CHAPTER 1 SUMMARY
What is marketing?
Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships. (Satisfying
costumers’ needs). We define marketing, as the process by which
companies create value for customers and build strong customer
relationship in order to capture value from customers in return.
Twofold goal of marketing
1. To attract new costumers by promising superior value.
2. To keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction.
The new marketing approaches do more than just send out messages. The
marketers want to become a part of your life and enrich your experience
with their brand.
Marketing mix
A set of marketing tools that work together to satisfy customer needs and
build customer relationships.
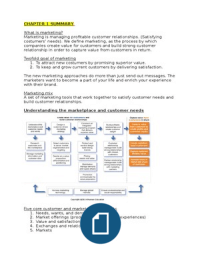
Understanding the marketplace and customer needs
Five core customer and marketplace concepts
1. Needs, wants, and demands
2. Market offerings (products, services, and experiences)
3. Value and satisfaction
4. Exchanges and relationships
5. Markets
,Customer needs, wants, and demands
Needs: they include basic physical needs for food, clothing, warmth and
safety. Social needs, for belongings and affection. And individual needs, for
knowledge and self-expression. The needs are basic part of human
makeup.
Wants: are the form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and
individual personality.
Demands: when backed by buying power, wants, become demands. Given
their want and resources.
Market offerings
Some combination of products, services, information, or experiences
offered to a market tot satisfy a need or want. They are not limited to
physical products, they also include services.
Marketing myopia
The mistake of paying more attention to the specific products a company
offers than to the benefits and experiences produced by these products. (A
product is only a tool to solve customers problems).
Creating brand experience: (for example), you don’t just visit ‘Walt Disney
resort’; you immerse yourself and your family in a world of wonder, a
world where dreams come true and things still work the way they should.
Exchange
The act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something
in return.
Market
The set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service. These
buyers share a particular need or want that can be satisfied through
exchange relationships.
Core marketing activities
1. Consumer research
2. Product development
3. Communication
4. Distribution
5. Pricing
6. Service
Customer managed relationships: - how can we reach our customers’?
- how should our customers’ reach us?
- how can our customers reach each other?
Designing a customer-driven marketing strategy
Marketing management (= customer and demand management)
,The art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable
relationships with them. The market managers’ aim is to find, attract,
keep, and grow target customers by creating, delivering and
communicating superior customer value.
A winning marketing strategy (2 questions)
1. What customers will we serve (what’s our target market)?
Dividing the market into market segments, and decide which market
they will go after.
2. How can we serve these customers best (what’s is our value
proposition)?
Decide how they will differentiate and position itself in the
marketplace.
A brand value proposition: is the set of benefits or values it promises to
deliver to consumers to satisfy their needs.
The production concept
The idea that consumer will favor products that are available and highly
affordable; therefore the organization should focus on improving
production and distribution efficiency. The product concept can lead to
marketing myopia. (companies focus to much on their own operation and
losing sight of the real subject.
The product concept
The idea that consumers will favor products that offer the most quality
performance, and features; therefore, the organization should devote its
energy to making continuous product improvement.
The selling concept
The idea that consumers will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless
the firm undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort.
The marketing concept
A philosophy in which achieving organizational goals depend on knowing
the needs and want of target markets and delivering the desired
satisfactions better than competitors do.
The societal marketing concept (good for all)
The idea that a company’s marketing decisions should consider
consumers’ wants, the company’s requirements, consumers’ long-run
interests, and society’s long-run interests.
Preparing an integrated marketing plan and program
The first 3 steps in the marketing process
1. Understanding the market place and customer needs.
2. Designing a customer-driven market strategy
3. Constructing a marketing program
,Building customers’ relationships
Customers’ relationship management
Is the most important concept of modern marketing. The overall process of
building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering
superior customer value and satisfaction.
Customer perceived value
The customers’ evaluation of the difference between all the benefits and
all the costs of a marketing offer relative to those of competing offers. A
customer buys from the firm that offers the highest customer perceived
value.
Customer satisfaction
The extent to which a product’s perceived performance matches a buyer’s
expectation.
Customer relationship levels and tools
Basic relationship: For example, Nike doesn’t phone call on all of it’s
customers to get to know them personally.
Full partnership: For example, Nike sales representatives work closely with
the sports authority, foot Locker and other large retailers.
In between those two extremes customer relationships are appropriate.
Frequency marketing programs
Marketers use specific marketing tools to develop stronger bonds with
customers. Frequency marketing
programs reward customers who buy frequently or in large amounts.
