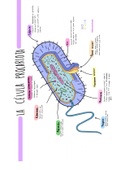
plasma membrane:
organisms:Enzymes:
interactions in living glycolip, d
O↓e80808
&
weak j
Alonic interactions
*
selectively permeable
*Biological catalyst (t reaction rare, activention
I
energy) bilayer->
6088
↳ notconsumed *
Assymetric bilayer
Nat_Cl
non-polar (hydrophobic) ↓
*
Hydrogen bonds * Alternative
pathway ofr eaction
cholesterol phospholipids Integral
non... *Inhibitors
enzymatic activity ........... proteins
to"
↳ reversible 4 Iuriversible 11
van der Waals
*
-
competitive:bind on active site exclusively
n
↑
* Fluidity:
-non-competitive (pure/mixed):binds close to active aucro
SFICC....FICs- - and unsaturated:
fatty
-
silt a affects affinity to substrate (mixed), binds far ---- i
finding
- -
↑
"pait'
-
Hydrophobic interactione
A from active site a changes enzyme conformation -
·
-n fluidity
-temp.
↑
H20 20 He0
1284,0
-
uncompetitive:Binds to enzyme-substrate complex ↑
cholesterol: fundity
polar (hydrophinc
A
⑲ ⑲ preventing reaction
He
no organic compounds:↑ fluidity
-
-
-
notab XAllosteric enzymes (activate or inhibitenzyme kinetics) -
pH changes:d enature proteins
n e e
passive membrane transport: MitosIS (eukaryotes)
proteins Binary fission (procaryotic): diploid cell
-> 2
①interphase
nic- R NHz
stage
-
C- simple ① B period:cell growth
-
G1 function a growth
* -
DiffUSIOn:
*
⑦ ( period:DNA replication and
-
20atPresentin non-essentine
-
No AN ③ D period:cell division Some stage
cellsgot
-
from high to low gradient 1.
Prophase: ↑ replication
S-DNA
*
-forms peptide bonds between each other * OSMOSIS: chromosomes condense
↳
46.13 phase checkpointchecks Ifcell
-
Structures: -centrosomes more to polar opposites a
ATP replicate. Itdoesn'tpass, then cell fixes
-
-
NO can
make spindles.
x
primary:Arsequence
t ofp eptide bands a function, prep.
*G2+ continues growth
only nucleus dissolving stops proteinsuntnesss
-
-water
x
secondary:a helix/ppleated sheet- > H bands for ceu division
xTertiary:3D bonds, lonic, discufide
-from high to low gradien 2. Prometaphase:
H
-
bridges ·
nucleus cssolves ② MitoSIS
* Quaternary:multiple polypeptides facilitated -microtubules attach to kinetochore ↳62 Checkpointc hecks ifCell Is ready. If
doesn'tpass then apoptosis.
BNA: need
x channel proteins (e.g. glucose)
3. MetaPhASS:
i n middle
chromosomes line ③ CytokineSIS splitting ofc ytoplasm
-
-
Active membrane transport
4. Anaphase: Furrowing (animals
8 juucleotide
↳
base-
need
* ATP puned apart
chromatic
sister ↳ cell plate formaten (plant)
-
Purine (2 rings):Adenine a guanine from
* high
low to gradient 5. TelOPHese: ↳ vesicles in middle fuse forming
new cell wall a separate.
pyramidine(Iring):thy mine (DNA), cytosine, chromosomes unfold
Primary:Rurp changes snake
-
wrd(I) (RNA)
nucleus formed
secondary:cotransport/exchanger
-
-
cytoplasm collapse in middle.
the
carbohydrates:
ExOcytOSIS G endocytosis
CHO triphosphate
Adenosine ofoxygen
oxidation:Losing ele Grons/gain
energy storage ofenergy electrons/loss ofoxygen
reduction:gaining
CH2OH
meiosis: - 4
haploid cens
CHON bond
on ester
CH,z06 602 602 6H20
+
xyH
+
=
H
In
-
H
In MelOSIS I 0
bXOH "H
-
I I 1 adenine
Kor nor prophase I:condensation, synapse a triphosphate oxidised reduced
OH
ou 1 ou on *
L -
n
recombination ofh omologous pairs pentose
-
en CGH,z0g 602 6202 6Hz0+ ATP
+
-
sugar
+
a que B glucose A prometaphase 1:nucleus gone, spindles
attach to centrioles ofpairs cellular respiration:
condensation CH20H CH20H Anhydride a ester bond hydrolysis
CHOH
CH2OH
⑦ GlyCOlYSIS (mutoplasm)
H -oXxyH
" H ->
H
In
- H
In metaphase 1:each homologous pair in middle
releases energy.
