Chapter 29
Government’s budgets annual statement of projected outlays and receipts during the next
financial year together with the laws and regulations that will support those outlays and receipts.
3 major purposes of the government’s budget:
1. To plan and finance the government’s activities
2. To stabilize the economy
3. To encourage the economy’s long-term growth and balance regional development
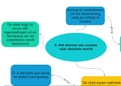
Fiscal policy is a government’s use of its budget to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as full
employment, sustained economic growth and price-level stability.
3 main items in the government’s budget:
1. Receipts: receipts come from 5 sources
a. Taxes on income and wealth (paid by individuals)
b. Taxes on business
c. Taxes on expenditure (VAT, special taxes on gambling, alcohol, petrol, luxury,
imports)
d. National Insurance contribution (contributions paid by workers & employers)
e. Other receipts and royalties (oil, stamp duties, car taxes)
2. Outlays: outlays are classified in 3 broad categories
a. Expenditure on goods and services
b. Transfer payments (to individuals, businesses, other levels of government)
c. Debt interest (interest on government minus interest received by the government on
its own investments)
3. Budget balance: the government’s budget balance is equal to its receipts minus it outlays
a. Budget surplus: receipts exceeds outlays
b. Budget deficit: outlay exceed receipts
c. Balanced budget: receipts equal outlays
Government debt is the total amount of borrowing by the government. It is the sum of past deficits
minus the sum of past surpluses plus payments to buy assets minus receipts from the sale of assets.
Budget deficit or the purchase of assets increases government debt and a budget surplus or the sale
of sale-owned assets reduces government debt.
The tax on labour income influences potential GDP and aggregate supply by changing the full-
employment quantity of labour. The income tax weakens the incentive to work and drives a wedge
between the take-home wage of workers and the cost of labour to firms. The result is a smaller
quantity of labour and a lower potential GDP.
Tax wedge is the gap that is created between the before-tax and after-tax wage rates.
Generational accounting is an accounting system that measures the lifetime tax burden and benefits
of each generation. Present value is an amount of money that, if invested today, will grow to equal a
given future amount when the interest that it earns is taken into account.
Fiscal imbalance is the present value of the government’s commitments to pay benefits minus the
present value of its tax revenues. This concept is used by economists to assess the government’s
obligations.
Government’s budgets annual statement of projected outlays and receipts during the next
financial year together with the laws and regulations that will support those outlays and receipts.
3 major purposes of the government’s budget:
1. To plan and finance the government’s activities
2. To stabilize the economy
3. To encourage the economy’s long-term growth and balance regional development
Fiscal policy is a government’s use of its budget to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as full
employment, sustained economic growth and price-level stability.
3 main items in the government’s budget:
1. Receipts: receipts come from 5 sources
a. Taxes on income and wealth (paid by individuals)
b. Taxes on business
c. Taxes on expenditure (VAT, special taxes on gambling, alcohol, petrol, luxury,
imports)
d. National Insurance contribution (contributions paid by workers & employers)
e. Other receipts and royalties (oil, stamp duties, car taxes)
2. Outlays: outlays are classified in 3 broad categories
a. Expenditure on goods and services
b. Transfer payments (to individuals, businesses, other levels of government)
c. Debt interest (interest on government minus interest received by the government on
its own investments)
3. Budget balance: the government’s budget balance is equal to its receipts minus it outlays
a. Budget surplus: receipts exceeds outlays
b. Budget deficit: outlay exceed receipts
c. Balanced budget: receipts equal outlays
Government debt is the total amount of borrowing by the government. It is the sum of past deficits
minus the sum of past surpluses plus payments to buy assets minus receipts from the sale of assets.
Budget deficit or the purchase of assets increases government debt and a budget surplus or the sale
of sale-owned assets reduces government debt.
The tax on labour income influences potential GDP and aggregate supply by changing the full-
employment quantity of labour. The income tax weakens the incentive to work and drives a wedge
between the take-home wage of workers and the cost of labour to firms. The result is a smaller
quantity of labour and a lower potential GDP.
Tax wedge is the gap that is created between the before-tax and after-tax wage rates.
Generational accounting is an accounting system that measures the lifetime tax burden and benefits
of each generation. Present value is an amount of money that, if invested today, will grow to equal a
given future amount when the interest that it earns is taken into account.
Fiscal imbalance is the present value of the government’s commitments to pay benefits minus the
present value of its tax revenues. This concept is used by economists to assess the government’s
obligations.