(example, hotels give room
upgrades to frequent guests).
Club marketing programs
That offers members special benefits and create member communities.
(Example, if you buy a Weber grill you can join the Weber nation, the site
for real people who lover their Weber grill). You get exclusive membership
grill classes online et cetera.
The changing nature of customer relationships
Underneath there are some trends in the way companies and customers
are relating to one another.
Relating with more carefully selected customers’:
A few firms still use true mass marketing (selling in a standardized way to
any customer who comes along). Today most marketers realize that they
don’t want relationships with every customer. Instead, they target fewer,
more profitable customers. Some are more costly to serve than to lose.
The company fires customers that cost more to serve than to lose.
Relating more deeply and interactively:
, Companies don’t rely on mass-media messages anymore.
Customer managed relationships
Marketing relationships in which customers, empowered by today’s new
digital technologies, interact with companies and with each other to shape
their relationships. Good customer relationship management creates
customer satisfaction. The aim of customer relationship management is to
create not only customer satisfaction but also customer delight.
Customer generated marketing
Brand exchanges created by consumers themselves (invited and
uninvited) by which consumers are playing an increasing role in shaping
their own brand experiences and those of other consumers.
Partner relationship management
To be good at costumer managed relationship marketers must also be
good at partner relationship management. This is; working closely with
others inside and outside the company to jointly bring more value to
customers.
Marketing channels consist of distributors, retailers and others who
connect the company to its buyers.
Supply chain; Describes a longer channel from raw materials to
components to final products that are carried to final buyers.
Supply chain management; companies today are strengthening their
connections with partners all along the supply chain. Success at delivering
customer value rests on how well their entire supply chain performs
against competitors’ supply chains.
Capturing value from customers’
Capturing value in return in the form of sales, market share, and profit.
Customer lifetime value
The value of the entire stream of purchases a customer makes over a
lifetime of patronage.
Stew Leonards’ policy: 1. The customer is always right.
2. If the customer is ever wrong, reread rule #1
Customers’ delight creates an emotional relationship with a brand, not just
a rational preference. That relationship keeps customers coming back.
Share of customer
Good customer relationship management can help marketers increase
their share of customer. This is the share they get of the customers’
purchasing in their product categories. Thus, banks want to increase
‘’share of wallet’’, car companies want to increase ‘’share of garage’’. To
What is marketing?
Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships. (Satisfying
costumers’ needs). We define marketing, as the process by which
companies create value for customers and build strong customer
relationship in order to capture value from customers in return.
Twofold goal of marketing
1. To attract new costumers by promising superior value.
2. To keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction.
The new marketing approaches do more than just send out messages. The
marketers want to become a part of your life and enrich your experience
with their brand.
Marketing mix
A set of marketing tools that work together to satisfy customer needs and
build customer relationships.
Understanding the marketplace and customer needs
Five core customer and marketplace concepts
1. Needs, wants, and demands
2. Market offerings (products, services, and experiences)
3. Value and satisfaction
4. Exchanges and relationships
5. Markets
,Customer needs, wants, and demands
Needs: they include basic physical needs for food, clothing, warmth and
safety. Social needs, for belongings and affection. And individual needs, for
knowledge and self-expression. The needs are basic part of human
makeup.
Wants: are the form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and
individual personality.
Demands: when backed by buying power, wants, become demands. Given
their want and resources.
Market offerings
Some combination of products, services, information, or experiences
offered to a market tot satisfy a need or want. They are not limited to
physical products, they also include services.
Marketing myopia
The mistake of paying more attention to the specific products a company
offers than to the benefits and experiences produced by these products. (A
product is only a tool to solve customers problems).
Creating brand experience: (for example), you don’t just visit ‘Walt Disney
resort’; you immerse yourself and your family in a world of wonder, a
world where dreams come true and things still work the way they should.
Exchange
The act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something
in return.
Market
The set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service. These
buyers share a particular need or want that can be satisfied through
exchange relationships.
Core marketing activities
1. Consumer research
2. Product development
3. Communication
4. Distribution
5. Pricing
6. Service
Customer managed relationships: - how can we reach our customers’?
- how should our customers’ reach us?
- how can our customers reach each other?
Designing a customer-driven marketing strategy
Marketing management (= customer and demand management)
,The art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable
relationships with them. The market managers’ aim is to find, attract,
keep, and grow target customers by creating, delivering and
communicating superior customer value.