IH
H
In H
In
bX- -
*
nor Kor nor bXOH H20
+
i OH i
② pyruvat oxidation a t r i c and cucle (matrix
:. . .
+
OH
Anaphase
* 1:pairs separat
on
Is .
. OH I Is InI Is ofm itochondrial
hydrolys"i 1
-
H
Telophase
*
cytokinesis oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondrian
③
.
H H
+
owner membrane
quycosidic band
7
② meiosis replications
(inner
2 no DNA membrane membrane
camellar
a glucose,
guscogen: 1-441-6 grycosidic bands A prophase 2:centrioles more r
GlycolySIS:2ATP, NADH, 2 pyruvates, H, O
!
-> branched
cenlose:i
glucose, bands
*metaphase 2:Chromosomes wine middle, Hexokinase
I-4 glycosidic ① Glucose -glucose-6-phosphate(20p)
↳> unbranched
microtubules attach
AREDP
chromatics
*Anaphase 2:Sister separate u
staron:a glucose E - C ② GGP pnosonogiacomutace, FN Cose-s-phosphate (FGP(
in strumen
A
Telophase 2 cytokinesis:cells separate ③ FGp Phosphofructokinase, Fructose-1, 6-bIphosphate(FI6B)
+
x amylose:1-4
glycosidic bands, unbranced
Pamylopecht:1-491-6 glycosidic bands, branched
grenum
grassic (lu n cuclel ④ FIS a cP+ dihydronyacetone
phosphate (DP)
photosynthesis slightreactions
Lipid 3 H
6C02 GH20 + +
C6,206 602
+
⑤DP
trosephosphate isomerase
- CP
HO- 's ⑥
GPogen-bisphosphogue
8
H
Photolysis ofH 20:
-
WV"- onsaturated I
x o n thylakoid:
Photosstern (13BP)
antenna complex
HO -
C -
H
photore I
1
H20 -> 2H
+
2e+ 013BP -3phosphoquecerate (3P)
Kinase
Mid-OH
02
+
⑬Torimapio
HO-C H AbAT
unsaturatea ~
-
-
go ⑧
e
/
3pmae ephosphoglycerate (2P)
H UV
⑨ 2P
enclase
- PEP
F1z0
Prokaryotic cells:
Eukaryotic cers: 8 ⑩ PEP - >
S
Kinase
pyruvate
ATP
* unisemlar A nucleus with linear DNA ADP
*
contains nucleotidfnucleus *
specialised organelles Pyruvate oxidation: I CO2, 2 NADH
-
as
NAD
circular DNA COA.SH
*
(ATP)
Mitochondria
private an
*
2 pyruvate "AceMICan-2CO2
x cell we(Peptidoglycan) +Capsyl H20 02 +Ht
xcytoskeleton (movement,
-
complex
x Flagena/bili (movements share, support ( I photon excites small pigments GP
in anternal complex. Transfers to chlorophy. citric cycle:2CO2, 3NADH, I FADHe,
*no mitochondria ↳ microfilaments, ② Chlorophyll oxidises 120 accepting e-passing to primary e-acceptor.
↳use plasma membrane to make ATP intermediate filaments,
mes.
microthy ③ e-passed down e-acceptors inside lumen. Htcons. Increases.
plant photosystem 14 excreated to make
NADPH
④
e-reaches
vacuole with tonoplast membrane (support, structures Atp. Enters calvin
Hexits through AtPCyntase, making cycle
⑤
-
chlorophyll (photosynthesis)
-chloroplasts with
cell well made of cost A Calvin Cycle: ~rubisco
① Fixation:3CO2 +3 RuP-3-phosphoglycerate
Animal
-
3-phosphoglycerate + 3ATP-> 1,3-biphosphoglycereut + ADP
-centrioles release microtubules to separate chromosomes
② Reduction: 1,3-biphosphoglycereut GNADPH +
->
66P 6NAD+ 6Pi+
-cysosomes during MIOSIS
41,pexcess so removed to
make (H,,00. oxidative phosphorylation:4CO2+38ATP
viruses:
③ Regeneration:56, P +
3AP 3RUBP+ADP
-
*InFeCOUS
*neel hostc ell to reproduce:
⑦ into hostcell
fermentation:cutosol
3
Entry Lactate
goes i t
② insection ofg enetic material - to
NADH NAD+ quycolysis
cytic
③ Replication pyruvate
w
- > Lactate
make At
4)Assembly a LysIs
Alcohol fermentation (yeast):
⑦ Entry
I
i n t o hostcell
② Insection ofgentic material pyruvent acetylcudenyce ->
exhylalcoro
③ Integration ofV irus DNAGHOSTDNALysogenic only in bacterin NANADA
CO2
glycolySIS citric and oxidation
④cell replicates
-> goes into
cycle is an
make
to ATP
⑤)
virus reproductionalysis a decomposition reaction
organisms:Enzymes:
interactions in living glycolip, d
O↓e80808
&
weak j
Alonic interactions
*
selectively permeable
*Biological catalyst (t reaction rare, activention
I
energy) bilayer->
6088
↳ notconsumed *
Assymetric bilayer
Nat_Cl
non-polar (hydrophobic) ↓
*
Hydrogen bonds * Alternative
pathway ofr eaction
cholesterol phospholipids Integral
non... *Inhibitors
enzymatic activity ........... proteins
to"
↳ reversible 4 Iuriversible 11
van der Waals
*
-
competitive:bind on active site exclusively
n
↑
* Fluidity:
-non-competitive (pure/mixed):binds close to active aucro
SFICC....FICs- - and unsaturated:
fatty
-
silt a affects affinity to substrate (mixed), binds far ---- i
finding
- -
↑
"pait'
-
Hydrophobic interactione
A from active site a changes enzyme conformation -
·
-n fluidity
-temp.
