TOPIC 7: TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
Structure of Transport Tissues
Dicotyledonous (dicots) plants:
- Have seeds that contain two cotyledons, a network veins, leaves that typically
have broad blades and petioles and tap roots with lateral branches.
Transport systems:
- Plants need transport systems to meet their metabolic demands to efficiently
move substances up and down and to compensate for their relatively small
SA:V ratio.
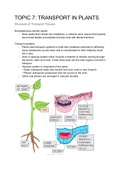
- Have a vascular system which involves a network of vessels running through
the leaves, stem and roots. These three parts are the main organs involved in
transport.
- Vascular system is comprised of two types:
- Xylem (transports water and mineral ions from roots to rest of plant)
- Phloem (transports substances from the source to the sink)
- Xylem and phloem are arranged in vascular bundles
,When drawing tissue plan diagrams (which is common in the practical paper 3) you
need to:
• Read the instructions carefully
• Draw a large diagram
• Use a sharp pencil and do not shade (including the nucleus)
• Use clear, continuous lines
• When using an eye-piece graticule, use it to ensure you have correct proportions or
if you are not using a microscope then endeavour to keep the proportions between
tissues to scale
If drawing from a low-power image:
⚬ Do not draw individual cells
⚬ Read the question carefully as you may only have to draw a portion of the image
⚬ Include the magnification on the drawing
If drawing from a high-power image:
⚬ Draw only a few of the required cells
⚬ Draw the cell wall of the plant cells
⚬ Include the magnification on the drawing
When labelling, remember:
⚬ Use a ruler for label lines (and scale line if appropriate)
⚬ Label-lines should stop exactly at the structure (do not use arrows)
⚬ Don’t cross label-lines over each other
⚬ Label all tissues and relevant structures (those requested)
Xylem:
- Functions are vascular tissue that carries dissolved minerals and water up the
plant, structural support, and food storage.
- In the roots, the vascular bundle is found in the centre and the centre core of
this is the xylem tissue. This helps the roots withstand the pulling strains they
are subjected to as the plant transports water upwards and grows
- In the stems the vascular bundles are located around the outside and the
xylem tissue is found on the inside to help support the plant.
- In the leaves the vascular bundles form the midrib and veins and therefore
spread from the centre of the leaf in a parallel line. Xylem tissue is found on
the upper side of the bundles.
, Phloem:
- Transport organic compounds, particularly sucrose from the source to the
sink. The transport of these compounds can occur up and down the plant.
- Is a complex tissue made up of various cell types; its bulk is made up of sieve
tube elements, which are the main conducting cells and companion cells.
- In the roots the vascular bundle in the centre and on the edges of the centre
core is the phloem tissue.
- In the stems the vascular bundles are located around the outside and the
phloem tissue is found on the outside.
- In the leaves the vascular bundle from the midrib and veins and therefore
spread from the centre of the leaf in a parallel line. The phloem tissue is found
on the lower side of the bundles.
Xylem structure and function:
- Made up of four cell types:
- Tracheids (long, narrow tapered cells with pits)
- Vessel elements (large with thickened cell walls no end plates when mature)
- Xylem parenchyma
- Sclerenchyma cells (fibres and sclereids)
Structure of Transport Tissues
Dicotyledonous (dicots) plants:
- Have seeds that contain two cotyledons, a network veins, leaves that typically
have broad blades and petioles and tap roots with lateral branches.
Transport systems:
- Plants need transport systems to meet their metabolic demands to efficiently
move substances up and down and to compensate for their relatively small
SA:V ratio.
- Have a vascular system which involves a network of vessels running through
the leaves, stem and roots. These three parts are the main organs involved in
transport.
- Vascular system is comprised of two types:
- Xylem (transports water and mineral ions from roots to rest of plant)
- Phloem (transports substances from the source to the sink)
- Xylem and phloem are arranged in vascular bundles
,When drawing tissue plan diagrams (which is common in the practical paper 3) you
need to:
• Read the instructions carefully
• Draw a large diagram
• Use a sharp pencil and do not shade (including the nucleus)
• Use clear, continuous lines
• When using an eye-piece graticule, use it to ensure you have correct proportions or
if you are not using a microscope then endeavour to keep the proportions between
tissues to scale
If drawing from a low-power image:
⚬ Do not draw individual cells
⚬ Read the question carefully as you may only have to draw a portion of the image
⚬ Include the magnification on the drawing
If drawing from a high-power image:
⚬ Draw only a few of the required cells
⚬ Draw the cell wall of the plant cells
⚬ Include the magnification on the drawing
When labelling, remember:
⚬ Use a ruler for label lines (and scale line if appropriate)
⚬ Label-lines should stop exactly at the structure (do not use arrows)
⚬ Don’t cross label-lines over each other
⚬ Label all tissues and relevant structures (those requested)
Xylem:
- Functions are vascular tissue that carries dissolved minerals and water up the
plant, structural support, and food storage.
- In the roots, the vascular bundle is found in the centre and the centre core of
this is the xylem tissue. This helps the roots withstand the pulling strains they
are subjected to as the plant transports water upwards and grows
- In the stems the vascular bundles are located around the outside and the
xylem tissue is found on the inside to help support the plant.
- In the leaves the vascular bundles form the midrib and veins and therefore
spread from the centre of the leaf in a parallel line. Xylem tissue is found on
the upper side of the bundles.
, Phloem:
- Transport organic compounds, particularly sucrose from the source to the
sink. The transport of these compounds can occur up and down the plant.
- Is a complex tissue made up of various cell types; its bulk is made up of sieve
tube elements, which are the main conducting cells and companion cells.
- In the roots the vascular bundle in the centre and on the edges of the centre
core is the phloem tissue.
- In the stems the vascular bundles are located around the outside and the
phloem tissue is found on the outside.
- In the leaves the vascular bundle from the midrib and veins and therefore
spread from the centre of the leaf in a parallel line. The phloem tissue is found
on the lower side of the bundles.
Xylem structure and function:
- Made up of four cell types:
- Tracheids (long, narrow tapered cells with pits)
- Vessel elements (large with thickened cell walls no end plates when mature)
- Xylem parenchyma
- Sclerenchyma cells (fibres and sclereids)