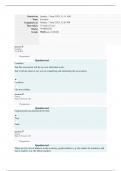
ELEMENT NUCLEUS NEUTRON PROTON ELECTRON
-pure substances that can’t be split -At the centre of an atom is a + nucleus. Protons and neutrons Every proton number -the particles that orbit the
into simpler substances (eg: hydrogen) -The nucleus is surrounded by - electrons. constitute the nuclei of is called an atomic nucleus of an atom.
-New elements are discovered from -The size of the nucleus is smaller than the atoms. number. -Are much smaller than the
time to time by nuclear reactions overall size of the atom. nucleus of the atom.
relative mass position charge
of protons 1 in the nucleus of the atom +
of neutrons 1 in the center of the atom none
of electrons 0.0005 in shells or orbitals that surround the nucleus of an atom -
DEFINTIONS
atomic (proton) number mass number isotopes relative atomic mass
number of a chemical element in the total number of protons and one of two or more species of atoms of ratio of the average mass of one atom of
periodic system neutrons in a nucleus a chemical element an element
-pure substances that can’t be split -At the centre of an atom is a + nucleus. Protons and neutrons Every proton number -the particles that orbit the
into simpler substances (eg: hydrogen) -The nucleus is surrounded by - electrons. constitute the nuclei of is called an atomic nucleus of an atom.
-New elements are discovered from -The size of the nucleus is smaller than the atoms. number. -Are much smaller than the
time to time by nuclear reactions overall size of the atom. nucleus of the atom.
relative mass position charge
of protons 1 in the nucleus of the atom +
of neutrons 1 in the center of the atom none
of electrons 0.0005 in shells or orbitals that surround the nucleus of an atom -
DEFINTIONS
atomic (proton) number mass number isotopes relative atomic mass
number of a chemical element in the total number of protons and one of two or more species of atoms of ratio of the average mass of one atom of
periodic system neutrons in a nucleus a chemical element an element