↑
H20 20 He0
1284,0
-
uncompetitive:Binds to enzyme-substrate complex ↑
cholesterol: fundity
polar (hydrophinc
A
⑲ ⑲ preventing reaction
He
no organic compounds:↑ fluidity
-
-
-
notab XAllosteric enzymes (activate or inhibitenzyme kinetics) -
pH changes:d enature proteins
n e e
passive membrane transport: MitosIS (eukaryotes)
proteins Binary fission (procaryotic): diploid cell
-> 2
①interphase
nic- R NHz
stage
-
C- simple ① B period:cell growth
-
G1 function a growth
* -
DiffUSIOn:
*
⑦ ( period:DNA replication and
-
20atPresentin non-essentine
-
No AN ③ D period:cell division Some stage
cellsgot
-
from high to low gradient 1.
Prophase: ↑ replication
S-DNA
*
-forms peptide bonds between each other * OSMOSIS: chromosomes condense
↳
46.13 phase checkpointchecks Ifcell
-
Structures: -centrosomes more to polar opposites a
ATP replicate. Itdoesn'tpass, then cell fixes
-
-
NO can
make spindles.
x
primary:Arsequence
t ofp eptide bands a function, prep.
*G2+ continues growth
only nucleus dissolving stops proteinsuntnesss
-
-water
x
secondary:a helix/ppleated sheet- > H bands for ceu division
xTertiary:3D bonds, lonic, discufide
-from high to low gradien 2. Prometaphase:
H
-
bridges ·
nucleus cssolves ② MitoSIS
* Quaternary:multiple polypeptides facilitated -microtubules attach to kinetochore ↳62 Checkpointc hecks ifCell Is ready. If
doesn'tpass then apoptosis.
BNA: need
x channel proteins (e.g. glucose)
3. MetaPhASS:
i n middle
chromosomes line ③ CytokineSIS splitting ofc ytoplasm
-
-
Active membrane transport
4. Anaphase: Furrowing (animals
8 juucleotide
↳
base-
need
* ATP puned apart
chromatic
sister ↳ cell plate formaten (plant)
-
Purine (2 rings):Adenine a guanine from
* high
low to gradient 5. TelOPHese: ↳ vesicles in middle fuse forming
new cell wall a separate.
pyramidine(Iring):thy mine (DNA), cytosine, chromosomes unfold
Primary:Rurp changes snake
-
wrd(I) (RNA)
nucleus formed
secondary:cotransport/exchanger
-
-
cytoplasm collapse in middle.
the
carbohydrates:
ExOcytOSIS G endocytosis
CHO triphosphate
Adenosine ofoxygen
oxidation:Losing ele Grons/gain
energy storage ofenergy electrons/loss ofoxygen
reduction:gaining
CH2OH
meiosis: - 4
haploid cens
CHON bond
on ester
CH,z06 602 602 6H20
+
xyH
+
=
H
In
-
H
In MelOSIS I 0
bXOH "H
-
I I 1 adenine
Kor nor prophase I:condensation, synapse a triphosphate oxidised reduced
OH
ou 1 ou on *
L -
n
recombination ofh omologous pairs pentose
-
en CGH,z0g 602 6202 6Hz0+ ATP
+
-
sugar
+
a que B glucose A prometaphase 1:nucleus gone, spindles
attach to centrioles ofpairs cellular respiration:
condensation CH20H CH20H Anhydride a ester bond hydrolysis
CHOH
CH2OH
⑦ GlyCOlYSIS (mutoplasm)
H -oXxyH
" H ->
H
In
- H
In metaphase 1:each homologous pair in middle
releases energy.
IH
H
In H
In
bX- -
*
nor Kor nor bXOH H20
+
i OH i
② pyruvat oxidation a t r i c and cucle (matrix
:. . .
