Module 4 - Waves
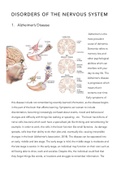
,Wave Terminology
Displacement, x [m] - the distance any part of the wave has moved from its
mean, rest or equilibrium position.
Amplitude, x0 [m] - maximum displacement.
Wavelength, λ [m] - smallest distance between two points that have the same
pattern of oscillation.
Period, T [s] - the time for one complete pattern of oscillation.
Frequency, f [Hz] - the number of oscillations per unit time.
Frequency = 1/Period
Phase difference, φ [m] - two points that have the same pattern of oscillation
are in phase (φ = 0)
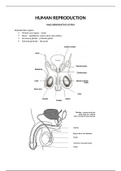
, Transverse vs Longitudinal Waves
Transverse Longitudinal
Oscillations are perpendicular to the Oscillations are parallel to the direction of
direction of energy transfer. energy transfer.
Examples include EM waves, surface water Examples include sound waves, P-waves.
waves, S-Waves.
Properties: diffraction, refraction, Properties: diffraction,
reflection superposition and interference. refraction, reflection superposition
and interference.
Can be polarised. Cannot be polarised.
Don't need a medium to travel through. Need a medium to travel through.
Travel fastest in gases or in a vacuum. Travel fastest in solids or liquids.
,Wave Terminology
Displacement, x [m] - the distance any part of the wave has moved from its
mean, rest or equilibrium position.
Amplitude, x0 [m] - maximum displacement.
Wavelength, λ [m] - smallest distance between two points that have the same
pattern of oscillation.
Period, T [s] - the time for one complete pattern of oscillation.
Frequency, f [Hz] - the number of oscillations per unit time.
Frequency = 1/Period
Phase difference, φ [m] - two points that have the same pattern of oscillation
are in phase (φ = 0)
, Transverse vs Longitudinal Waves
Transverse Longitudinal
Oscillations are perpendicular to the Oscillations are parallel to the direction of
direction of energy transfer. energy transfer.
Examples include EM waves, surface water Examples include sound waves, P-waves.
waves, S-Waves.
Properties: diffraction, refraction, Properties: diffraction,
reflection superposition and interference. refraction, reflection superposition
and interference.
Can be polarised. Cannot be polarised.
Don't need a medium to travel through. Need a medium to travel through.
Travel fastest in gases or in a vacuum. Travel fastest in solids or liquids.