A winning marketing strategy (2 questions)
1. What customers will we serve (what’s our target market)?
Dividing the market into market segments, and decide which market
they will go after.
2. How can we serve these customers best (what’s is our value
proposition)?
Decide how they will differentiate and position itself in the
marketplace.
A brand value proposition: is the set of benefits or values it promises to
deliver to consumers to satisfy their needs.
The production concept
The idea that consumer will favor products that are available and highly
affordable; therefore the organization should focus on improving
production and distribution efficiency. The product concept can lead to
marketing myopia. (companies focus to much on their own operation and
losing sight of the real subject.
The product concept
The idea that consumers will favor products that offer the most quality
performance, and features; therefore, the organization should devote its
energy to making continuous product improvement.
The selling concept
The idea that consumers will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless
the firm undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort.
The marketing concept
A philosophy in which achieving organizational goals depend on knowing
the needs and want of target markets and delivering the desired
satisfactions better than competitors do.
The societal marketing concept (good for all)
The idea that a company’s marketing decisions should consider
consumers’ wants, the company’s requirements, consumers’ long-run
interests, and society’s long-run interests.
Preparing an integrated marketing plan and program
The first 3 steps in the marketing process
1. Understanding the market place and customer needs.
2. Designing a customer-driven market strategy
3. Constructing a marketing program
,Building customers’ relationships
Customers’ relationship management
Is the most important concept of modern marketing. The overall process of
building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering
superior customer value and satisfaction.
Customer perceived value
The customers’ evaluation of the difference between all the benefits and
all the costs of a marketing offer relative to those of competing offers. A
customer buys from the firm that offers the highest customer perceived
value.
Customer satisfaction
The extent to which a product’s perceived performance matches a buyer’s
expectation.
Customer relationship levels and tools
Basic relationship: For example, Nike doesn’t phone call on all of it’s
customers to get to know them personally.
Full partnership: For example, Nike sales representatives work closely with
the sports authority, foot Locker and other large retailers.
In between those two extremes customer relationships are appropriate.
Frequency marketing programs
Marketers use specific marketing tools to develop stronger bonds with
customers. Frequency marketing
programs reward customers who buy frequently or in large amounts.
(example, hotels give room
upgrades to frequent guests).
Club marketing programs
That offers members special benefits and create member communities.
(Example, if you buy a Weber grill you can join the Weber nation, the site
for real people who lover their Weber grill). You get exclusive membership
grill classes online et cetera.
The changing nature of customer relationships
Underneath there are some trends in the way companies and customers
are relating to one another.
Relating with more carefully selected customers’:
A few firms still use true mass marketing (selling in a standardized way to
any customer who comes along). Today most marketers realize that they
don’t want relationships with every customer. Instead, they target fewer,
more profitable customers. Some are more costly to serve than to lose.
The company fires customers that cost more to serve than to lose.
Relating more deeply and interactively:
, Companies don’t rely on mass-media messages anymore.
Customer managed relationships
Marketing relationships in which customers, empowered by today’s new
digital technologies, interact with companies and with each other to shape
their relationships. Good customer relationship management creates
customer satisfaction. The aim of customer relationship management is to
create not only customer satisfaction but also customer delight.
Customer generated marketing
Brand exchanges created by consumers themselves (invited and
uninvited) by which consumers are playing an increasing role in shaping
their own brand experiences and those of other consumers.
Partner relationship management
To be good at costumer managed relationship marketers must also be
good at partner relationship management. This is; working closely with
others inside and outside the company to jointly bring more value to
customers.
Marketing channels consist of distributors, retailers and others who
connect the company to its buyers.
Supply chain; Describes a longer channel from raw materials to
components to final products that are carried to final buyers.
Supply chain management; companies today are strengthening their
connections with partners all along the supply chain. Success at delivering
customer value rests on how well their entire supply chain performs
against competitors’ supply chains.
Capturing value from customers’
Capturing value in return in the form of sales, market share, and profit.
Customer lifetime value
The value of the entire stream of purchases a customer makes over a
lifetime of patronage.
Stew Leonards’ policy: 1. The customer is always right.
2. If the customer is ever wrong, reread rule #1
Customers’ delight creates an emotional relationship with a brand, not just
a rational preference. That relationship keeps customers coming back.
Share of customer
Good customer relationship management can help marketers increase
their share of customer. This is the share they get of the customers’
purchasing in their product categories. Thus, banks want to increase
‘’share of wallet’’, car companies want to increase ‘’share of garage’’. To