Nervous System:
Mammals use both the endocrine and nervous systems to
monitor changes in their internal and external environments
and to respond to them.
The nervous system organisation:
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Motor, Relay and Sensory
Neurones.
Glial Cells (e.g. Schwann cells).
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
(CNS): SYSTEM (PNS):
Coordination, Relay Neurones, Sensory Neurones – Receptors
White Matter (Myelinated) to CNS.
and Grey Matter (Non-
Motor Neurones – CNS to
myelinated).
effector.
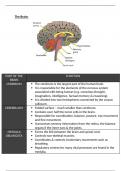
BRAIN: SPINAL CORD: AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SOMATIC NERVOUS
Cerebrum, Corpus SYSTEM: SYSTEM:
Collosum, Medulla
Involuntary, controls Voluntary, controls
Oblangata, Hypothalamus.
homeostatic mechanisms, conscious activities, and
and stimulates cardiac and stimulates skeletal
smooth muscle.
SYMPATHETIC: PARASYMPATHETIC:
Antagonistic relationship.
Mammals use both the endocrine and nervous systems to
monitor changes in their internal and external environments
and to respond to them.
The nervous system organisation:
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Motor, Relay and Sensory
Neurones.
Glial Cells (e.g. Schwann cells).
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
(CNS): SYSTEM (PNS):
Coordination, Relay Neurones, Sensory Neurones – Receptors
White Matter (Myelinated) to CNS.
and Grey Matter (Non-
Motor Neurones – CNS to
myelinated).
effector.
BRAIN: SPINAL CORD: AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SOMATIC NERVOUS
Cerebrum, Corpus SYSTEM: SYSTEM:
Collosum, Medulla
Involuntary, controls Voluntary, controls
Oblangata, Hypothalamus.
homeostatic mechanisms, conscious activities, and
and stimulates cardiac and stimulates skeletal
smooth muscle.
SYMPATHETIC: PARASYMPATHETIC:
Antagonistic relationship.