22.11.19
L7 – Growth Hormone
Lecture:
Background:
o Pulsatile (diagnostics required to be measured 6x/day bc pulsative
15 min half life
o Single chain polypeptide (191 AA w/ 2 disulphide bridges)
22KDa weight
o Secreted by ant pit (somatotroph cells)
o Inhibited by somatostatin and upregulated by GnRH (released by hypothalamus)
Match peaks/troughs of GH
o PIT1 = regulates GH expression
Defect in PI1= short stature, sec hypothyroidism and learning disability
o Secreted maximally 1h after falling asleep/in exercise
Rapid ↑ w/ stress, cold or surgery
o Recombinantly made for injections of GH (human diff from other species)
History
o 1920s = pit removal = dwarfish (restored w/ pit extract)
o 1940s = GH isolation from cow ant pit
o 1956 = GH isolation in human ant pit
o 1966 = human GH sanga sequences (192 AAs)
CJD (mad cow) disease infection passed on
o 1990s = recombinant hGH therapeutically used
GH receptor
o Found most in the liver
o Single glycoprotein (MW – 130K)
o Single membrane extracellular domain w/ intracellular component
o Antagonist = pegvisomant (binds w/higher affinity than GH and stops JAK2
dimerization)
How it works
o GH + receptor = dimerization of 2 receptors = complex → intracellular tyrosine
kinase cascade from JAK2 that leads to phosphorylation of JAK2
Leads to cascade reaction = dissociation of STAT from complex → dimerized
STAT → nuclear transcription (target IGF-1)
‘JAK-STAT’ pathway
Laron syndrome (gene knockout of GH receptors)
o Growth hormone resistance
o Autosomal recessive disorder
o 95cm tall 10-year-old boy (looks 3)
o GH levels higher than normal (- feedback)
o IGF-1 (stimulated by GH) undetectable
o Small penis, obesity, mental retardation, prominent forehead and depressed nasal
bridge
Actions of GH
o Direct effects
, 22.11.19
Antagonistic to insulin (diabetogenic effects)
Increased lipolysis (increased FAs in plasma)
↑ free FA
Lower blood glucose (glycolysis and glycogen synth)
Liver = glucogenesis and glycogenesis
Unlike insulin = reduce glucose uptake into cells (increase plasma glucose
level)
Osteoblast differentiation
Muscle = glycogenesis, increased AA transport into muscle (increases muscle
growth/decrease urea plasma levels)
Increased energy usage
GH = ↑BMR, ↑ lean body mass
Protein metabolism controlled by IGF-1
Possible link between GH and fluid retention by ↑ GFR = swollen hands in
acromegaly
o Indirect actions of IGFs (somatomedins)
IGF synth in hepatocytes
(stim via GH)
↑ glycolysis and glucose
uptake
IGF promotes
Linear bone growth
(growth plates via
epiphyseal disc of
cartilage)
o Fuse after
puberty or
acromegaly
Protein synth (in
muscles like GH)
Growth/cell prolif in
soft tissue
o 0-5 growth based on GH plateau until puberty (age 13) via sex steroids until closure
of epiphyses plate at 20 y/o
o Ovaries express IGF
Disorders of GH
o 60 people/mil have excess GH
Diagnosed w/>0.8mU/L chemiluminescence assay after 75g oral glucose
tablet
Adrenal tumor > 1cm
o Hypopituitarism = dwarf
o Giantism = slow growing tumor of somatotrophs in youth (excess GH)
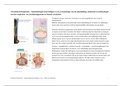
o Acromegaly = thickening of soft tissues/bones (excess GH)
Not lateral growth bc closed epiphyseal plates
Big hands, feet, nose, chin, strong brow bone, big tongue, large feet/hands
Thickened, greasy skin, sweating, headaches, tiredness
L7 – Growth Hormone
Lecture:
Background:
o Pulsatile (diagnostics required to be measured 6x/day bc pulsative
15 min half life
o Single chain polypeptide (191 AA w/ 2 disulphide bridges)
22KDa weight
o Secreted by ant pit (somatotroph cells)
o Inhibited by somatostatin and upregulated by GnRH (released by hypothalamus)
Match peaks/troughs of GH
o PIT1 = regulates GH expression
Defect in PI1= short stature, sec hypothyroidism and learning disability
o Secreted maximally 1h after falling asleep/in exercise
Rapid ↑ w/ stress, cold or surgery
o Recombinantly made for injections of GH (human diff from other species)
History
o 1920s = pit removal = dwarfish (restored w/ pit extract)
o 1940s = GH isolation from cow ant pit
o 1956 = GH isolation in human ant pit
o 1966 = human GH sanga sequences (192 AAs)
CJD (mad cow) disease infection passed on
o 1990s = recombinant hGH therapeutically used
GH receptor
o Found most in the liver
o Single glycoprotein (MW – 130K)
o Single membrane extracellular domain w/ intracellular component
o Antagonist = pegvisomant (binds w/higher affinity than GH and stops JAK2
dimerization)
How it works
o GH + receptor = dimerization of 2 receptors = complex → intracellular tyrosine
kinase cascade from JAK2 that leads to phosphorylation of JAK2
Leads to cascade reaction = dissociation of STAT from complex → dimerized
STAT → nuclear transcription (target IGF-1)
‘JAK-STAT’ pathway
Laron syndrome (gene knockout of GH receptors)
o Growth hormone resistance
o Autosomal recessive disorder
o 95cm tall 10-year-old boy (looks 3)
o GH levels higher than normal (- feedback)
o IGF-1 (stimulated by GH) undetectable
o Small penis, obesity, mental retardation, prominent forehead and depressed nasal
bridge
Actions of GH
o Direct effects
, 22.11.19
Antagonistic to insulin (diabetogenic effects)
Increased lipolysis (increased FAs in plasma)
↑ free FA
Lower blood glucose (glycolysis and glycogen synth)
Liver = glucogenesis and glycogenesis
Unlike insulin = reduce glucose uptake into cells (increase plasma glucose
level)
Osteoblast differentiation
Muscle = glycogenesis, increased AA transport into muscle (increases muscle
growth/decrease urea plasma levels)
Increased energy usage
GH = ↑BMR, ↑ lean body mass
Protein metabolism controlled by IGF-1
Possible link between GH and fluid retention by ↑ GFR = swollen hands in
acromegaly
o Indirect actions of IGFs (somatomedins)
IGF synth in hepatocytes
(stim via GH)
↑ glycolysis and glucose
uptake
IGF promotes
Linear bone growth
(growth plates via
epiphyseal disc of
cartilage)
o Fuse after
puberty or
acromegaly
Protein synth (in
muscles like GH)
Growth/cell prolif in
soft tissue
o 0-5 growth based on GH plateau until puberty (age 13) via sex steroids until closure
of epiphyses plate at 20 y/o
o Ovaries express IGF
Disorders of GH
o 60 people/mil have excess GH
Diagnosed w/>0.8mU/L chemiluminescence assay after 75g oral glucose
tablet
Adrenal tumor > 1cm
o Hypopituitarism = dwarf
o Giantism = slow growing tumor of somatotrophs in youth (excess GH)
o Acromegaly = thickening of soft tissues/bones (excess GH)
Not lateral growth bc closed epiphyseal plates
Big hands, feet, nose, chin, strong brow bone, big tongue, large feet/hands
Thickened, greasy skin, sweating, headaches, tiredness