PART 1: INTRODUCTION TO CONSTITUTIONAL LAW
TEXTBOOK READING
P1 – 4
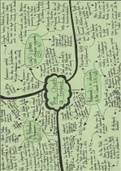
THE LAW
Why law?
1. Presupposes a society (island analogy)
a. Need a structure of authority to make rules
2. community needs authority that will govern interaction w/ each other
3. by subjecting we adhere to the law: the rule of law
a. NB: relevant worldwide, the notion of constitutional democracy
The social contract
Theory 1
Humans in og state enter the social contract bc we are afraid of our own destruction
( social contract = a conscious decision)
Theory 2
Humans in og state can govern themselves by means of decision making
Bc we are able to make decisions we should also be held accountable for our actions
The western philosophy
Requires:
o Separated individuals
o Imagined agreement between individuals
The African philosophy
There is you and the bigger community you need to serve
Ubuntu: I am bc you are
o Thus not necessary to “sign” social contract bc it is recognized as a social
responsibility
1
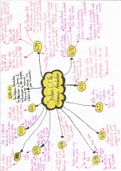
, What is law?
Characteristics of the law
Law = a balancing act, rules that will regulate human interaction
Gives some degree of certainty
Rules = applied / interpreted by institutions of the state
o Institutions of state:
Legislative – creating law
Judicial – apply + interpret the law
Executive – enforces law
o Inst. of state play important role in applying, interpreting + enforcing the law
Enforcement implies consequence for non-compliance: sanction =
punishment (fine/imprisonment/compensation)
Content of law depends on the history of the specific country
o E.g. JVR (roman/Dutch law) + African customary law = SA mixed law
Sources of the law
General characteristics of the law manifests in specific law that is found in sources of
the law:
o Constitution of RSA
o Legislation (statutes, acts)
Public elects legislative authorities
Consists of African customary law, common law + custom law
o Case law (court decisions; judicial precedent)
o International law
Drafted agreement between states
Generally, the law should reflect the values of a society
o Economic
o Political
o Social
o Moral
If it does not reflect, it could result in a legitimacy crisis
o Members of society lose their belief in their legal system
2
TEXTBOOK READING
P1 – 4
THE LAW
Why law?
1. Presupposes a society (island analogy)
a. Need a structure of authority to make rules
2. community needs authority that will govern interaction w/ each other
3. by subjecting we adhere to the law: the rule of law
a. NB: relevant worldwide, the notion of constitutional democracy
The social contract
Theory 1
Humans in og state enter the social contract bc we are afraid of our own destruction
( social contract = a conscious decision)
Theory 2
Humans in og state can govern themselves by means of decision making
Bc we are able to make decisions we should also be held accountable for our actions
The western philosophy
Requires:
o Separated individuals
o Imagined agreement between individuals
The African philosophy
There is you and the bigger community you need to serve
Ubuntu: I am bc you are
o Thus not necessary to “sign” social contract bc it is recognized as a social
responsibility
1
, What is law?
Characteristics of the law
Law = a balancing act, rules that will regulate human interaction
Gives some degree of certainty
Rules = applied / interpreted by institutions of the state
o Institutions of state:
Legislative – creating law
Judicial – apply + interpret the law
Executive – enforces law
o Inst. of state play important role in applying, interpreting + enforcing the law
Enforcement implies consequence for non-compliance: sanction =
punishment (fine/imprisonment/compensation)
Content of law depends on the history of the specific country
o E.g. JVR (roman/Dutch law) + African customary law = SA mixed law
Sources of the law
General characteristics of the law manifests in specific law that is found in sources of
the law:
o Constitution of RSA
o Legislation (statutes, acts)
Public elects legislative authorities
Consists of African customary law, common law + custom law
o Case law (court decisions; judicial precedent)
o International law
Drafted agreement between states
Generally, the law should reflect the values of a society
o Economic
o Political
o Social
o Moral
If it does not reflect, it could result in a legitimacy crisis
o Members of society lose their belief in their legal system
2