How many vertebrae in the sacral section ? correct answers 5 How many vertebrae in the coccyx section ? correct answers 4 fused What are the 3 spinal stabilization systems correct answers Control subsystem (neural) Passive subsystem (spinal column) Active subsystem (spinal muscles) Chapter 5 Review Questions: list the 4 classifications of bone and give an example for each. correct answers Short: carpals & tarsals Long: femur, tibia, fibula, humérus, radius, ulna Flat: scapula, ribs, ilium Irregular: vertebrae, ischium, pubis Chapter 5 review questions: Define the following anatomical terms and provide the term used to identify the opposite: anterior, medial, inferior, distal, supine, supination, flexion and abduction correct answers - Anterior = front of body / posterior - Medial = closer to midline / lateral - Inferior = lower body / superior - Distal = part of away from body / proximal - on your back / prone - forearm external rotation so palms at up / pronation - reduced joint angle / extension - away from midline / adduction Chapter 5 review questions: the skeleton provides all the following essential functions except? correct answers A: protection of the vital organs and soft tissue B: production of red blood cells C: Storage for minerals calcium and phosphate D: Attachments for organs and blood vessels Answer is: D Chapter 5 Review Questions: The adult human body contains approximately most of which are found in the Skelton correct answers A: 270, appendicular B: 206, appendicular C: 175, axial D: 230, axial Answer is: B Chapter 5 Review Questions: What are the three categories of joints correct answers A: fibrous, cartilaginous and synovial B: fibrous, synovial and Condyloid C: cartilaginous, synovial and syndesmoses D: cartilaginous, synovial and hinge Answer is: A Chapter 5 Review Questions: True or false ligaments are bands of connective tissue that connects muscle to bone to allow movement of the skeletal joint? correct answers False ! Ligaments connect bone to bone Ligaments are tough short band of fibrous connective tissue composed mainly of long stringy collagen molecules ligaments connect bones to other bones holding them together in an articulation Chapter 5 Review Questions: what components are involved in the spinal stabilization system? correct answers A: Active subsystem and control subsystem B: Control subsystem , passive subsystem and active subsystem C: Active subsystem passive subsystem central subsystem D: passive sub system and central subsystem Answer is: B What are the four muscle tissue characteristics ? correct answers Excitability contractility extensibility elasticity Excitability refers to ? correct answers ability to respond to an electrical impulse Called an action potential which initiates the muscle contraction Contractility refers to ? correct answers The response of the muscle cell to the electrical impulse the muscle cell response by shortening pulling the two ends of the muscle towards each other Extensibility refers to ? correct answers The muscle to be lengthened without damaging the tissue Elasticity refers to ? correct answers The muscle to return to its resting length after being either shorten or lengthen What are the three types of muscle tissue ? correct answers Skeletal ,cardiac, smooth READ CARD!! 3 types of muscle tissue correct answers SKELETAL: Attached to bones, single long cylindrical cells with a striated or banded appearance, voluntary contraction can be consciously controlled, contractile proteins arranged regular or in parallel, along the length of the cell CARDIAC: The walls of the heart branched chains of cylindrical cells with striations or bands, contraction is involuntary cannot be consciously controlled contractile proteins are arranged regular or in parallel the force of production is along the length of the cell SMOOTH: Walls of the hollow organs such as the stomach intestines bladder and blood vessels appear irregular shaped thing sells with no striations or bands contraction is involuntary cannot be consciously controlled contractile proteins are irregular and random force production in all directions equally True or false ? the human body contains over 600 individual skeletal muscles? correct answers True True or false? Skeletal muscles make up about 23% of a woman's body weight in about 40% of a man's body weight ? correct answers True What is the function of skeletal muscles? correct answers - provide the force for human movement - maintain upright posture - to generate heat used to maintain constant body temperature Muscle cells are primarily water ......% , a well organized set of proteins % and a limited amount of or inorganic salts such as sodium potassium calcium in chloride correct answers 73% 24% What do you call the thousands of elongated rod shaped cells in each skeletal muscle correct answers Muscle fibers Inside each muscle fibre there is plenty of thinner fibres called what ? correct answers Myofibrils Each Myofibril is composed of a long series of ? correct answers Sarcomeres Each sarcomere comprises two types of protein a thin filament called ? in a thick filament called ? correct answers Actin Myosin Surrounding the muscle fibre is a thin elastic membrane called the what correct answers Sarcolemma Covering the sarcolemma is Fine sheet of connective tissue known as the what ? correct answers Endomysium Muscle fibres are grouped Into bundles of how many fibers? correct answers 10 to 150 fibers A bundle of muscle fibers I s referred to as a ? correct answers Fascicle A fascicle is held together by another connective tissue layer called the? correct answers Perimysium The muscle fibres