🫀
Cardiovascular & respiratory
system
Thema A: Cardiac electrophysiology
CO2: Cardiac anatomy
Learning objectives
To be able to recognise the various structures that constitute the
tissues of the cardiac conduction system
Integration of anatomy with electrophysiology of the heart, that can
be recognised by the surface ECG
Study basic cardiac anatomy and orientation of the heart in the
thorax
Study the morphological structure and functional aspects of the
atria and ventricles, in relation to functional aspects
Learn the function of the 4 cardiac valves
Learn how the cardiac muscle provides itself from blood (coronary
arterial system)
Cardiac muscle
Muscle fiber > myofibrils > sarcromere
Cardiac muscle:
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 1
, Large T-tubules, located at the level of Z-disk
One T-tubule per sarcomere
Large mitochondria, densely packed between myofibrils
Skeletal muscle cell vs. cardiac muscle cell
Skeletal Cardiac
Peripheral nucleus
(beneath the plasma Central nucleus
membrane)
single multinucleated
Intercalated disks
protoplasmic unit (fiber
juxtanucleur
cytoplasma
(+mitochorndria)
Intercalated disk
Cardiac muscle cells are mechanically, chemically and electrically connected to
one anther so that single myocytes function as a whole > functional
syncytium.
Due to this stimulation of an individual muscle cell results in the contraction of
all the muscle cells
Fascia adherens
the site at which the thin filaments in the terminal sarcromere anchor onto
the plasma membrane
Maculae adherens (desmosomes)
help prevent the cells from pulling apart under contraction strain.
Gap junctions
Ionic continuity between adjacent cardiac muscle cells
Electrical and metabolic coupling between adjacent cells
2 Connexons (hemichannels) > Connexins
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 2
, Cardiac muscle fibers are surrounded by a thin layer of endomysium that
contains a rich network of blood capillaries
Contraction
Purkinje fibers exhibit spontaneous rhythmic contraction that leads to
depolarization in cardiac myocytes
Voltage-sensor proteins (DHSRs) > gated ca2+ release channels
calcium triggered calcium release mechanism > delay of start depolarization
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 3
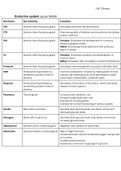
, Cardiac conduction system
progenitor cells of cardiac conduction system are cardiomyocytes. Cardiac
conduncting cells accumulate locally form nodes
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 4
Cardiovascular & respiratory
system
Thema A: Cardiac electrophysiology
CO2: Cardiac anatomy
Learning objectives
To be able to recognise the various structures that constitute the
tissues of the cardiac conduction system
Integration of anatomy with electrophysiology of the heart, that can
be recognised by the surface ECG
Study basic cardiac anatomy and orientation of the heart in the
thorax
Study the morphological structure and functional aspects of the
atria and ventricles, in relation to functional aspects
Learn the function of the 4 cardiac valves
Learn how the cardiac muscle provides itself from blood (coronary
arterial system)
Cardiac muscle
Muscle fiber > myofibrils > sarcromere
Cardiac muscle:
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 1
, Large T-tubules, located at the level of Z-disk
One T-tubule per sarcomere
Large mitochondria, densely packed between myofibrils
Skeletal muscle cell vs. cardiac muscle cell
Skeletal Cardiac
Peripheral nucleus
(beneath the plasma Central nucleus
membrane)
single multinucleated
Intercalated disks
protoplasmic unit (fiber
juxtanucleur
cytoplasma
(+mitochorndria)
Intercalated disk
Cardiac muscle cells are mechanically, chemically and electrically connected to
one anther so that single myocytes function as a whole > functional
syncytium.
Due to this stimulation of an individual muscle cell results in the contraction of
all the muscle cells
Fascia adherens
the site at which the thin filaments in the terminal sarcromere anchor onto
the plasma membrane
Maculae adherens (desmosomes)
help prevent the cells from pulling apart under contraction strain.
Gap junctions
Ionic continuity between adjacent cardiac muscle cells
Electrical and metabolic coupling between adjacent cells
2 Connexons (hemichannels) > Connexins
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 2
, Cardiac muscle fibers are surrounded by a thin layer of endomysium that
contains a rich network of blood capillaries
Contraction
Purkinje fibers exhibit spontaneous rhythmic contraction that leads to
depolarization in cardiac myocytes
Voltage-sensor proteins (DHSRs) > gated ca2+ release channels
calcium triggered calcium release mechanism > delay of start depolarization
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 3
, Cardiac conduction system
progenitor cells of cardiac conduction system are cardiomyocytes. Cardiac
conduncting cells accumulate locally form nodes
Cardiovascular & respiratory system 4