Importance of Learning from experience shapes adaptive thought and behaviour
memory
- Interaction between sensory inputs and stores knowledge Perception
- Memory drives attention
- Conscious and unconscious decisions from memory
- Central to personal identity (Eroded in dementia patients)
- Facilitates language and culture
Case of Clive Overview
Wearing - A conductor and musicologist
- Developed amnesia in 1985
- Then encephalitis (Herpes virus enter the brain via olfactory pathway)
- Profound impairment of memory
- Only able to retain short-term memory (20 seconds)
Case of Overview
patient HM - Bilateral medial temporal lobectomy in 1953 (To treat epilepsy)
(Henry - Removed hippocampus in both hemispheres
Molaison) - Cured epilepsy but strong consequences for memory
Effects on HM (Scoville & Milner (1957); Milner (1966))
- Anterograde amnesia – Loss of ability to maintain memory after surgery
(E.g. Read same magazines; Eat lunch several times…)
- Retrograde amnesia – Forgetting events 11 years before surgery but
childhood memories preserved
Implications
- Memory loss of new and some pre-operation memory
- Suggests the critical role of hippocampus for new learning
- But not for storing old memories
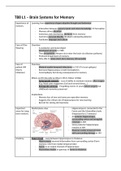
Important Medial plane view - Hippocampus is connected to the
areas for Long- Fornix and the Mammillary body
term memory (Important for LT memory)
- All anterior hippocampus,
surrounding cortex and amygdala
removed in HM
- Some posterior hippocampus
remains in HM
- Bilateral medial temporal lesion
with surrounding damage in HM
Anatomy Papez circuit – Loop between hippocampus to thalamus
- Hippocampus received information from surrounding cortex (Form
memory, info from medial temporal lobe)
- Fornix as an output channel of hippocampus
- Mammillary bodies as gateway of fornix to thalamus