Carbohydrates:
Condensation reaction: When two small molecules join to create a bigger
molecule called water
Hydrolysis reaction: When a water molecule breaks down to create two smaller
molecules
Carbohydrate formula: C x (H 2 O) y
Polysaccharides: Large molecules formed by many monosaccharides
Monosaccharides: Simple sugars
Formula: (CH2O)n
N can be between 3 and 7
Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides (double sugars)
Example of a monosaccharide is glucose
C6H1206 – hexose sugars
They are the main energy source and are very soluble for transportation in
cells
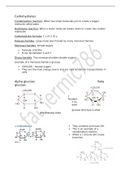
Alpha glucose: Beta
glucose:
Number
1 on
each
glucose structure is what
differentiates them.
They combine and loose OH.
This is an example of a
condensation reaction
Whilst a 1-6 bond will create
branches
Condensation reaction: When two small molecules join to create a bigger
molecule called water
Hydrolysis reaction: When a water molecule breaks down to create two smaller
molecules
Carbohydrate formula: C x (H 2 O) y
Polysaccharides: Large molecules formed by many monosaccharides
Monosaccharides: Simple sugars
Formula: (CH2O)n
N can be between 3 and 7
Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides (double sugars)
Example of a monosaccharide is glucose
C6H1206 – hexose sugars
They are the main energy source and are very soluble for transportation in
cells
Alpha glucose: Beta
glucose:
Number
1 on
each
glucose structure is what
differentiates them.
They combine and loose OH.
This is an example of a
condensation reaction
Whilst a 1-6 bond will create
branches