WGU D236 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY EXAM -LATEST UPDATE 100% QURANTEED A+
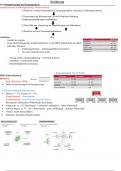
WGU D236 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY EXAM -LATEST UPDATE 100% QURANTEED A+ 1. How does this explain why a nutritionally deficient child would have edema? Starling’s Law describes how fluids move across the capillary membrane. There are two major opposing forces that act to balance each other, hydrostatic pressure (pushing water out of the capillaries) and osmotic pressure (including oncontic pressure, which pushes fluid into the capillaries). Both electrolytes and proteins (oncontic pressure) in the blood affect osmotic pressure, high electrolyte and protein concentrations in the blood would cause water to leave the cells and interstitial space and enter the blood stream to dilute the high concentrations. On, the other hand, low electrolyte and protein concentrations (as seen in a nutritionally deficient child) would cause water to leave the capillaries and enter the cells and interstitial fluid which can lead to edema. 2.How does the RAAS (Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System) result in increased blood volum e and increased blood pressure? A drop in blood pressure is sensed by the kidneys by low perfusion, which in turn begins to secrete renin. Renin then triggers the liver to produce angiotensinogen, which is converted to Angiotensin I in the lungs and then angiotensin II by the enzyme Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II stimulates peripheral arterial vasoconstriction which raises BP. Angiotensin II is also stimulating the adrenal gland to release aldosterone, which acts to increase sodium and water reabsorption increasing blood volume, while also increased potassium secretion in urine. 3. How can hyperkalemia lead to cardiac arrest? Normal levels of potassium are between 3.5 and 5.2 mEq/dL. Hyperkalemia refers to potassium levels higher that 5.2 mEq/dL. A major function of potassium is to conduct nerve impulses in muscles. Too low and muscle weakness occurs and too much can cause muscle spasms. This is especially dangerous in the heart muscle and an irregular heartbeat can cause a heart attack. 4. The body uses the Protein Buffering System, Phosphate Buffering System, and Carbonic Acid-Bicarbonate System to regulate and maintain homeostatic pH, what is the consequence of a pH imbalance? Proteins contain many acidic and basic group that can be affected by pH changes. Any increase or decrease in blood pH can alter the structure of the protein (denature), thereby affecting its function as well. 5. Describe the laboratory findings associated with metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis. (ie relative pH and CO2 levels). 1. How does this explain why a nutritionally deficient child would have edema? Starling’s Law describes how fluids move across the capillary membrane. There are two major opposing forces that act to balance each other, hydrostatic pressure (pushing water out of the capillaries) and osmotic pressure (including oncontic pressure, which pushes fluid into the capillaries). Both electrolytes and proteins (oncontic pressure) in the blood affect osmotic pressure, high electrolyte and protein concentrations in the blood would cause water to leave the cells and interstitial space and enter the blood stream to dilute the high concentrations. On, the other hand, low electrolyte and protein concentrations (as seen in a nutritionally deficient child) would cause water to leave the capillaries and enter the cells and interstitial fluid which can lead to edema. 2. How does the RAAS (Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System) result in increased blood volume and increased blood pressure? A drop in blood pressure is sensed by the kidneys by low perfusion, which in turn begins to secrete renin. Renin then triggers the liver to produce angiotensinogen, which is converted to Angiotensin I in the lungs and then angiotensin II by the enzyme Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II stimulates peripheral arterial vasoconstriction which raises BP. Angiotensin II is also stimulating the adrenal gland to release aldosterone, which acts to increase sodium and water reabsorption increasing blood volume, while also increased potassium secretion in urine. 3. How can hyperkalemia lead to cardiac arrest? Normal levels of potassium are between 3.5 and 5.2 mEq/dL. Hyperkalemia refers to potassium levels higher that 5.2 mEq/dL. A major function of potassium is to conduct nerve impulses in muscles. Too low and muscle weakness occurs and too much can cause muscle spasms. This is especially dangerous in the heart muscle and an irregular heartbeat can cause a heart attack. 4. The body uses the Protein Buffering System, Phosphate Buffering System, and Carbonic Acid-Bicarbonate System to regulate and maintain homeostatic pH, what is the consequence of a pH imbalance? Proteins contain many acidic and basic group that can be affected by pH changes. Any increase or decrease in blood pH can alter the structure of the protein (denature), thereby affecting its function as well. 5. Describe the laboratory findings associated with metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis. (ie relative pH and CO2 levels).
Written for
- Institution
-
Chamberlain College Of Nursing
- Course
-
NURSING GR 6512
Document information
- Uploaded on
- March 1, 2023
- Number of pages
- 28
- Written in
- 2022/2023
- Type
- Exam (elaborations)
- Contains
- Questions & answers
Subjects
-
wgu d236 pathophysiology exam latest update 100 quranteed a
-
1 how does this explain why a nutritionally deficient child would have edema
-
2how does the raas renin angiotensin aldosterone system
Also available in package deal