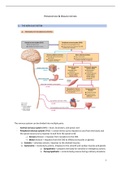
1. THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
a. DIVISION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
The nervous system can be divided into multiple parts:
- Central nervous system (CNS) = brain, brainstem, and spinal cord
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = cranial nerves (carry impulses to and from the brain) and
the spinal nerves (carry impulses to and from the spinal cord)
→ Sensory division = impulses from receptors to the CNS
→ Motor division = impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands)
↘ Somatic = voluntary actions. Impulses to the skeletal muscles.
↘ Autonomic = involuntary actions. Impulses to the smooth and cardiac muscles and glands.
↘ Sympathetic = prepares the body for stressful or emergency actions.
↘ Parasympathetic = controls body process during ordinary situations.
1
,Sympathetic
- Anatomy: they are coming from the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae.
- Preganglionic nerves are very short and the postganglionic are very long.
- Function: catabolic, action, fight, and flight reactions.
- Pharmacology: uses noradrenalin as a neurotransmitter that is released by the post-ganglionic
neurons.
Parasympathetic
- Anatomy: bulbo (III, VII, IX, X) - brainstem and sacral (little vertebrae at the end of the spinal
cord)
- Preganglionic nerves (vagal nerves). On the end/target organs, there are small ganglia.
- Function: anabolic, rest and digest.
- Pharmacology: uses acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter that is released by the post-ganglionic
neurons.
2
, b. NEUROTRANSMITTERS IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Somatic (motor neurons) = It comes from the brain and thanks to action potential it directly goes to
the neurons where acetylcholine is released.
Parasympathetic (to gut, heart and lungs) = long preganglionic and short postganglionic. Primary
neurotransmitter = acetylcholine. It then stimulates the postganglionic nerves that also released
acetylcholine. There are receptors for neurotransmitters on the organs that will respond.
Sympathetic = two methods:
- To adrenal medulla (on the top of kidney): by stimulating these glands using acetylcholine, it
releases adrenalin (80 – 90%) or noradrenalin (10 – 20%) into the blood.
- Neuronal communication using a two-neuron chain:
• Preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine. Postganglionic neurons release either
noradrenalin (sweat gland) or acetylcholine (vessels, heart, and lungs)
c. RECEPTORS
Cholinergic system
Agonists:
- Acetylcholine = endogenous agonist that binds and activates both nicotine and muscarine
receptors.
- Nicotine = exogenous agonist that only binds and activates nicotine receptors.
- Muscarine = exogenous agonist that only binds and activates muscarine receptors.
Antagonist = a drug that binds to receptors and blocks their response.
Adrenergic system
Agonists:
- Noradrenaline = endogenous agonist that binds on alpha receptors (α1 and α2)
- Adrenaline = endogenous agonist that binds on beta receptors (β1, β2 and β3)
- Synthetic agonists = salbutamol (short-acting β2-agonist) and salmeterol (long-acting β2-
agonist). They are produced with a very similar structure to the natural one.
Antagonist = there are many drugs that bind to a specific receptor to block its response.
3
, d. ANS AND HEART
Parasympathetic nerve (vagal nerve) = travels the preganglionic to the heart and then the very small
postganglionic to the SA node (acetylcholine) and the AV node (noradrenaline). It doesn’t travel to the
ventricular myocardium. It only stays in the upper part of the heart.
Sympathetic nerve = acetylcholine is released until ganglia. It triggers the postganglionic nerve that
releases noradrenaline that travels to the SA node, the AV node and the ventricular myocardium.
Effects
SYMPATHETIC PARASYMPATHETIC
CRONOTROPIC (frequency) +++ ---
DROMOTROPIC (conduction) ++ --
INOTROPIC (force) ++ /
LUSITROPIC (relaxation) ++ /
e. SYMPATHETIC NERVES ON BLOOD VESSELS
- Blood vessels only have sympathetic nerves. They don’t have parasympathetic nerves.
- The sympathetic fibres do not end in a single synapse. There are multiple ones. If an action
potential comes, only 1/40 is activated and releases noradrenaline. This neurotransmitter will
then excite receptors on the smooth muscle (β1 or α1). When the smooth muscle is excited, it
constricts and the blood flows easily.
- Varicosities, spread over the smooth muscle layers, spreads the signal over a large area, but
act slowly and effects last long.
Noradrenaline works on the
extravascular side and adrenaline on
the intravascular side of the vessel.
4