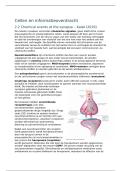
« Glomerular Structure »
• Glomerulus: is the filtration unit of
the nephron.
• Mesangium: mesangial cells +
connective tissues.
❖ Endothelial cells
• Endothelial cells: have thousands of perforation (holes) within the cells, the size of the
hole is about 70 – 100 nm.
This is why the capillary called fenestrated capillary.
, ❖ Glomerular Basement membrane
• Glomerular Basement Membrane made of collagen type IV.
This collagen consists of triple helix of α-peptide chains.
❖ Clinical Condition:
1. Good pasture's disease:
• The body produce autoantibodies against globular non-collagenous component (anti-
Glomerular Basement Membrane antibodies) in the kidney. Also, there are similar
antigens found in the alveoli, which are attacked by (anti-Alveolar Basement
Membrane antibodies) leading to:
1. Hematuria from kidney.
2. Hemoptysis from lungs.
2. Hereditary Nephritis:
• It is a mutation in the α genes which make the α-peptide chains, this mutation produce
weak type IV collagen, so the patient suffer from early hematuria.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
• The basement membrane is electro-negatively charged; because there are many
depositions of negatively charged molecules (poly-anionic proteoglycans).
• The proteoglycans are also present in the endothelial & epithelial (visceral) cells.
Therefore, they are electro-negatively charged these are called as a group
sialoglycoprotein.
This means, all the filtration membrane (endothelial cells + Basement Membrane +
visceral epithelial cells) is electro- negatively charged.
❖ Visceral epithelial Cells
• Attached with Glomerular Basement Membrane with finger like process.
• These cells inter-digitate with one another to form filtration slits.
• Fluids & Substances move from fenestrated capillaries, then through the network of
type IV collagen of basement membrane, then through filtration slits.
• Recent concept, filtration slits have diaphragm called filtration diaphragm. It is very
thin and made of special type of protein called nephrin.
• In Renal pathology, the nephrin is either mutated or autoantibodies are formed against
it once damaged, the filtration diaphragm leads to filtration of large amounts of
proteins.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
, • An experiment done with the use of Dextran (which can be synthesized with different
sizes and charges). Then was introduced intravenously, they noticed:
• Large molecules cannot be filtered, this barrier is called size barrier
small molecules like glucose & amino acids are freely filtered, but plasma
proteins cannot because they are large.
• Positively charged molecules are more easily filtered, this is called charge
barrier cationic molecules are more filtered than anionic molecules.
• Platelets + RBC + WBC cannot be filtered in healthy kidney because they are too large.
• Plasma proteins (Globulin + Fibrinoid) cannot be filtered because of their large sizes.
However, (Albumin) is just has the right size to be filtered, but fortunately is expelled/
rebelled because it is negatively charged.
❖ Clinical Condition:
1. Minimal Change Glomerulopathy:
• Why does it called minimal change? Because it causes only little alteration in the
glomeruli.
• We cannot see any change in light microscope, but we can see in electron microscope
that the foot process (podocytes) are disrupted and swollen.
• Although there is little change, but there is heavy proteinuria (a lot of albumins leak
into urine).
• It makes doctors nervous because everything is normal, so what happens ?!!
Actually, in this disease, some cytokines produced in the body that neutralize the
negative charges in the filtration membrane, so albumin freely filtered Albuminuria.
❖ Mesangial cells
• Mesangial cells are active cells that have many properties:
1. Contractile cells because they present around the capillary, so they affect the
filtration rate. ALSO, they are receptors for Angiotensin II.
2. They can phagocytose can engulf Ab-Ag complexes.
3. They can proliferate can proliferate by tumor and constrict filtration.
4. Can deposit mesangium connective tissues + collagen.
• Mesangial cells when irritated due to some disease process, they can produce many
biologically active products which can enhance the inflammation within the glomeruli.
, « Introduction to renal physiology 1 »
❖ Functions of
Renal system
:
1. Excretory function.
2. Regulatory functions
3. Endocrine functions.
4. Metabolic functions.
❖ Excretory functions
1. Metabolic waste products (ex: urea & creatinine):
• The gall standard test for renal function is creatinine, why?
Because creatinine level in the blood is mainly dependent on renal function. If
kidney is not working well (no GFR & no filtration), so creatinine level goes up and
urea also goes up. However, urea level goes up in many other conditions such as, when
you sweat too much, you undergo dehydration and everything will concentrate in the
blood specifically urea.
• In severe dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea or excessive sweating), urea will
concentrate.
• In high protein diet, urea level goes up because it is break down product of amino
acids.
2. Drugs (gut metabolites) and toxins:
• The drug acts on certain cells in the body, and the remaining goes out of the body. Note
WHY? Lipid soluble substances can
Because we don’t want drugs to remain forever in our body, so if they remain lipid cross biological membranes
soluble, they will be either be excreted through liver or nephrons. like:
1. GIT mucosal membrane.
Through liver 2. Blood Brain Barrier (BBB).
• Drugs enter the hepatocytes, which push these drugs by special transporters into biliary 3. Placental Barrier.
canaliculi, and go throughout bile to get out, but these drugs will never be excreted,
rather will be absorbed again by portal circulation. MEANS, we cannot execrate them
by hepatobiliary system.
Through Kidney
• When lipid soluble drugs go to nephrons, they will be absorbed by epithelial cells of
the nephrons which have lipid cell membrane, then will go again to the body. MEANS,
we cannot excrete them by renal system.
❖ Summary:
• When drugs or any substances are lipid soluble → we cannot excrete them by
BOTH hepatobiliary and renal system.
