JAVA
JAVA: Java is a high level programming language developed by Sun Microsystems.
James Gosling started Java Language project in 1991.Initial name of java was Oak which
was a tree outside his office.Then it was changed to Green & finally Java.The first JDK
was released in jan 23,1996 called JDK1.0.It promised Write Once Run Anywhere
(WORA).
Then ORACLE bought sun Microsystems in jan 27,2010.So Java is now owned
by ORACLE.Recently JDK 15 is released on sep 15,2020.
Features:
i) Platform Independent (Any OS using JVM)
ii) Object Oriented
iii) Robust
iv) Architectural Neutral (Multiple Processors support same Java code)
v) Portable (WORA)
vi) Modularity
vii) Simple & Secure
Categories:
i) JSE ( Java Standard Edition) : Desktop Applications (Core Java)
ii) JEE (Java Enterprise Edition): Web Applications (Advance Java)
iii) JME( Java Micro Edition) : Mobile devices
1
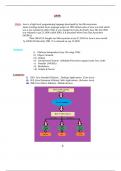
,1.) OOPS: OOPs is a concept by which a we can develop applications.
i) Features: COPIE AMM.
C= Class
O= Object
P= Polymorphism
I=Inheritance
E= Encapsulation
A=Abstarction
M= Message Passing
M= Modularity
ii) Benefits: Reusability (Inheritance)
Modularity (Break & then integrate)
Scability
Rapid Applications Development (RAD)
2.) Programming Languages:
i) NRO ( Non Related to OOPS) : C, PASCAL
ii) RTO ( Related to OOPS) :
a.) OBPL ( Object based Programming Language) : Polymorphism is supported partially.
eg. Java Script
b.) OOPL ( Object Oriented Programming Language) : Polymorhphism is supported fully.
eg. Java , c#.
2
, CLASS
Class: Class is a “non-Primitive” data type.It is a design or a blue print by which we can
create a set of homogeneous objects.Class is used to describe the “type” and “behaviour”
of an object.Classes are of two types
i) Pre-defined Classes : * System Class
* Scanner Class
* String Class
* Random Class
* Arrays Class
* File Class
ii) User-defined Classes : defined by user
Classification:
i) Variables : (data members)
ii) Methods : (behaviour,functions)
iii) Constructors (no argument,parameterized)
VARIABLES
Variable: A variable is a name given to a memory location.Different types of variables are used
to store different values depending upon their size.eg.byte,short,int,long,float,double
char,boolean.All of these are basic or primitive data types.
i) byte - 1B
ii) short - 2B
iii) int - 4B
iv) long - 8B ( eg. 4L )
v) float - 4B ( eg. 3.8 f )
vi) double - 8B ( eg. 3.8 )
vii) char - 2B
viii) boolean - 1 bit
3
, i) Local Variables : (inside a method) - These are blanked,so these must be initialized
before use.These are created when a method is called & destroyed
when exited.
ii) Non- Static Variables : (inside a class/outside a method ) - These are not blanked.
These have a default value depends upon their data-type.So
we don't need to initialize them as in local variables.We need to
create objects to access these variables.These are created when
an object is created & destroyed when the object is destroyed.
One copy of these variables is created by JVM per object.
These are also called “Instance” variables.
iii) Static variables : (inside a class/outside a method ) - These are declared with “static”
keyword.We don't need to create objects to access these variables
because these are accessed with the name of class.These are created
at the start of the execution of a program & destroyed at the end of
the execution of a program.These are also called “Class” variables.
OBJECTS
Object: Object is a memory allocation which is allocated during run time inside a heap.Heap is a
part of JVM.Address of this object is called Reference ID and to refer this memory
allocation we assign a name .
Objects are products of the classes as the class is just a design or blue print of these
objects.
ARRAY
Array: Array is a data-structure and all elements of an array are indexed. It is a group of
homogeneous data types as a single entity.Index and size of an array is always of int type.
Size of an array should be greater than 0 always .When size of an array is zero,loop does't
run because condition fails. For a zero size of an array there will be no indexing. The
application will be crashed if the size is negative.
