Failure
Heart
Causes:
HF
and AF heavily linked both Cardiomyopathy
are
commonly causing the other.
· -
-
Coronary syndromes
-
Heart Failure Cardiac outputinsufficient for metabolic demand. AF-M1 HTN
- -
-
half of patients die within few
Very
·
poor prognosis, years.
·
Can be a result excessive
of Pre/Afterload, or
pump failure (systolic or Diastolic).
Systolic Failure: impaired contraction. Poor cardiac output, Ejection fraction 40%. CHFEE).
Causes:IHD, M1, cardiomyopathy.
·
Diastolic Failure:impaired relaxation. Poor ventricle filling, EF preserved (HFPEE).
Causes:ventricular
hypertrophy, obesity, Constrictive Pericarditis, Tamponade/effusion.
·
Congestive Heart Failure:combo of Right / Left-sided HF.
RVF
Symptoms: LVE
Symptoms:
Raised JVP, RV heave. Postural
Pulmonary Hypertension Hypotension
- -
-
Peripheral oedema Resting/exercise Dyspnoea, Orthopnoea
- -
Ascites Cyanosis
-
-
Cold peripheries
fatigue
-
-
fatigue
-
Diagnosis:
ECG:any abnormality, especially (V hypertrophy.
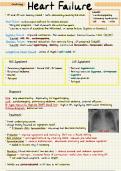
CXR:cardiomegaly, pulmonary oedema, Interstitial edema, pleural effusion.
B-type Naturitic Peptide (BNP) blood test:high in HF, signifying ventricular stretching.
Erdiogram:definitive test.
Treatment:
·
treat
underlying cause.
focused relief.
drugs mostly symptom
·
on
B-blockers, ACEi, Spironolactone -
only drugs that decrease mortality.
HF CXR
B-blocker improve symptoms mortality. and Don't setting.
in Acute
-
use
-
inhibitor
ACE antihypertensive by inhibiting RAAS, reduces pre/afterload
-
e
Spironolactone inhibits aldosterone, decreases mortality and redema symptom
-
-
added to Diuretic if
only necessary.
Diuretic/fluid restriction/low salt diet reduce preload and redema symptom
-
-
force contraction. Useful when there is
Digoxin inotropic, increases
coexisting AF.
-
of
notused much works in HEpEE.
anymore,
·
NSAIDs are contraindicated in HE due to Nat retention.