Overview of Physiology and Major Systems of
the Body
Anatomy and physiology is the study of how the human body works. Anatomy focuses on the
structure of the body and how it is designed, and physiology looks at how the body functions. The
physiology of the body depends on the anatomy of the body. The physiology of how the organs
function depends on the structure of the bones which are hard structures made of mineral deposits
that protect the organs from damage. It is important to study anatomy and physiology together
because they are so closely related.
The human body has many levels of organization (Figure 1.1 ). Studying the human body at
the chemical level is to look at atoms which are the smallest building blocks of matter. Atoms
combine to form molecules which then combine to form macromolecules (such as proteins and
nucleic acids). Macromolecules combine to form organelles (working structures) inside of each
human cell. Examples of organelles are the nucleus and mitochondria of the cell. The cells are the
smallest units of living organisms and comprise the cellular level of structural organization. There
are many different types of cells in the body that perform various functions, together they form
the tissue level.
,Figure 1.1 Levels of organization in the human body
Tissue is considered groups of cells that can perform a common function. The four basic tissue
types in the human body are epithelium, muscle, connective and nervous tissue, each of which is
made up of specific cell types that perform specific functions.
Epithelial tissue (Figure 1.2) covers the body surface and lines the cavities of the body. The cells
that make up epithelial tissue are specialized for tasks such as secretion and absorption. The
structure of epithelial tissue contains closely packed cells with very little matrix (layer outside the
cells). Epithelial tissue can be found as one layer or in many layers. These cells are under constant
cell division to replace dead cells that shed away.
,Figure 1.2 Epithelial tissue lining the cavities inside the body shown in pink
Muscle tissue enables us to move (Figure 1.3). The cells that make up muscle tissue are
specialized for muscle contraction.
, Figure 1.3 Anterior view multiple layers of muscular tissue (Visible in context with skeleton, internal
organs, arteries, and veins)
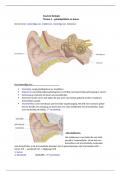
Connective tissue (Figure 1.4) offers support and protection of body organs and includes bones,
tendons, blood, and ligaments. Connective tissue cells are specialized to bind tissues together and
play a supportive role.
the Body
Anatomy and physiology is the study of how the human body works. Anatomy focuses on the
structure of the body and how it is designed, and physiology looks at how the body functions. The
physiology of the body depends on the anatomy of the body. The physiology of how the organs
function depends on the structure of the bones which are hard structures made of mineral deposits
that protect the organs from damage. It is important to study anatomy and physiology together
because they are so closely related.
The human body has many levels of organization (Figure 1.1 ). Studying the human body at
the chemical level is to look at atoms which are the smallest building blocks of matter. Atoms
combine to form molecules which then combine to form macromolecules (such as proteins and
nucleic acids). Macromolecules combine to form organelles (working structures) inside of each
human cell. Examples of organelles are the nucleus and mitochondria of the cell. The cells are the
smallest units of living organisms and comprise the cellular level of structural organization. There
are many different types of cells in the body that perform various functions, together they form
the tissue level.
,Figure 1.1 Levels of organization in the human body
Tissue is considered groups of cells that can perform a common function. The four basic tissue
types in the human body are epithelium, muscle, connective and nervous tissue, each of which is
made up of specific cell types that perform specific functions.
Epithelial tissue (Figure 1.2) covers the body surface and lines the cavities of the body. The cells
that make up epithelial tissue are specialized for tasks such as secretion and absorption. The
structure of epithelial tissue contains closely packed cells with very little matrix (layer outside the
cells). Epithelial tissue can be found as one layer or in many layers. These cells are under constant
cell division to replace dead cells that shed away.
,Figure 1.2 Epithelial tissue lining the cavities inside the body shown in pink
Muscle tissue enables us to move (Figure 1.3). The cells that make up muscle tissue are
specialized for muscle contraction.
, Figure 1.3 Anterior view multiple layers of muscular tissue (Visible in context with skeleton, internal
organs, arteries, and veins)
Connective tissue (Figure 1.4) offers support and protection of body organs and includes bones,
tendons, blood, and ligaments. Connective tissue cells are specialized to bind tissues together and
play a supportive role.