• Glomerulus: is the filtration unit of
the nephron.
• Mesangium: mesangial cells +
connective tissues.
❖ Endothelial cells
• Endothelial cells: have thousands of perforation (holes) within the cells, the size of the
hole is about 70 – 100 nm.
This is why the capillary called fenestrated capillary.
, ❖ Glomerular Basement membrane
• Glomerular Basement Membrane made of collagen type IV.
This collagen consists of triple helix of α-peptide chains.
❖ Clinical Condition:
1. Good pasture's disease:
• The body produce autoantibodies against globular non-collagenous component (anti-
Glomerular Basement Membrane antibodies) in the kidney. Also, there are similar
antigens found in the alveoli, which are attacked by (anti-Alveolar Basement
Membrane antibodies) leading to:
1. Hematuria from kidney.
2. Hemoptysis from lungs.
2. Hereditary Nephritis:
• It is a mutation in the α genes which make the α-peptide chains, this mutation produce
weak type IV collagen, so the patient suffer from early hematuria.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
• The basement membrane is electro-negatively charged; because there are many
depositions of negatively charged molecules (poly-anionic proteoglycans).
• The proteoglycans are also present in the endothelial & epithelial (visceral) cells.
Therefore, they are electro-negatively charged these are called as a group
sialoglycoprotein.
This means, all the filtration membrane (endothelial cells + Basement Membrane +
visceral epithelial cells) is electro- negatively charged.
❖ Visceral epithelial Cells
• Attached with Glomerular Basement Membrane with finger like process.
• These cells inter-digitate with one another to form filtration slits.
• Fluids & Substances move from fenestrated capillaries, then through the network of
type IV collagen of basement membrane, then through filtration slits.
• Recent concept, filtration slits have diaphragm called filtration diaphragm. It is very
thin and made of special type of protein called nephrin.
• In Renal pathology, the nephrin is either mutated or autoantibodies are formed against
it once damaged, the filtration diaphragm leads to filtration of large amounts of
proteins.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
, • An experiment done with the use of Dextran (which can be synthesized with different
sizes and charges). Then was introduced intravenously, they noticed:
• Large molecules cannot be filtered, this barrier is called size barrier
small molecules like glucose & amino acids are freely filtered, but plasma
proteins cannot because they are large.
• Positively charged molecules are more easily filtered, this is called charge
barrier cationic molecules are more filtered than anionic molecules.
• Platelets + RBC + WBC cannot be filtered in healthy kidney because they are too large.
• Plasma proteins (Globulin + Fibrinoid) cannot be filtered because of their large sizes.
However, (Albumin) is just has the right size to be filtered, but fortunately is expelled/
rebelled because it is negatively charged.
❖ Clinical Condition:
1. Minimal Change Glomerulopathy:
• Why does it called minimal change? Because it causes only little alteration in the
glomeruli.
• We cannot see any change in light microscope, but we can see in electron microscope
that the foot process (podocytes) are disrupted and swollen.
• Although there is little change, but there is heavy proteinuria (a lot of albumins leak
into urine).
• It makes doctors nervous because everything is normal, so what happens ?!!
Actually, in this disease, some cytokines produced in the body that neutralize the
negative charges in the filtration membrane, so albumin freely filtered Albuminuria.
❖ Mesangial cells
• Mesangial cells are active cells that have many properties:
1. Contractile cells because they present around the capillary, so they affect the
filtration rate. ALSO, they are receptors for Angiotensin II.
2. They can phagocytose can engulf Ab-Ag complexes.
3. They can proliferate can proliferate by tumor and constrict filtration.
4. Can deposit mesangium connective tissues + collagen.
• Mesangial cells when irritated due to some disease process, they can produce many
biologically active products which can enhance the inflammation within the glomeruli.
, « Introduction to renal physiology 1 »
❖ Functions of
Renal system
:
1. Excretory function.
2. Regulatory functions
3. Endocrine functions.
4. Metabolic functions.
❖ Excretory functions
1. Metabolic waste products (ex: urea & creatinine):
• The gall standard test for renal function is creatinine, why?
Because creatinine level in the blood is mainly dependent on renal function. If
kidney is not working well (no GFR & no filtration), so creatinine level goes up and
urea also goes up. However, urea level goes up in many other conditions such as, when
you sweat too much, you undergo dehydration and everything will concentrate in the
blood specifically urea.
• In severe dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea or excessive sweating), urea will
concentrate.
• In high protein diet, urea level goes up because it is break down product of amino
acids.
2. Drugs (gut metabolites) and toxins:
• The drug acts on certain cells in the body, and the remaining goes out of the body. Note
WHY? Lipid soluble substances can
Because we don’t want drugs to remain forever in our body, so if they remain lipid cross biological membranes
soluble, they will be either be excreted through liver or nephrons. like:
1. GIT mucosal membrane.
Through liver 2. Blood Brain Barrier (BBB).
• Drugs enter the hepatocytes, which push these drugs by special transporters into biliary 3. Placental Barrier.
canaliculi, and go throughout bile to get out, but these drugs will never be excreted,
rather will be absorbed again by portal circulation. MEANS, we cannot execrate them
by hepatobiliary system.
Through Kidney
• When lipid soluble drugs go to nephrons, they will be absorbed by epithelial cells of
the nephrons which have lipid cell membrane, then will go again to the body. MEANS,
we cannot excrete them by renal system.
❖ Summary:
• When drugs or any substances are lipid soluble → we cannot excrete them by
BOTH hepatobiliary and renal system.