in the fascicle surrounded by the perimysium all amalgamate at the end of the muscle and form the what? correct answers The tendon of the muscle which attaches to the bone READ CARD!! Muscle contraction correct answers When the muscle cell is stimulated by a nerve impulse the thick filaments myosin pull on thin filaments actin causing them to slide past each other until they completely overlap pulling the end of the sarcomere closer together How many types of muscle contractions are there ? correct answers 3 What are the three types of muscle contractions ? correct answers Isotonic concentric Isotonic Eccentric Isometric Describe all three types of muscle contraction and give an example for each. correct answers Isotonic concentric: Movement occurs when the muscle contracts with enough force to shorten example the lifting phase of a bicep curl Isotonic eccentric: The muscle generates tension as it lengthens example lowering phase of a bicep curl the stretch Isometric: Static contraction the muscle exerts force to counteract an opposing force like gravity, no change in muscle length occurs example holding the arm at a fixed angle of 90° with resistance in the hand READ CARD!! Slow twitch muscle fibers characteristics correct answers Contain a higher amount of mitochondria compared with fast twitch fibres Contract slowly and produce a smaller amount of force than fast twitch fibres but are resistant to fatigue Work aerobically for the most part READ CARD!! Fast twitch muscle fibers characteristics correct answers Have the ability to produce and use ATP more quickly Contract quickly and produce a great deal of force but fatigue quickly Work anaerobically (without oxygen) for the most part What is an agonist muscle? correct answers muscle that contracts during movement What is an antagonist muscle? correct answers A muscle that relaxes during joint movement Can you name the antagonist for each of these muscle pairs? Rectus abdominis Bicep brachii Quadriceps Anterior tibialis correct answers Erector spinae Triceps brachii Hamstrings Gastrocnemius and soleus Why is a synergist? correct answers Muscles that perform two functions in the context of the action of a muscle or muscles What are the 4 main used in a bicep curl ? correct answers Bicep brachii (agonist) Brachialis (agonist) Tricep branchii (antagonist) Brachioradialis (synergist) forearm What is the best way to cue clients to stabilize the shoulder girdle is to ask them to correct answers Lift the shoulder blades (elevation) pull the shoulder blades back (retraction) and pull them down (depression) This is called the set position True or false? Trainers should cue the set position before clients perform any upper-body movements. correct answers True!!! What do we call the shoulder joint? correct answers Glenohumeral joint The rotator cuff is also known as the SITS muscles what does SITS stand for ? correct answers Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis What muscles function is the adduction or retraction of the scapula ? correct answers Rhomboids (major and minor) What does SITS stand for ? correct answers The 4 muscles in the shoulder Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis Describe the muscles, origin and insertion for the DELTOID correct answers Anterior, medial, posterior Clavicule, scapula (spine of the scapula) Upper humerus Describe the origin and insertion of the LATISSIMUS DORSI correct answers Vertebrae T6 - S5 Upper humerus Describe the origin, insertion and function of the TRICEP BRACHII correct answers Upper humerus, scapula Ulna Extension Describe the origin insertion and function of the TRICEP BRACHII correct answers Upper humerus and scapula Ulna Elbow extension Describe the function of the PSOAS MAJOR correct answers Hip flexion (leg up) Describe the function of the ADDUCTOR MAGNUS correct answers Adduction (leg back in from the side) Describe the function of the RECTUS FEMORIS correct answers Hip flexion (leg up) Describe the function of the HAMSTRINGS (bicep femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus) correct answers Hip extension (leg back down) Describe the function of the QUADRICEPS (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedus) correct answers Knee extension (leg extensions) Describe the function of the GASTROCNEMIUS correct answers Knee flexion (heel kickbacks and ankle plantar function) Describe the function of the HAMSTRINGS (biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus) correct answers Knee flexion (heel kickbacks) Describe the function of the TIBIALIS ANTERIOR correct answers Dorsiflexion, ( raise toes up) inversion (turn foot inwards) Describe the function of the RECTUS ABDOMINIS correct answers Spinal flexion, posterior pelvic tilt Describe the function of the erector spinae correct answers Spinal extension What is hypertrophy? correct answers Muscle grows stronger and larger What is atrophy? correct answers Muscles can become smaller and weaker What are some of the benefits of resistance training ? Name a few. correct answers - Makes everyday activities easier - improves sports performance - improves strength for cardiorespiratory exercise - improves posture - healthy body weight - reduce loss of muscles mass due to inactivity and aging - helps prevent osteoporosis - reduces the incidence of joint and muscle overuse injury Define muscular strength correct answers The maximum amount of force a muscle or muscle group can generate Define muscular power correct answers The explosiveness of strength, strength and speed (power = force x distance / time Define muscular endurance correct answers Ability to exert force