ATLS Practice Test 2 Answers & Explanations | 2022 latest update
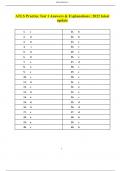
ATLS Practice Test 2 Answers & Explanations | 2022 latest update 1. d. 21. e. 2. a. 22. c. 3. c. 23. d. 4. d. 24. d. 5. e. 25. d. 6. a. 26. b. 7. c. 27. c. 8. b. 28. b. 9. b. 29. d. 10. d. 30. c. 11. c. 31. d. 12. d. 32. b. 13. b. 33. d. 14. a. 34. c. 15. d. 35. a. 16. e. 36. e. 17. c. 37. d. 18. c. 38. c. 19. c. 39. a. 20. e. 40. d. d. The patient has taken a turn for the worse. He is in shock. It is imperative that you now repeat the primary survey, going through the ABCDE’s, in an effort to stabilize the patient prior to transfer. Questions that need to be answered include: Is the airway compromised? Is breathing compromised? Is the patient bleeding from elsewhere besides the chest? And so forth. Once relatively stable, the transfer should proceed because the patient will certainly need surgical intervention emergently. Note: Clamping the chest tube will not stop any hemorrhage in the chest, and would probably only impair breathing. a. Traumatic brain injuries tend to cause increased intracranial pressure (ICP) due to bleeding and swelling. In order to prevent secondary brain injury, it is important to maintain normal cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP). CPP = MAP – ICP. If the MAP is too low, ischemia and infarction will result. Therefore, hypotension must be avoided. Note: Administering an osmotic diuretic, such as mannitol, is an intervention reserved for when ICP is dangerously high; giving it inappropriately may lower the blood pressure too much . c. The pliability, or compliance, of a child’s chest wall allows impacting forces to be transmitted to the underlying pulmonary parenchyma, causing a pulmonary contusion. Rib fractures and mediastinal injuries are not common. Therefore, a pulmonary contusion may be present in the absence of rib fractures. d. This patient requires an airway and assisted ventilation immediately. Bagmask ventilation is not effective. A cspine injury must be assumed. Therefore, one member of the trauma team should manually stabilize the patient’s head and neck using inline immobilization techniques while another member of the trauma team intubates him. e. The presentation is that of neurogenic shock. The only correct choice is e., which is the presentation of spinal shock. Neurogenic shock results from impairment of the descending sympathetic pathways in the cervical or upper thoracic spinal cord. This condition results in the loss of vasomotor tone and sympathetic stimulation to the heart. Loss of vasomotor tone causes vasodilation of visceral and lowerextremity blood vessels, pooling of blood, and, consequently, hypotension. Loss of sympathetic innervation to the heart may cause the development of bradycardia, or at least a failure of tachycardia in response to hypovolemia. In this condition, the blood pressure may not be restored by fluid infusion alone, and massive fluid resuscitation may result in fluid overload and pulmonary edema. The blood pressure may often be restored by the judicious use of vasopressors after moderate volume replacement. Atropine may be used to counteract hemodynamically significant bradycardia. Spinal shock refers to the flaccidity (loss of muscle tone) and loss of reflexes seen after spinal cord injury. The “shock” to the injured cord may make it appear completely nonfunctional, although the cord may not necessarily be destroyed. The duration of this state is variable. a. Of the choices, only choice a. is a contraindication to tetanus toxoid. c. This patient is hemorrhaging from his aorta and spleen. The most important intervention at this point is laparotomy and stopping the hemorrhage. Simultaneously, packed red cells and possibly other blood products should be transfused; however, this is not as important as stopping the bleeding. b. Leakage of amniotic fluid indicates that there is rupture of the membranes. As well as indicating trauma to the mother and fetus, it may cause induction of labor, and increase the risk of maternal and neonatal infection. In such a circumstance, labor may have to be induced artificially. Hospital admission is indicated. b. carboxyhemoglobin level 10% is an indication of inhalation injury. The other choices are correct.
Written for
- Institution
- ATLS
- Course
- ATLS
Document information
- Uploaded on
- July 10, 2023
- Number of pages
- 8
- Written in
- 2022/2023
- Type
- Exam (elaborations)
- Contains
- Questions & answers
Subjects
-
atls practice test 2 answers amp explanations | 202