Vraag + Geodata + Kennis = Informatie Besluiten
Werkelijkheid Conceptueel model Geodata model
Ruimtelijke en niet ruimtelijke data:
- Een entiteit of object of feature bijvoorbeeld kadastrale grenzen of bebouwing
- Attributen die horen bij deze feature zoals perceelnummer, eigenaar, oppervlakte
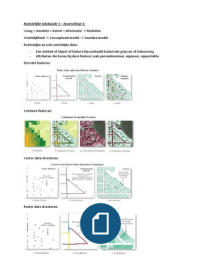
Discrete features:
Continue features:
Vector data structures:
Raster data structures:
, Vector representatie:
- Objecten worden weergegeven als punten, lijnen en vlakken
- Punten hebben coördinaten; lijnen verbinden punten, vlakken worden begrensd door lijnen
- Attributen zijn gerelateerd aan de objecten (punt/lijn/vlak)
Raster representatie:
Verdeling van de ruimte in cellen van gelijke grootte, thema bepaalt waarde van de cel
(Nominaal/Ordinaal/Interval/Ratio)
Definities GIS:
• a set of tools for collecting, storing, retrieving at will, transforming, and displaying spatial
data from the real world for a particular set of purposes (Burroughs)
• an information system used to manipulate, summarize, query, edit, and visualize spatial and
non-spatial information stored in a computer database (Goodchild)
• a digital system for the acquisition, management, analysis, and visualization of spatial data
for the purposes of planning, administering, and monitoring the natural and socioeconomic
environment (Konecny)
• a computerized system that facilitates the phases of data entry, data analysis and data
presentation especially in case when we are dealing with georeferenced data (Principles of
GIS, 2004).
• an automated system for the capture, storage, retrieval, analysis, and display of spatial data
(Slocum et al.)
• a computer-based system designed to manage and use geospatial data to solve spatial
problems (Loand Yeung)
• the collection of software, hardware, outputs, personnel, and practices that together
facilitate the analysis and mapping of geographic entities and phenomena (Schuurman)
Hardware – PC, laptop, tablet, smartphone, GPS-tracker, cloud, server
Software – desktop or online version of ArcGIS but also google maps