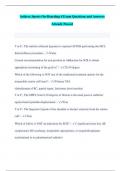
The reactivity series
• Metal + oxygen ~ metal oxide
• Metal + wate r~ metal hydroxide + hydrogen
• Metal + acid ~ salt + hydrogen
• When an element in group 1 takes part in a reaction, its atoms lose their
outer electron and form a positively charged ion. The more easily these
'
positive ions form, the more reactive the metal is.
• Group 1 elements reactivity increases as you go down the group
because:
o The atoms become larger as the outer electron is placed further
from the nucleus and the force of attraction between the nucleus
and the outer electron decreases, so the outer electron can be
lost easily.
(Methods of these tests are in science folder)
Metals reacting with oxygen
Most metal in ores are chemically bonded to other elements in compounds.
These metals have been oxidised (gained oxygen) by the oxygen in the air to
form their oxides. To extract the metals from their oxides, the metal oxide must
be reduced (lose oxygen).
Iron + oxygen ~ iron oxide
• The product has a larger mass as the metals react with oxygen
(conservation of mass).
Element Type Reaction type Oxide Nature
Highly exotherm ic - magnesium Magnesi um oxide, MgO - solid
Magnesium Metal Basic
burns with bright white flame white powder
Non- Exothermic - carbon glows orange Carbon dioxide, CO2 -
Carbon Acidic
metal when heated strongly colourless gas with no odour
Sulfur dioxide, 502 -
Non- colourless gas with choking Acidic
Sulfur Burns slowly with a blue flame
metal smell
• Metal + oxygen ~ metal oxide
• Metal + wate r~ metal hydroxide + hydrogen
• Metal + acid ~ salt + hydrogen
• When an element in group 1 takes part in a reaction, its atoms lose their
outer electron and form a positively charged ion. The more easily these
'
positive ions form, the more reactive the metal is.
• Group 1 elements reactivity increases as you go down the group
because:
o The atoms become larger as the outer electron is placed further
from the nucleus and the force of attraction between the nucleus
and the outer electron decreases, so the outer electron can be
lost easily.
(Methods of these tests are in science folder)
Metals reacting with oxygen
Most metal in ores are chemically bonded to other elements in compounds.
These metals have been oxidised (gained oxygen) by the oxygen in the air to
form their oxides. To extract the metals from their oxides, the metal oxide must
be reduced (lose oxygen).
Iron + oxygen ~ iron oxide
• The product has a larger mass as the metals react with oxygen
(conservation of mass).
Element Type Reaction type Oxide Nature
Highly exotherm ic - magnesium Magnesi um oxide, MgO - solid
Magnesium Metal Basic
burns with bright white flame white powder
Non- Exothermic - carbon glows orange Carbon dioxide, CO2 -
Carbon Acidic
metal when heated strongly colourless gas with no odour
Sulfur dioxide, 502 -
Non- colourless gas with choking Acidic
Sulfur Burns slowly with a blue flame
metal smell