Primary Structure of Nucleic Acid
Structure of a nucleotide / Compare + contrast primary structure of DNA,RNA
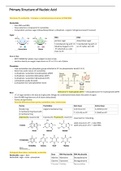
Nucleotide
- form DNA and RNA
- linear polymers composed of 4 nucleotides
- Composition: pentose sugar (ribose/deoxyribose) + phosphate + organic nitrogenous base (H receiver)
Sugar
RNA DNA
pentose sugar deoxyribose sugar
5 membered ring with 1'C 5 membered ring with -H
linked by Oxygen to 4'C on 2'C rather and -OH
5'C attached as a side
chain to 4'C
RNA & DNA
- NOT PLANAR b/c planar ring is subject to steric strain
- electron density on oxygen repel atoms so 2'C or 3'C is out of plane
Phosphate
- Free nucleotides have phosphate groups attached at 5'C via phosphoester bond (P-O-C)
- Determine acidic nature of nucleotides
- 1 phosphate: nucleotide monophosphate (AMP)
- 2 phosphate: nucleotide diphosphate (ADP)
- 3 phosphate: nucleotide triphosphate (ATP)
- γ phosphate usually donated
- α phosphate form phosphodiester bond
Base Adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP) → Deoxyadenosine-5'C-triphosphate (dATP)
- 1'C of sugar joined to the base by β glycosidic linkage via condensation (base above the plane of sugar)
- form PLANR ring (electrons of all atoms delocalised)
- Purine and pyrimidine
- Describe differences btwn purine, pyrimidine, keto, amino bases
Purine Pyrimidine Keto base Amino base
Double ring: single 6-membered ring G (C=O) on 6'C A (-NH2) on 6'C
5 membered ring fused with T, U (C=O) on 4'C C (-NH2) on 4'C
6 membered ring
Adenine (A), Guanine (G) Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U) Important for H-bonding
Label precursors of T → label DNA
Label precursors of U → label RNA
Distinguish btwn base, nucleoside, nucleotide
Nucleoside: sugar + base Base RNA Nucleoside DNA Nucleoside
Nucleotide: sugar + base + phosphate Adenine Adenosine Deoxyadenosine
Guanine Guanosine Deoxyguanosine
Cytosine Cytidine Deoxycytidine
Structure of a nucleotide / Compare + contrast primary structure of DNA,RNA
Nucleotide
- form DNA and RNA
- linear polymers composed of 4 nucleotides
- Composition: pentose sugar (ribose/deoxyribose) + phosphate + organic nitrogenous base (H receiver)
Sugar
RNA DNA
pentose sugar deoxyribose sugar
5 membered ring with 1'C 5 membered ring with -H
linked by Oxygen to 4'C on 2'C rather and -OH
5'C attached as a side
chain to 4'C
RNA & DNA
- NOT PLANAR b/c planar ring is subject to steric strain
- electron density on oxygen repel atoms so 2'C or 3'C is out of plane
Phosphate
- Free nucleotides have phosphate groups attached at 5'C via phosphoester bond (P-O-C)
- Determine acidic nature of nucleotides
- 1 phosphate: nucleotide monophosphate (AMP)
- 2 phosphate: nucleotide diphosphate (ADP)
- 3 phosphate: nucleotide triphosphate (ATP)
- γ phosphate usually donated
- α phosphate form phosphodiester bond
Base Adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP) → Deoxyadenosine-5'C-triphosphate (dATP)
- 1'C of sugar joined to the base by β glycosidic linkage via condensation (base above the plane of sugar)
- form PLANR ring (electrons of all atoms delocalised)
- Purine and pyrimidine
- Describe differences btwn purine, pyrimidine, keto, amino bases
Purine Pyrimidine Keto base Amino base
Double ring: single 6-membered ring G (C=O) on 6'C A (-NH2) on 6'C
5 membered ring fused with T, U (C=O) on 4'C C (-NH2) on 4'C
6 membered ring
Adenine (A), Guanine (G) Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U) Important for H-bonding
Label precursors of T → label DNA
Label precursors of U → label RNA
Distinguish btwn base, nucleoside, nucleotide
Nucleoside: sugar + base Base RNA Nucleoside DNA Nucleoside
Nucleotide: sugar + base + phosphate Adenine Adenosine Deoxyadenosine
Guanine Guanosine Deoxyguanosine
Cytosine Cytidine Deoxycytidine