+
OH
Anaphase
* 1:pairs separat
on
Is .
. OH I Is InI Is ofm itochondrial
hydrolys"i 1
-
H
Telophase
*
cytokinesis oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondrian
③
.
H H
+
owner membrane
quycosidic band
7
② meiosis replications
(inner
2 no DNA membrane membrane
camellar
a glucose,
guscogen: 1-441-6 grycosidic bands A prophase 2:centrioles more r
GlycolySIS:2ATP, NADH, 2 pyruvates, H, O
!
-> branched
cenlose:i
glucose, bands
*metaphase 2:Chromosomes wine middle, Hexokinase
I-4 glycosidic ① Glucose -glucose-6-phosphate(20p)
↳> unbranched
microtubules attach
AREDP
chromatics
*Anaphase 2:Sister separate u
staron:a glucose E - C ② GGP pnosonogiacomutace, FN Cose-s-phosphate (FGP(
in strumen
A
Telophase 2 cytokinesis:cells separate ③ FGp Phosphofructokinase, Fructose-1, 6-bIphosphate(FI6B)
+
x amylose:1-4
glycosidic bands, unbranced
Pamylopecht:1-491-6 glycosidic bands, branched
grenum
grassic (lu n cuclel ④ FIS a cP+ dihydronyacetone
phosphate (DP)
photosynthesis slightreactions
Lipid 3 H
6C02 GH20 + +
C6,206 602
+
⑤DP
trosephosphate isomerase
- CP
HO- 's ⑥
GPogen-bisphosphogue
8
H
Photolysis ofH 20:
-
WV"- onsaturated I
x o n thylakoid:
Photosstern (13BP)
antenna complex
HO -
C -
H
photore I
1
H20 -> 2H
+
2e+ 013BP -3phosphoquecerate (3P)
Kinase
Mid-OH
02
+
⑬Torimapio
HO-C H AbAT
unsaturatea ~
-
-
go ⑧
e
/
3pmae ephosphoglycerate (2P)
H UV
⑨ 2P
enclase
- PEP
F1z0
Prokaryotic cells:
Eukaryotic cers: 8 ⑩ PEP - >
S
Kinase
pyruvate
ATP
* unisemlar A nucleus with linear DNA ADP
*
contains nucleotidfnucleus *
specialised organelles Pyruvate oxidation: I CO2, 2 NADH
-
as
NAD
circular DNA COA.SH
*
(ATP)
Mitochondria
private an
*
2 pyruvate "AceMICan-2CO2
x cell we(Peptidoglycan) +Capsyl H20 02 +Ht
xcytoskeleton (movement,
-
complex
x Flagena/bili (movements share, support ( I photon excites small pigments GP
in anternal complex. Transfers to chlorophy. citric cycle:2CO2, 3NADH, I FADHe,
*no mitochondria ↳ microfilaments, ② Chlorophyll oxidises 120 accepting e-passing to primary e-acceptor.
↳use plasma membrane to make ATP intermediate filaments,
mes.
microthy ③ e-passed down e-acceptors inside lumen. Htcons. Increases.
plant photosystem 14 excreated to make
NADPH
④
e-reaches
vacuole with tonoplast membrane (support, structures Atp. Enters calvin
Hexits through AtPCyntase, making cycle
⑤
-
chlorophyll (photosynthesis)
-chloroplasts with
cell well made of cost A Calvin Cycle: ~rubisco
① Fixation:3CO2 +3 RuP-3-phosphoglycerate
Animal
-
3-phosphoglycerate + 3ATP-> 1,3-biphosphoglycereut + ADP
-centrioles release microtubules to separate chromosomes
② Reduction: 1,3-biphosphoglycereut GNADPH +
->
66P 6NAD+ 6Pi+
-cysosomes during MIOSIS
41,pexcess so removed to
make (H,,00. oxidative phosphorylation:4CO2+38ATP
viruses:
③ Regeneration:56, P +
3AP 3RUBP+ADP
-
*InFeCOUS
*neel hostc ell to reproduce:
⑦ into hostcell
fermentation:cutosol
3
Entry Lactate
goes i t
② insection ofg enetic material - to
NADH NAD+ quycolysis
cytic
③ Replication pyruvate
w
- > Lactate
make At
4)Assembly a LysIs
Alcohol fermentation (yeast):
⑦ Entry
I
i n t o hostcell
② Insection ofgentic material pyruvent acetylcudenyce ->
exhylalcoro
③ Integration ofV irus DNAGHOSTDNALysogenic only in bacterin NANADA
CO2
glycolySIS citric and oxidation
④cell replicates
-> goes into
cycle is an
make
to ATP
⑤)
virus reproductionalysis a decomposition reaction