Benefits:
i.) Huge storage of data
ii.) Random access of data using indexing
Limitations:
i.) Fixed size
ii.) Same type of data
4
JAVA: Java is a high level programming language developed by Sun Microsystems.
James Gosling started Java Language project in 1991.Initial name of java was Oak which
was a tree outside his office.Then it was changed to Green & finally Java.The first JDK
was released in jan 23,1996 called JDK1.0.It promised Write Once Run Anywhere
(WORA).
Then ORACLE bought sun Microsystems in jan 27,2010.So Java is now owned
by ORACLE.Recently JDK 15 is released on sep 15,2020.
Features:
i) Platform Independent (Any OS using JVM)
ii) Object Oriented
iii) Robust
iv) Architectural Neutral (Multiple Processors support same Java code)
v) Portable (WORA)
vi) Modularity
vii) Simple & Secure
Categories:
i) JSE ( Java Standard Edition) : Desktop Applications (Core Java)
ii) JEE (Java Enterprise Edition): Web Applications (Advance Java)
iii) JME( Java Micro Edition) : Mobile devices
1
,1.) OOPS: OOPs is a concept by which a we can develop applications.
i) Features: COPIE AMM.
C= Class
O= Object
P= Polymorphism
I=Inheritance
E= Encapsulation
A=Abstarction
M= Message Passing
M= Modularity
ii) Benefits: Reusability (Inheritance)
Modularity (Break & then integrate)
Scability
Rapid Applications Development (RAD)
2.) Programming Languages:
i) NRO ( Non Related to OOPS) : C, PASCAL
ii) RTO ( Related to OOPS) :
a.) OBPL ( Object based Programming Language) : Polymorphism is supported partially.
eg. Java Script
b.) OOPL ( Object Oriented Programming Language) : Polymorhphism is supported fully.
eg. Java , c#.
2
, CLASS
Class: Class is a “non-Primitive” data type.It is a design or a blue print by which we can
create a set of homogeneous objects.Class is used to describe the “type” and “behaviour”
of an object.Classes are of two types
i) Pre-defined Classes : * System Class
* Scanner Class
* String Class
* Random Class
* Arrays Class
* File Class
ii) User-defined Classes : defined by user
Classification:
i) Variables : (data members)
ii) Methods : (behaviour,functions)
iii) Constructors (no argument,parameterized)
VARIABLES
Variable: A variable is a name given to a memory location.Different types of variables are used
to store different values depending upon their size.eg.byte,short,int,long,float,double
char,boolean.All of these are basic or primitive data types.
i) byte - 1B
ii) short - 2B
iii) int - 4B
iv) long - 8B ( eg. 4L )
v) float - 4B ( eg. 3.8 f )
vi) double - 8B ( eg. 3.8 )
vii) char - 2B
viii) boolean - 1 bit
3
, i) Local Variables : (inside a method) - These are blanked,so these must be initialized
before use.These are created when a method is called & destroyed
when exited.
ii) Non- Static Variables : (inside a class/outside a method ) - These are not blanked.
These have a default value depends upon their data-type.So
we don't need to initialize them as in local variables.We need to
create objects to access these variables.These are created when
an object is created & destroyed when the object is destroyed.
One copy of these variables is created by JVM per object.
These are also called “Instance” variables.
iii) Static variables : (inside a class/outside a method ) - These are declared with “static”
keyword.We don't need to create objects to access these variables
because these are accessed with the name of class.These are created
at the start of the execution of a program & destroyed at the end of
the execution of a program.These are also called “Class” variables.
OBJECTS
Object: Object is a memory allocation which is allocated during run time inside a heap.Heap is a
part of JVM.Address of this object is called Reference ID and to refer this memory
allocation we assign a name .
Objects are products of the classes as the class is just a design or blue print of these
objects.
ARRAY
Array: Array is a data-structure and all elements of an array are indexed. It is a group of
homogeneous data types as a single entity.Index and size of an array is always of int type.
Size of an array should be greater than 0 always .When size of an array is zero,loop does't
run because condition fails. For a zero size of an array there will be no indexing. The
application will be crashed if the size is negative.
Benefits:
i.) Huge storage of data
ii.) Random access of data using indexing
Limitations:
i.) Fixed size
ii.) Same type of data
4