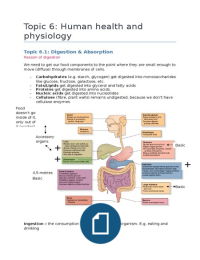
physiology
Topic 6.1: Digestion & Absorption
Reason of digestion
We need to get our food components to the point where they are small enough to
move (diffuse) through membranes of cells.
- Carbohydrates (e.g. starch, glycogen) get digested into monosaccharides
like glucose, fructose, galactose, etc.
- Fats/Lipids get digested into glycerol and fatty acids
- Proteins get digested into amino acids.
- Nucleic acids get digested into nucleotides
- Cellulose (fibre, plant walls) remains undigested, because we don’t have
cellulase enzymes
Food
doesn’t go
inside of it,
only out of
it (wastes).
Accessory
organs
+
Basic
+
+
4,5 metres
Basic
Basic
Ingestion – the consumption of a substance by an organism. E.g. eating and
drinking
,Digestion – The process in the alimentary canal, by which food is broken up
physically through teeth and enzymes, converted into a substance suitable for
absorption and assimilation. Complex molecules are converted into simple
molecules.
Absorption – The process of absorbing substances into cells or across the
tissues/organs through diffusion/osmosis/active transport.
Assimilation – The conversion of nutriment into a useable form (liquid/solid) that
is incorporated into tissues/organs through digestion. E.g. Amino acid – insulin.
Fatty acid – phospholipid. Monosaccharides – energy and glycogen.
Excretion – the process, act or function of discharging or ejecting waste product
of metabolism especially from the system of an organism. E.g. urine and sweat.
Egestion – The discharge or expulsion of undigested material (food) form a cell
in case of unicellular organisms and from the digestive tract via the anus, in case
of multicellular organisms. E.g. puking (cells), or poop (multicellular)
The small Intestine
Function of the small intestine: it is the place where 90% of the digestion and
absorption of food occurs.
Structure of the small intestine –
external view
- Is about 4.5-meter-long in adults:
the thickness of your thumb.
- It consists of 3 sections:
duodenum starts at the base of
the stomach, Jejunum in the
middle and Ileum is at the end,
and connects the large intestine at
the base of your right hip.
Structure of the small intestine – internal view
The circular and
longitudinal muscles of
the small intestine
contract rhythmically
and function to
- Move the food
along the small
intestine
- Mix the food
with the
enzymes
secreted from
the walls of the
small intestine
, The structure and functioning of the villius
- The villus/villi is/are microscopic structures
found on the inner lining of the small
intestine
- They are primarily responsible (90%) for
absorbing digested food (monomers of
carbs/fats/proteins and nucleic acids),
mineral ions and vitamins from the lumen
of the intestine, into the blood stream, and
lymphatic system.
- Villi play a vital role in increasing the
absorptive surface area of the small
intestine
The membrane area of each epithelial cell on the villus that faces the lumen of
the small intestine is also extended into surfaces called microvilli.
Villi Microvilli
How is the VILLUS structurally suited to function
effectively in absorbing digested food by the processes
of diffusion and active transport?
- Large surface area – lots of area/potential to insert
transport proteins with membrane
- Blood supply – to transport absorbed monomers away…
so that a concentration gradient is maintained, allowing
more monomers to be absorbed
- Small diffusion distance – 2 sets of cells to get
monomers into the blood…
- Moist, to keep nutrients in solution, allows monomers to
stay in solution, easier for movement/transport to
membrane surface.
- Capillary network: carbs, amino acids, salts
- Lacteal: lymphressel fats