THE SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES AND SPINAL REFLEXES
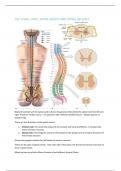
Bilateral symmetry of the spinal cord is due to the grooves that divide the spinal cord into left and
right. Posterior median sulcus – on posterior side. Anterior median fissure – deeper groove on
anterior side.
There are two branches of the spinal nerves:
1. Ventral root: this sends the output to the somatic and visceral effectors. It contains the
axons of motor neurons.
2. Dorsal root: this brings the sensory information to the spinal cord. It contains the axons of
the sensory neurons.
Dorsal root ganglia contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons.
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. One each side of the spine, the dorsal and ventral roots join to
form a spinal nerve.
Mixed nerves carry both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers.
, THE SPINAL MENINGES
The Spinal Meninges are specialized membranes isolate spinal cord from surroundings.
Functions of the spinal meninges include:
Protecting spinal cord
Carrying blood supply
Continuous with cranial meninges
Meningitis is the viral or bacterial infection of meninges. It is an infection of the membranes
surrounding the spinal cord, not of the spinal cord itself.
The three meningeal layers:
1. Dura mater
The dura mater is the layer that forms the outermost covering of the spinal cord.
2. Arachnoid mater
The arachnoid mater is the middle meningeal layer
The interlayer spaces of arachnoid mater (subarachnoid space) contain
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which carries dissolved gases, nutrients and waste.
3. Pia mater
The pia mater is the inner meningeal layer
Bilateral symmetry of the spinal cord is due to the grooves that divide the spinal cord into left and
right. Posterior median sulcus – on posterior side. Anterior median fissure – deeper groove on
anterior side.
There are two branches of the spinal nerves:
1. Ventral root: this sends the output to the somatic and visceral effectors. It contains the
axons of motor neurons.
2. Dorsal root: this brings the sensory information to the spinal cord. It contains the axons of
the sensory neurons.
Dorsal root ganglia contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons.
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. One each side of the spine, the dorsal and ventral roots join to
form a spinal nerve.
Mixed nerves carry both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers.
, THE SPINAL MENINGES
The Spinal Meninges are specialized membranes isolate spinal cord from surroundings.
Functions of the spinal meninges include:
Protecting spinal cord
Carrying blood supply
Continuous with cranial meninges
Meningitis is the viral or bacterial infection of meninges. It is an infection of the membranes
surrounding the spinal cord, not of the spinal cord itself.
The three meningeal layers:
1. Dura mater
The dura mater is the layer that forms the outermost covering of the spinal cord.
2. Arachnoid mater
The arachnoid mater is the middle meningeal layer
The interlayer spaces of arachnoid mater (subarachnoid space) contain
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which carries dissolved gases, nutrients and waste.
3. Pia mater
The pia mater is the inner meningeal layer