repeatedly over time Canfitpro recommends how many resistance workouts a week ? correct answers 3 or more Generally speaking, how many hours between workouts is needed to avoid overtraining, injury and poor results ? correct answers 48h How many reps for strength,power, hypertrophy and muscular endurance for best results ? Approximate correct answers Strength = 2 to 6 Power = 2 to 6 Hypertrophie = 8 to 12 Muscular endurance = 14 to 20 What is 1 rep max? correct answers The maximum load that they could lift, pull or push in a single rep How long should a resistance training session be for beginners? correct answers 20 to 30 mins What is isometric training and give an example? correct answers When the length of the muscle remains unchanged. Like side plank, wall sit What is isotonic training and give an example? correct answers Both eccentric and concentric, muscle shortens and lengthens, bicep curl What is isokinetic training and give an example? correct answers Specialized equipment that controls the speed of movement through the ROM Recommended resistance training sessions for nonexerciser ? correct answers 2-3 per week Recommended resistance training sessions for occasional exerciser? correct answers 2-3 per week Recommended resistance training sessions for a recreational exerciser correct answers 3-4 per week recommended resistance training sessions for committed and dedicated exercisers? correct answers 4-6 per week What is the possible program focus for Non exercisers and occasional exercisers ? correct answers Learning proper technique learning correct exercises developing core strength getting muscular endurance What is a possible program focus for a recreational exerciser? correct answers Exercise variety refining proper technique learning new exercises developing core strength gaining muscle endurance gaining muscle strength READ CARD! Resistance training guidelines. correct answers For nonexercisers and occasional exercise or simple movements requiring minimal challenge to balance stability and coordination and involving fewer muscle groups like weight machines stability ball simple body weight exercises closed kinetic chain movements What would be routine choices for a non-exerciser and an occasional exerciser? correct answers Total body workout balance to work out basic circuit READ CARD !! Resistance training guidelines correct answers For recreational exercisers any of the preceding plus moderately complex movements involving some challenges to balance stability and coordination involving one or more muscle groups intermediate level exercises with weight machines stabile balls body weight free weights basic exercises with pulleys kettle bells suspension straps and so on What would be a routine choice for a recreational exerciser? correct answers Total body or split program intermediate circuit When training for muscular endurance what is the intensity percentage of the one RM number of reps number of sets and rest between sets.? correct answers Less then 70% of 1RM 12-15 1-3 30secs to 1min When training for muscular strength and hypertrophy what is the intensity percentage of one RM number of reps number of sets rest between sets? correct answers 70-80% 8-12 1-4 30sec to 2min When training for muscular power and maximal strength what is the intensity percentage of one RM number of reps number of sets rest between sets? correct answers 80% - 100% 1-8 1-6 Over 2mins To develop a sound resistance training program considered principles such as correct answers Exercise selection muscle balance exercise order rest breathing speed technique Loading Chapter 6 review questions: List and describe the three types of muscle tissue correct answers Skeletal muscles are attached to bone with the long cylindrical cells that are striated or banded and arranged in parallel Cardiac muscles are change of cylindrical cells are arranged in parallel that make up the walls of the heart Smooth muscles are irregular shaped and arranged in random patterns smooth muscles make up the walls of hollow organs like the stomach intestine bladder and blood vessels Chapter 6 Review Questions: Briefly describe the significance of the core correct answers The core muscles act as stabilizers and mobilizers. A stable Cor provides the arms and legs with a solid anchor to produce force and movement for every day activities as well as fitness training Chapter 6 Review Questions: what type of muscle contraction is responsible for elbow flexion during a bicep curl? correct answers A: eccentric B: concentric C: isometric D: none of the above Answer: b Chapter 6 Review Questions: People with anterior tilt typically have tight ................... ................. and muscles correct answers A: External oblique, illiopsoas, gluteus Maximus B: Erector spinae, hamstring, external oblique C: Gluteus maximus, hamstrings, rectus Femoris D: Erector spinae, illiopsoas, rectus femoris. Answer is: D Chapter 6 Review Questions: The rotator cuff is described by the acronym SITS which stands for. correct answers A: Supraspinatus, interosseous, teres minir and Sartorius B: subcapularis, interosseous, trapezius and serratus anterior C: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis D: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, trapezius and subcapularis Answer is: c Chapter
Written for
- Institution
- CAN FIT PRO
- Course
- CAN FIT PRO
Document information
- Uploaded on
- January 24, 2024
- Number of pages
- 85
- Written in
- 2023/2024
- Type
- Exam (elaborations)
- Contains
- Questions & answers
Subjects
- can fit pro
- can fit
-
can fit pro exam prep 2024all possible
-
can fit pro exam prep 2024