Lecture 5
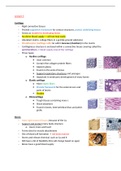
Cartilage
- Rigid connective tissues
- Provide supportive framework for various structures, protect underlying tissues
- Serves as models for developing bones
- No direct blood supply -> will not heal easily
- Abundant matrix, college fibers in a gel-like ground substance
- Chondrocytes (cartilage cells) lie within lacunae (chambers) in the matrix
- Cartilaginous structure is enclosed within a connective tissue covering called the
perichondrium -> blood supply around the cartilage
- Three types:
o Hyaline cartilage
most common
Contain fine collagen protein fibers
Appears glassy
Found on the ends of bones
Support respiratory structures and passages
Important in embryonic development of many bones
o Elastic cartilage
More elastic fibers
Provide framework for the external ears and
parts of larynx
Flexible
o Fibrocartilage
Tough tissues containing many c
Shock absorbers
Found in knees, intervertebral discs and pelvic
girdle
Bones
- Most rigid connect tissues, because of the Ca
- Support and protect many body structure
o Heart, brain and heart
- Forms sites for muscle attachments
- Site of blood cell formation -> red bone marrow
- Stores and release chemical, such as Ca and K
- Still have a bit of flexibility (this will change based on ages)
- Bones have a good blood supply
, - Two types:
o Compact bone
Osteocytes cells, lie within lacunae
Central canals contain blood vessels and distribute blood to the cells
through tiny tubes call canaliculi
Dense and compact, very solid type of bone
Strength
o Spongy bone
Spongier, more space
Lighter
Holes for bone marrow -> make blood cells
Blood
- liquid connecting tissues
- transport substances throughout the body
- composed of formed elements suspended in a liquid
matrix called plasma
- Red blood cells
o carry oxygen
- white blood cells
o protection against infection
- platelets
o blood clotting
Epithelial membrane
- Serous membrane
o Line cavities that do not open to the outside
o Consist of simple squamous epithelium and a layer of areolar connective tissue
E.g. pleura, pericardium and peritoneum
o Exist as double layered membranes
Parietal portion -> cavity wall
Visceral portion -> organ
**Contain a small amount of lubricating fluid between the 2 layers**
- Mucous membrane
o line cavities and tubes that open to the outside body
o Consist of some type epithelium and a layer of areolar connective tissue
Cartilage
- Rigid connective tissues
- Provide supportive framework for various structures, protect underlying tissues
- Serves as models for developing bones
- No direct blood supply -> will not heal easily
- Abundant matrix, college fibers in a gel-like ground substance
- Chondrocytes (cartilage cells) lie within lacunae (chambers) in the matrix
- Cartilaginous structure is enclosed within a connective tissue covering called the
perichondrium -> blood supply around the cartilage
- Three types:
o Hyaline cartilage
most common
Contain fine collagen protein fibers
Appears glassy
Found on the ends of bones
Support respiratory structures and passages
Important in embryonic development of many bones
o Elastic cartilage
More elastic fibers
Provide framework for the external ears and
parts of larynx
Flexible
o Fibrocartilage
Tough tissues containing many c
Shock absorbers
Found in knees, intervertebral discs and pelvic
girdle
Bones
- Most rigid connect tissues, because of the Ca
- Support and protect many body structure
o Heart, brain and heart
- Forms sites for muscle attachments
- Site of blood cell formation -> red bone marrow
- Stores and release chemical, such as Ca and K
- Still have a bit of flexibility (this will change based on ages)
- Bones have a good blood supply
, - Two types:
o Compact bone
Osteocytes cells, lie within lacunae
Central canals contain blood vessels and distribute blood to the cells
through tiny tubes call canaliculi
Dense and compact, very solid type of bone
Strength
o Spongy bone
Spongier, more space
Lighter
Holes for bone marrow -> make blood cells
Blood
- liquid connecting tissues
- transport substances throughout the body
- composed of formed elements suspended in a liquid
matrix called plasma
- Red blood cells
o carry oxygen
- white blood cells
o protection against infection
- platelets
o blood clotting
Epithelial membrane
- Serous membrane
o Line cavities that do not open to the outside
o Consist of simple squamous epithelium and a layer of areolar connective tissue
E.g. pleura, pericardium and peritoneum
o Exist as double layered membranes
Parietal portion -> cavity wall
Visceral portion -> organ
**Contain a small amount of lubricating fluid between the 2 layers**
- Mucous membrane
o line cavities and tubes that open to the outside body
o Consist of some type epithelium and a layer of areolar connective tissue